DNS server on windows 2008
Domain Name System (DNS) is a system for naming systems and network services such as TCP/IP networks, internet and corporate networks. DNS works as a name resolution, when a user enters the DNS name of a computer in an application; DNS resolves the name and provides the other information such as its IP address services etc.
How DNS works?
Let’s take an example. User enters https://www.google.com/ instead of the IP address of the Google server. The user’s friendly name is then resolved when the DNS client software install on user’s machine, sends the request to DNS server. If the DNS server has the information of the client (user) request, it replies to the request directly. Else, DNS passes the information to other DNS server that can help provide the address. This process continues till the time DNS resolves the https://www.google.com/ information with specific IP address.
DNS Namespace
DNS name consists of two or more parts separated by periods or dots (.). The rightmost part of the name is called top level Domain (TLD). Other parts are sub-domain of the top level Domain. Some common TLD names used in DNS are
– .com
– .gov
– .edu
– .net
– .org
How to setup DNS on Windows Server 2008
To install DNS, We need to upgrade the Windows 2008 server to a Domain Controller (DC) first and then install and configure DNS.
To make Windows 2008 server to a Domain Controller, follow these steps,
1. Click on Start > Run
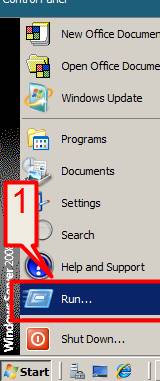
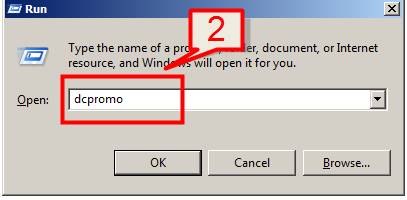
2. Type dcpromo > Click OK
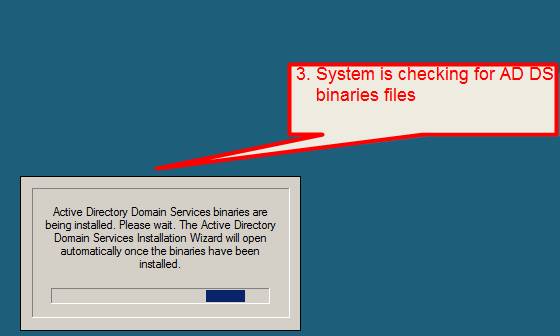
