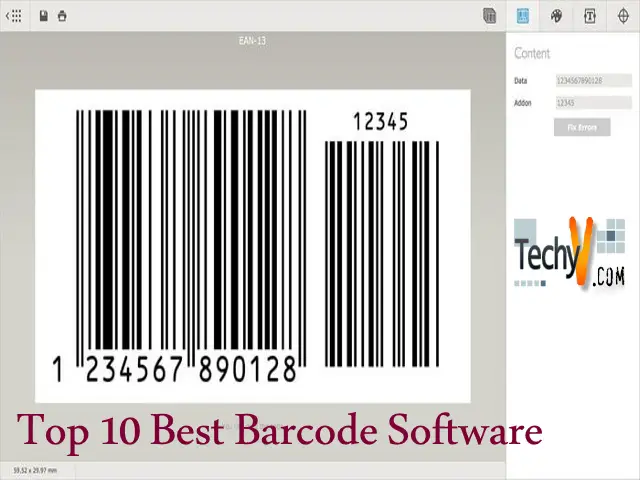
Active Directory Developed in (2000, 2003, and 2008)
Originally created in 1999 and primarily used for online information, an active directory is a structured directory used by Microsoft Windows. In essence, an active directory used on Microsoft Windows is the basis of the computer and servers to store data and information about networks and domain.

Usually an active directory makes a variety of functions, such as: the capability to offer information regarding objects, facilitating their organization for an easier access, providing the access for the end users and administrators, also allowing the administrator to set up the directory security.
In general, an active directory can be defined as a hierarchical structure. Usually, this structure is divided into three main categories: the resources, including hardware, the services for end users and the objects, representing the main function of the domain and the network. In general, the active directory is the nerve center of the Microsoft Windows operating system, being a replacement of the primitive SAM database.
Active Directory was first released with Windows 2000 Server edition, followed by a revised directory to extend and properly improve administration in Windows 2003 Server. Previously improved and revised, Microsoft released the last active directory with Windows Server 2008 and renamed it Active Directory Domain Services.
Active Directory Domain Services is the basic and main function is configuring information, authentication requests, usually providing information about all the objects stored in it. In general, the functionality of Active Directory is used to efficiently manage users, groups, computers, printers and any other object directory from one central location.
The changes from Active Directory object can be stored and recorded, facilitating the visualization of the changes of the object, also showing the current and previous values of the changed attributes. Another important feature used by Active Directory is the Fine-Grained Password, where the password policies are set up for distinct domain groups.
The Read-Only Domain feature is consisting of a read-only version of the Active Directory database, which can be deployed in environments. As the security of the domain cannot be guaranteed, it requires other users to log on in order to maintain the server.
Usually, the Read-Only Domain Controllers prevent the changes which previously made at branch locations for preventing the corruption of the Active Directory, also dissolving the need of usages of the staging site for office domain controllers or even to send the installation media along with the domain administrator of the branch location.
As the fourth feature of the Active Directory, the Restart able Active Domain Services can be stopped and maintained. While the directory service is offline, other services of the domain controller can continue their functionality.
The Database Mounting Tool, is, practically a snapshot of the Active Directory database and can be mounted using this specific tool. This function gives the permission of the domain administrator to visualize the objects within the snapshots, offering the possibility to determine and restore the necessary requirements.
Active Directory 2000 is a central repository. As being a hierarchical and multi-master database, the active directory with a storage capacity of millions of objects. Being a multi-master, the changes made in the database is processed at any domain controller in any build, giving specific information doesn’t matter if the domain controller is connected to the network or not.
The main and basic difference between the three versions of Active Directory is that Windows Server 2000 incorporates and uses features from Windows 2000, while Windows Server 2003 includes features and compatibility from Windows XP, as for Windows Server 2008 uses and incorporates compatibility features from Windows Vista.
Another important difference is highlighted at the installation process, where Windows 2000 prompts the administrator users to select administrative functions or application server functions, which can only be installed on one server, having the basic disadvantage to prefer the functions one at the time. In Windows 2003, we can see an improvement and a consolidation of the installation and management functions. As for the Windows 2008 all the structure and the development of the installation process has visible changes and highly improved.
Being more accurate than its previous version, Windows 2003 group policy can be applied for almost 720, instead of 620 group policies in Windows 2000. Facts, which makes Windows 2003 more secured than the previous version, but less performing than the latest version.
In Windows 2000, the basic functions of renaming the domain were missing and were previously implemented in both Windows 2003 and 2008. Also an impressive improved version can be highlighted in regards of the extended editions, where the Windows 2000 only had Server and Advanced Server edition, while Windows 2003 has Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter and Web server Editions. The basic Windows 2000 supports only 32 bits operating systems, while both Windows 2003 and 2008 offers support for 32 bits and 64 bits operating system.
Basically in Windows Server 2003, the function levels were an extension of the older native concept used and implemented in Windows 2000. In Windows 2008, the function levels from the Windows 2003 were further extended, in order to contain new features and impressive benefits. Usually, these latest improved features are used to initiate new Active Directory features, after the Domain Controllers are using and running Windows Server 2008 operating system.
The latest benefits and features of Windows 2008 implemented the Group nesting application, which allows the placement of a group as a member of another group, having the same scope. The Universal security group feature allows the impressive usage of Universal security group types. Another important new implemented feature is the Sid History, enabling the usage only when the objects are migrating between domains. As an important feature, which was missing in Windows 2000 is the group converting between security groups and distribution groups.
In essence, Windows 2008 incorporates all the available features from the previous versions of Active Directory 2000 and 2003 forest function level, adding new improved benefits and the latest additional functions and features. Between the additional Active Directory improvements, we can clearly visualize the new forest functional level, the enhanced command line and automated management, improved automated monitoring and notification, better management with server management, improved compliance with established standards, answer file creation and read-only domain controller installation.