Data Link Layer
The Data Link layer is basically use for transfer frame data from one node (hop) to next adjacent node. It’s a second layer of OSI model.
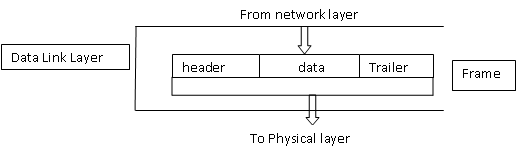
Basically it takes data packets from network layer put a header and trailer make frames and send it to physical layer.
Data Link Layer has two sub layers:
- Logical Link Control (LLC)
- Multiple Access Control (MAC)
Logical Link Control
Logical link control use for design and procedure for communication between two adjacent nodes means node to node communication. Its functions are Framing, flow and error control and software implementation protocol.
- Framing. Framing add source address and destination address defines where the packet is go and source address helps recipient acknowledge the receipt. There are four types of frames time based, character counting, byte stuffing and bit stuffing.
- Second is Variable size framing in which we need to define start and end position which is done by either character oriented approach or bit oriented approach.
- Flow Control. Its take that how much data to be transfer before receive acknowledgement from receiver so that receiver side not become overwhelming data.
- Error Control. Error control is use for error detection and correction. Its main function is to check if either frame is lost or damaged during transmission and coordinate the retransmission of those frame by sender. For error detection its use (CRC) Cycle Redundancy Cycle checksum method and for error correction its use hamming distance method.
- Protocol. To implement data link layer we use protocol is nothing but a set of rules that need to be implemented in network and run by two nodes involve in data exchange at the data link layer.
There are five types of protocol simplest, stop and wait are noise less channel and stop and wait ARQ, go back N ARQ, Selective repeat ARQ are for noisy channel .
Media Access Control:
- When nodes or stations are connected and use a common link we need multiple access protocol to coordinate access to the link.
- There are three types of multiple access protocol.
- Random Access protocol: MA, ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA
- Control Access Protocol : polling, reservation, token passing
- Channelization protocol : FDMA, TDMA, CDMA
- In random access no station is superior to another station and none is assigned the control over others.
- In control access the station consult to another to find which station has a right to send. A station cannot send unless it has been authorized by another station.
- In Channelization is a multiple access method in which the available bandwidth of link is shared in a time, through code between different stations.
The data link layer Ethernet consist of a logical link control llc and media access control MAC:
- In standard Ethernet, the MAC sub layer governs the operation of the access method. It frames data received from upper layer and passes them to the physical layer.
- The Mac sub layer responsible for the operation of CSMA/CD access method and framing.
- Each station on Ethernet network has a unique 48 bit address imprinted on his NIC card.
Protocols of data link layer are ATM, Ethernet, Frame relay, Token ring and TCP/IP’s Serial Link Interface Protocol (SLIP) and Point-To-Point Protocol (PPP).