3. The system will check if Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) binaries are installed, if not then it will start installing them.
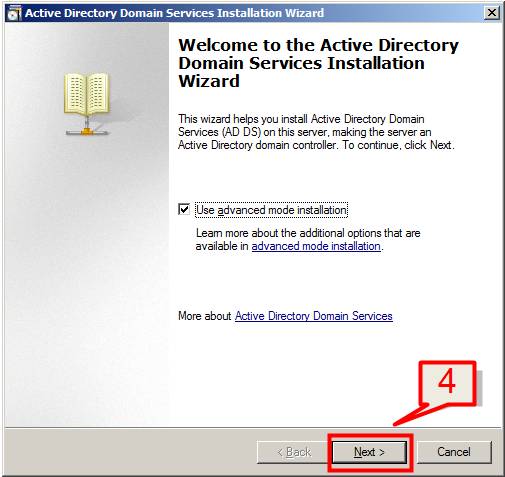
4. The Active Directory Domain Services Installation Wizard will start, enable the checkbox beside Use Advanced mode installation and Click Next (For Expert or Advanced user), or keep it unselected and click on Next
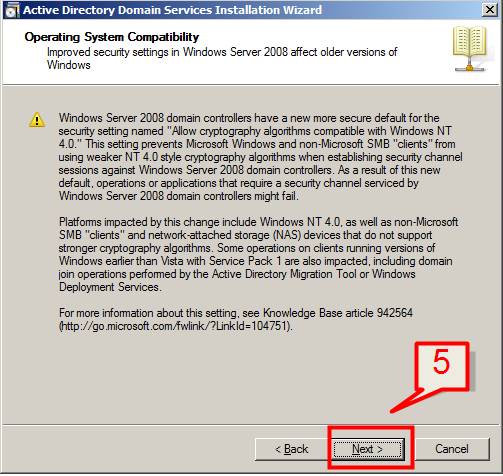
5. The Operating System Compatibility page will be displayed, which will brief about some improved security settings in Windows Server 2008. Click Next
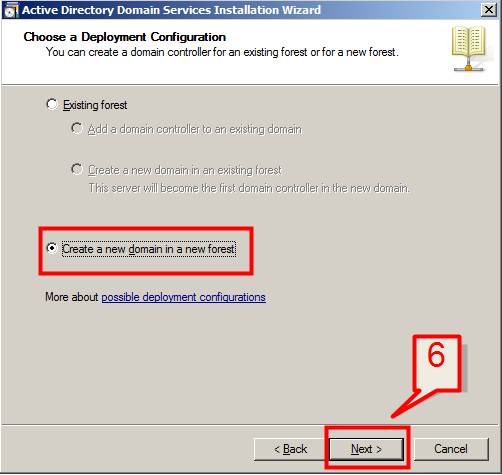
6. Since we are creating a new DC from scratch, Choose Create a new domain in a new forest, and Click Next
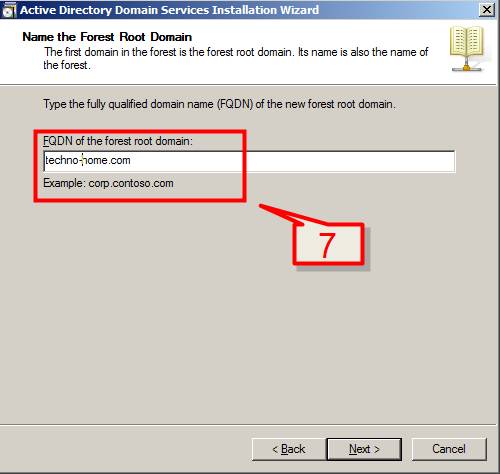
7. Enter the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the new forest root domain inside the textbox, Click Next.
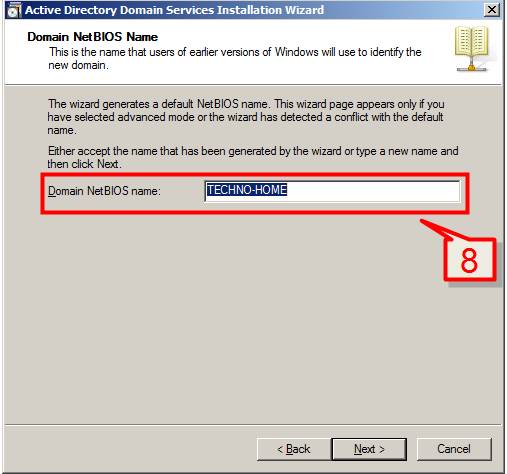
8. If on the first screen, you selected Use advanced mode installation on the Welcome page, the Domain NetBIOS Name page appears. On this page, type the NetBIOS name of the domain if necessary or accept the default name and then Click Next.
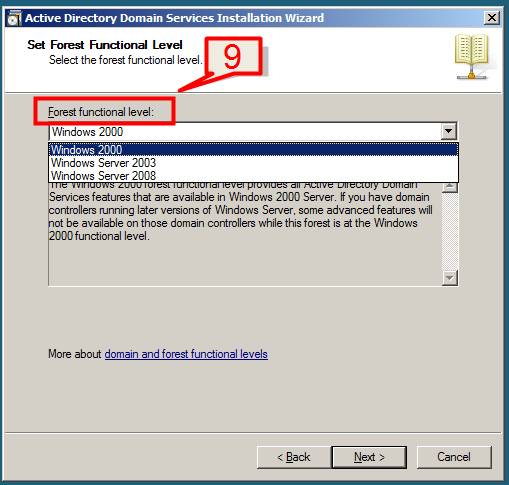
9. Select the Forest Functional Level, choose the type and click on Next.
Note: Functional levels determine the features of Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) that are enabled in a domain or forest. If you are creating a new domain or a new forest, the levels can be chosen to highest values that the environment can support. E.g. If your environment will support both 2003 and 2008 server then you would choose Windows Server 2003 as your Forest Functional Level.
