Technology has been advancing not only in making it but also in cracking/ breaking it, where we could see a humongous increase in the number of network attacks day to day. There are two types of network security attacks, namely a) Active attacks and b) Passive attacks.
Passive attacks:The intruder or the attacker can passively record the computer activity but cannot modify the activity.
Active attacks:In this type of attack besides eavesdropping, the intruder can also transmit, delete or modify the messages.
MITM attack is an example of an active network security attack. TheMan-in-the-middle attack technique works very much like the name sounds. The attacker places himself (logically) in the middle of the conversation between two devices, and he can watch what is happening between the systems, he can alter the packets or insert his information. Here, the intruder becomes the end point instead of the router or any similar device. Here the traffic is being redirected, i.e. the data is sent to the attacker (man in the middle) and the attacker then transfers it to the other end device (ex: router). An important point here is that the legit users will never know about the traffic redirection.

PRINCIPLE:
The most common technique used in accomplishing this attack is ARP Spoofing. It is because there is no security associated with this.
Before going to know what ARP Spoofing is let us have a brief idea about IP address and MAC addresses. A MAC address is the unique address given to each network adapter whereas the IP address is used to identify the device on a network. Fundamentally, we do not use this address to communicate between devices over the Internet, but we use the MAC address. The IP address helps in moving along, once the traffic is started.
ARP Spoofing: The intruder in this attack sends falsified messages over LAN. Here, the MAC address of attacker and the IP address of legit user’s device are linked.
EXAMPLE:
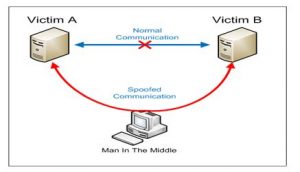
We can see two victims A and B with their respective IP and Mac addresses in the below picture. The victim A wishes to communicate with the victim B and requires the MAC address of B. To obtain this, the victim A makes an ARP request to B using its IP address. Meanwhile, our man in the middle interferes and sends a falsified message to A giving his MAC address and here the intruder impersonates as B (mentioning B’s IP address). Now the connection has been established between the attacker and the legit users where the attacker can perform MITM attack.One who is readingthis getsa doubt that how the attacker can know the IP addresses of the victims. Let us discuss this in the next section.

MITM TOOLS:
The MITM works over a local subnet. Various tools are available to perform this attack and these tools help the attacker in sniffing the hosts and their IP addresses that are on the subnet. The tools are:
- Ettercap
- Dsniff
- Cain
- Karma
- Airjack
- Defending against MITM attack:
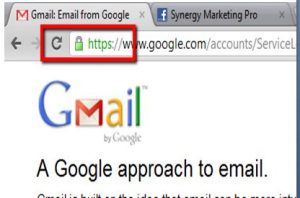
- The traditional tools or techniques that come along with the PC doesn’t help in preventing the attack. But one can make it work out to some extent by using the encrypted network connections provided by HTTPS (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure) or VPN (Virtual Private Network).
- Secure DNS extension.
- Strong mutual authentication.
- Setting a static ARP cache. The host cannot update the manually set records.
The most important thing to remember is: never connect to a free open Wi-Fi, especially while carrying out the online bank transactions. We may enjoy the free internet access, but this may give the attacker a chance to hack your sensitive data. Use the open Wi-Fi only when necessary and if you do so use the browsers with HTTPS plugins.

Hence, say no to free Wi-Fi andthereby, no to MITM attack.
MAN IN THE MIDDLE ATTACK?
NO
THANK YOU