Asked By
abhishek
0 points
N/A
Posted on - 11/17/2017

What is Kerberos protocol? How is Kerberos network security used? From where is the word Kerberos derived? Who developed the Kerberos protocol?
Implementations Of Kerberos In Network Security Protocol

Kerberos protocol is used to authenticate client-server application using secret-key cryptography. It is used on the basis of tickets, to allow client-server communication over an unsecured network by proving their identity to each other in a secure method. The word Kerberos is named after the Greek mythology Cerberus, a three-headed guard dog of Hades, The Greek god. The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and IBM developed it as a joint venture between them.
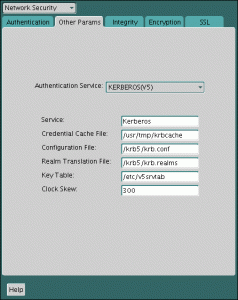
Implementations Of Kerberos In Network Security Protocol

Kerberos or Kerberos protocol is a protocol used for authenticating service requests between trusted hosts over an untrusted network like the internet, for example. This protocol is integrated into all major operating systems like Microsoft Windows, OS X, Linux, and FreeBSD. The name “Kerberos” was taken from Greek mythology, Kerberos (Cerberus), which is a three-headed dog who guards the gates of Hades.
The three heads of the Kerberos protocol represent a client, a server, and a KDC or Key Distribution Center which serves as Kerberos’ trusted third-party authentication service. Beginning in Windows 2000, the Kerberos protocol has been incorporated into the operating system as the default authentication system and is an essential component of the Windows Active Directory service.
The Kerberos protocol is also used by broadband service providers to authenticate set-top boxes and DOCSIS cable modems accessing their networks. Kerberos was originally developed for Project Athena at the MIT or Massachusetts Institute of Technology.