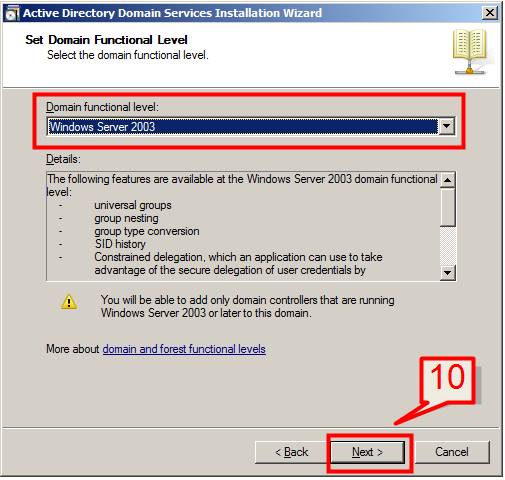
10. If we choose Windows Server 2003 as Forest functional level, and then we need to select the domain functional level in next screen. Select Windows Server 2003 and Click Next,
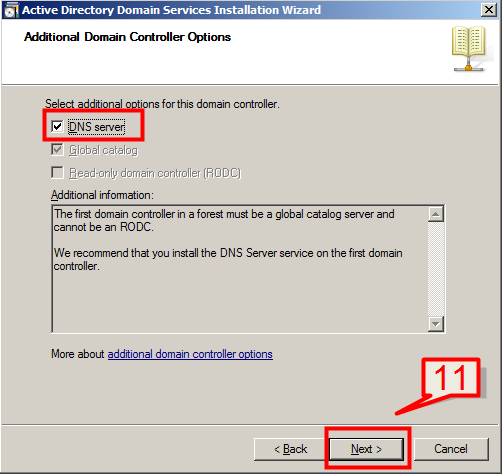
11. In Additional Domain Controller Options page, select to install the domain Name Service (DNS) to your server.
Note: The First domain controller in a forest must be a Global Catalog that’s why the checkbox besides Global Catalog is selected and it can’t be cleared. Also the first domain controller in a new forest or in a new domain cannot be a Read Only Domain Controller (RODC)
Select DNS Server and Click Next.
12. If static IP is not assigned to your server you will see similar to the following screen now you need to assign static IP and start the above process.
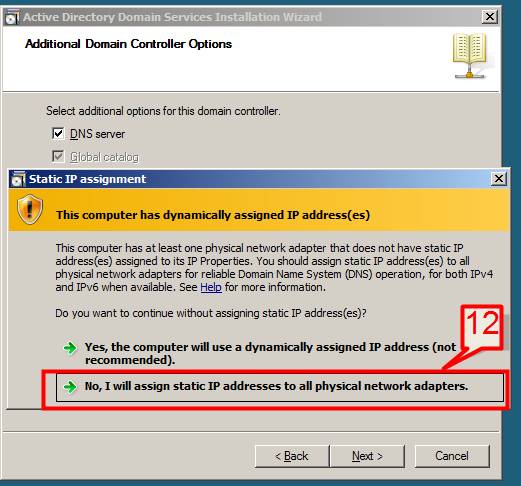
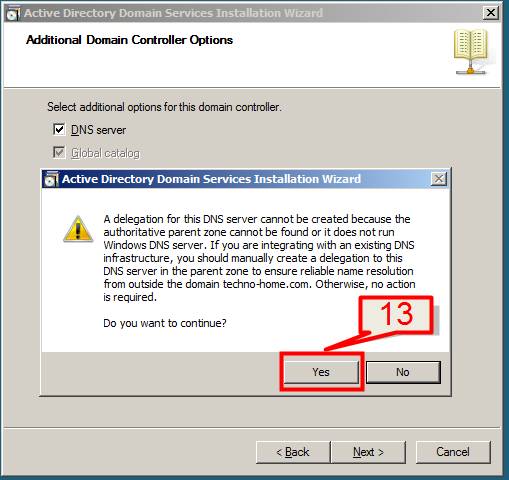
13. The Additional Domain Controller Wizard to start configuring DNS, if the wizard cannot create a delegation for the DNS server, it displays a screen to create the delegation manually. To continue, Click Yes.
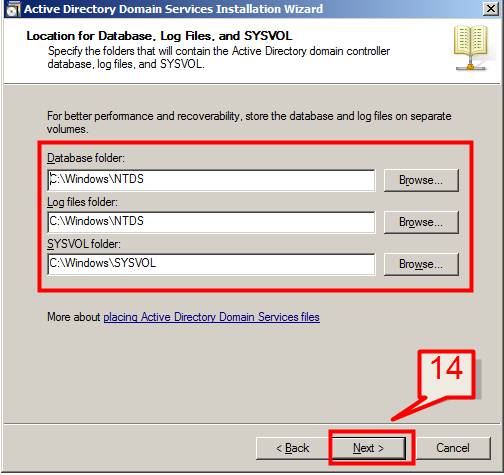
14. The next dialog will show to provide the location where the domain controller database, log files and SYSVOL are stored on the server.
Note: The database folder stores information about the users, computers and other objects on the network.
Log folder stores information related to AD DS, such information about an object being updated.
SYSVOL stores Group Policy objects and scripts. By default, SYSVOL is part of OS files in the Windows directory.
