Recently, the WannaCry ransomware cyberattack has created chaos in the technology world for days, giving its makers over $50,000 of earnings, but did you know that it is not the first type of worm to spread so far? In the history of technology, the Internet has been repeatedly disrupted by outbreaks and infections. Below is the list of popular malware that hits the tech industry in the past years.
- Morris Worm:

The Morris Worm was one of the first computer worms that were released through the Internet in 1988. It was also the first to acquire momentous media attention during that time. It was written by Robert Tappa Morris, a graduate student at Cornell University. It was surreptitiously launched and spread to the MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) computer systems. According to Morris, he has written the code not to cause damage, but to measure the size of the Internet. The Morris Worm works by running the BSD (Berkeley Software Distribution) variant of UNIX.
The worm was undetectable; however, an error in the design led to the creation of several copies and resulted to severe over-taxing of the entire computers on which it was unintentionally installed. It could infect the computer multiple times and every additional process would cause the machine to slow down, and eventually become unusable. According to Clifford Stoll, who had helped in fighting the worm, he made a survey and estimated that there are 2,000 computers that became infected in just fifteen hours and it usually takes two days to remove the virus. The Morris Worm has caused $100,000 to $10,000,000 damage and Morris was convicted of violating the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (U.S.C. Title 18). He was sentenced to 400-hrs of community service, a $10,050 fine, and three years probation.
Interestingly, Morris’ father is a chief scientist of NSA and the WannaCry ransomware cyberattack is a code purloined from the NSA.
- ILOVEYOU:
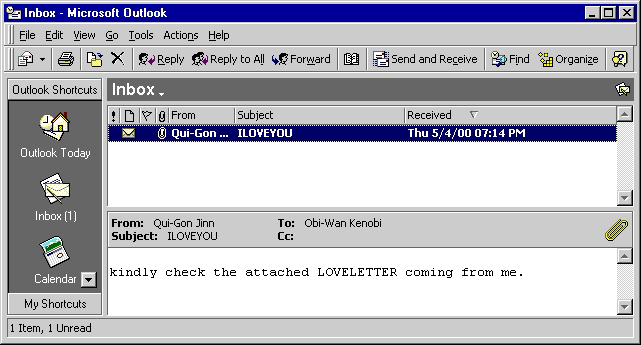
The ILOVEYOU bug is a computer worm that started in the Philippines on May 5, 2000. It came as an email message, which runs in MS Outlook, with a subject line of “ILOVEYOU” and included an attachment with a filename, “LOVE-LETTER-FOR-YOU.txt.vbs”. File extension, such as .vbs was usually hidden by default, which led the users to think it was just a normal file. Opening the attachment will launch the Visual Basic script. It affected millions of Window-based computer systems by overwriting random files such as Office files, images, audios, etc. and sending a copy of itself to all the email addresses found in the recipient’s address book.
The ILOVEYOU worm began spreading via corporate email systems. Since the virus targeted mailing lists, the email messages normally appeared to come from a family member or friends, and therefore victims considered it as “safe”. This outbreak has cost $5.5 to $8.7-billion damages around the world and the estimated amount to remove the ILOVEYOU worm is $15-billion. Two Filipino Computer Programmers (Onel de Guzman and Reonel Ramones) were investigated and claimed that they have unknowingly released the worm. The ILOVEYOU virus has attained the world record of being the most contagious computer virus during that time.
- Code Red:
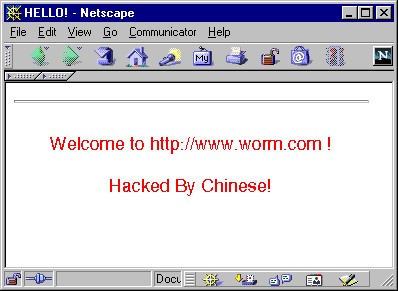
The Code Red worm was found originally on July 15, 2001. Marc Maiffret and Ryan Permeh of eEye Digital Security were the first to discover the Code Red worm. It took advantage of a flaw, which was discovered by Riley Hassell. The group has named the worm as Code Red since they were drinking Code Red Mountain Dew during that time.
The worm was initially released on July 13, 2001, but a huge number of infected computers became visible on July 19, 2001. At this time, the total number of infected hosts reaches more than 350,000. There is no confirmation about the identity of the Code Red’s creator, though the message on the server suggested that it started in China. The same year, another variant called Code Red II also appeared.
Similar to WannaCry, Code Red has caught out servers that hadn’t been updated with a patch.
- MyDoom:
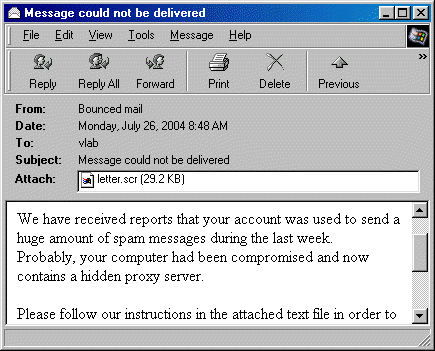
MyDoom is a computer worm that started spreading in the inboxes around the world, affecting Microsoft Windows machines, in 2004. It then became the fastest spreading computer worm, surpassing previous records set by the ILOVEYOU and Sobig Worm.
MyDoom is transmitted through email and was usually disguised as delivery failures, with subject lines Mail Delivery System, Error, Test, or Mail Transaction Failed, in diverse languages such as English and French. The mail has included an attachment that once executed will resend the worm to the recipient’s local files like the address book. The MyDoom worm also copies itself to KaZaa’s (a P2P file sharing app) shared folder to spread the virus.
The worm contains a text message stating “andy; I’m just doing my job, nothing personal, sorry”, which led to speculation that the creator of MyDoom was paid. Initially, many security firms believed that the worm was originated in Russia, however, they failed to confirm the real identity of MyDoom’s actual author. Several versions of MyDoom have appeared until 2009, affecting several countries including the United States and South Korea.
- SQL Slammer:
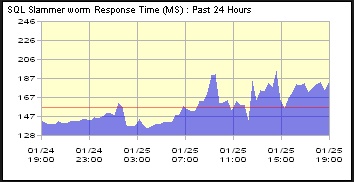
SQL Slammer is a computer worm that caused a DDOS (denial-of-service) attack and rapidly infected 75,000 machines within ten minutes. The perpetrator aims to slow down Internet traffic as it spread. SQL Slammer is a small piece of code, roughly 376 bytes that exploited a buffer overflow bug in SQL Server and Desktop Engine. It produces random IP addresses and sends itself to those addresses. Unlike the other worms mentioned above, SQL Slammer doesn’t have a code and only stays in memory due to its size; that’s why it’s easier to remove the worm.
SQL Slammer started to slow down systems around the world on January 25, 2003, and although a patch had been released 6 months before the worm has spread, several organizations hadn’t applied it yet, which makes their machines vulnerable.