Accept the default settings and Click Next
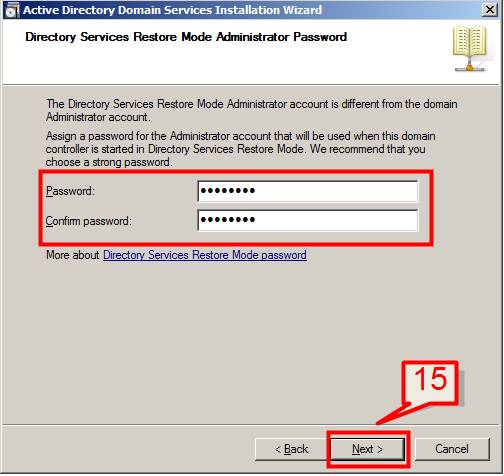
15. In the Directory Services Restore Mode Administrator Password page, type a password and confirm password and click Next.
Note: This password is used to start Domain controller in Directory Services Restore Mode.
16. AD DS installation wizard summary page will then display. Review the settings that have been done. This screen also provides option to Export Settings that can be save in an answer file and later we can do an unattended operation.
Review the summary and Click Next
17. DNS installations will the start.
18. This is followed by installation of Group Policy Management console.
19. DNS installation will then complete. Click Finish.
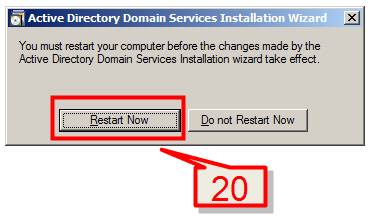
20. Click on Restart Now to restart your server for the changes to take effect.
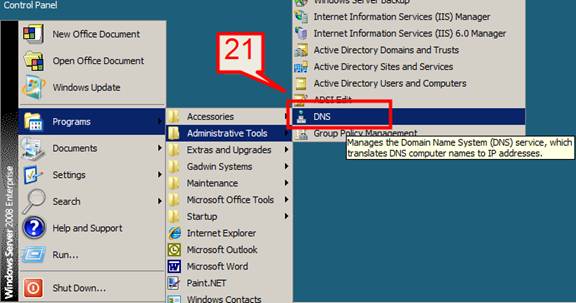
21. Once server is rebooted and after login, DNS is installed and can be seen from Start -> Administrative Tools -> DNS
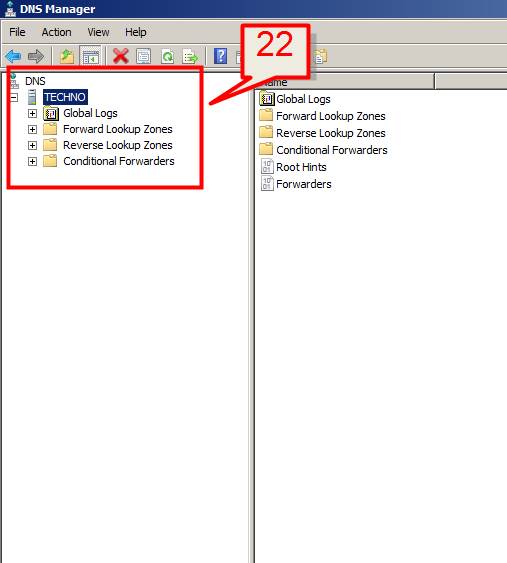
DNS Server Configuration
22. Open DNS from Start -> Administrative Tools -> DNS
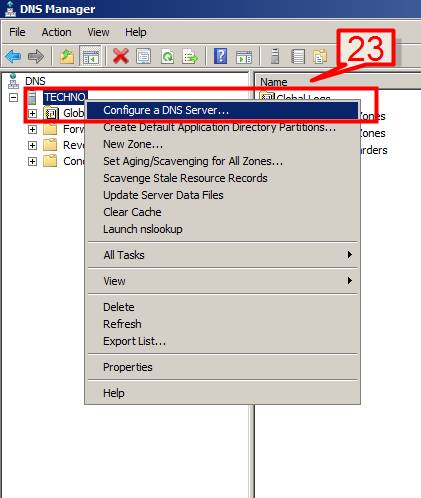
23. Highlight the DNS server name -> right click -> choose Configure a DNS server
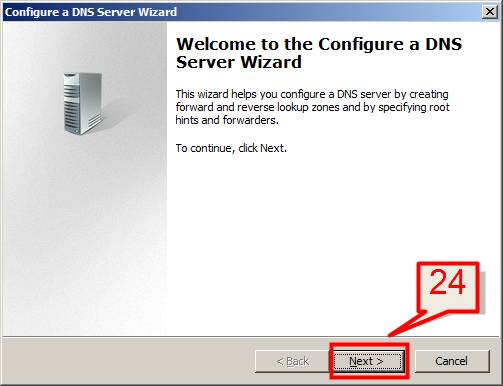
24. On Configure a DNS Server Wizard, Click Next
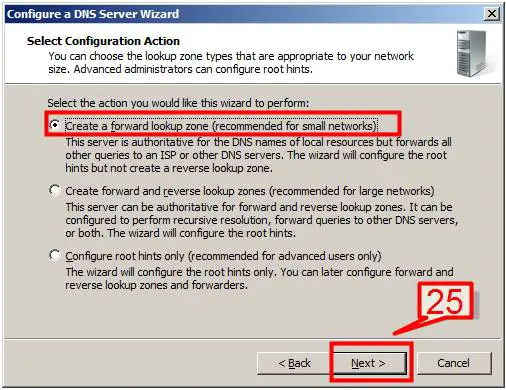
25. Select the first option to create a forward lookup zone and Click Next
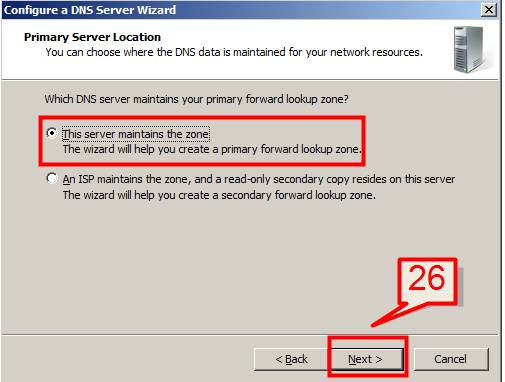
26. Select the default option (This server maintains the zone) and Click Next
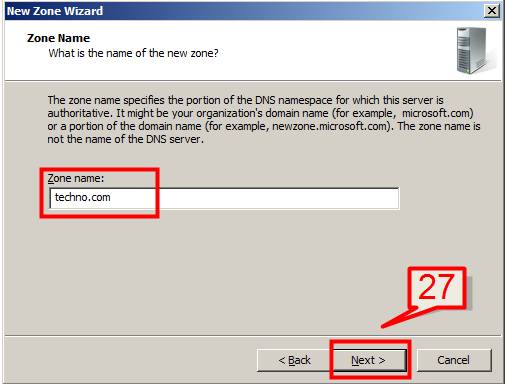
27. On Next screen, enter the domain name that you want to create your first zone file for. Click Next
28. On new Zone wizard, select the default and Click Next
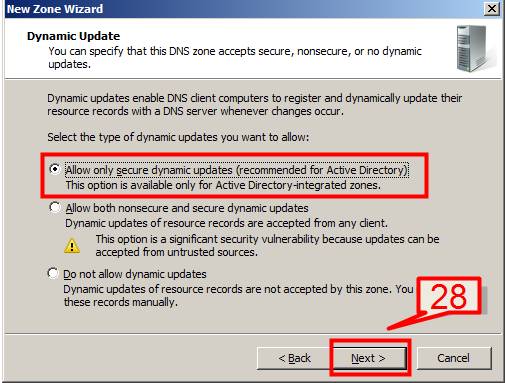
29. Select No, it should not forward queries on DNS server wizard screen and Click Next
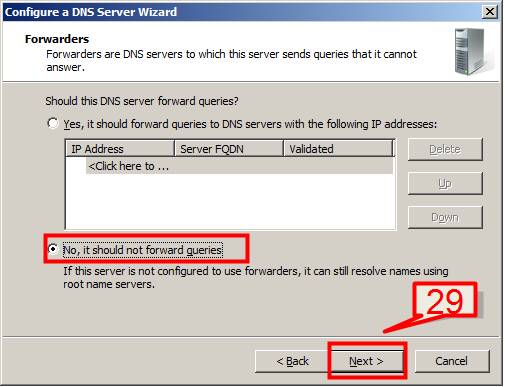
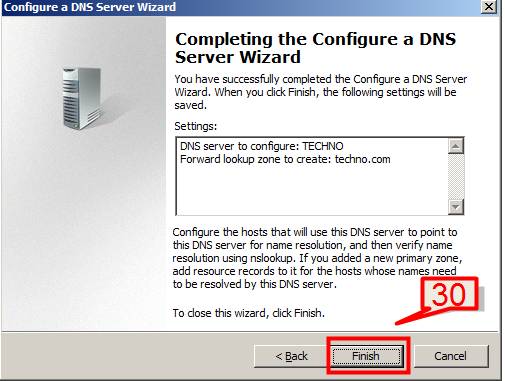
30. Click Finish when DNS server configuration is done.