Growing a business is difficult, but scaling SaaS is especially hard. SaaS companies mostly struggle to achieve revenue growth and profitability. These companies must pay close attention to metrics and make data-driven decisions that show their ability to generate recurring revenue and conversion rates, retain customers, and attract customers at a reasonable acquisition cost. To make such decisions, one must track the KPIs. KPIs or Key Performance Indicators are performance measuring values that depict how effectively a company achieves key business objectives to keep sales moving forward efficiently. They can help you leverage your most productive assets and identify issues to eliminate negative impacts on your organization’s growth. Here, we will review the top KPIs every SaaS company should track.
1. Customer Churn Rate
Churn rates measure how much business one has lost within a certain period. Dividing the number of customers who discontinue service during a specified time by the average total number of customers gives the churn rate. It is one of the fundamental metrics in tracking the day-to-day vitality of your business. Companies that sell to smaller businesses should expect higher churn, while those to enterprises should expect lower churn.
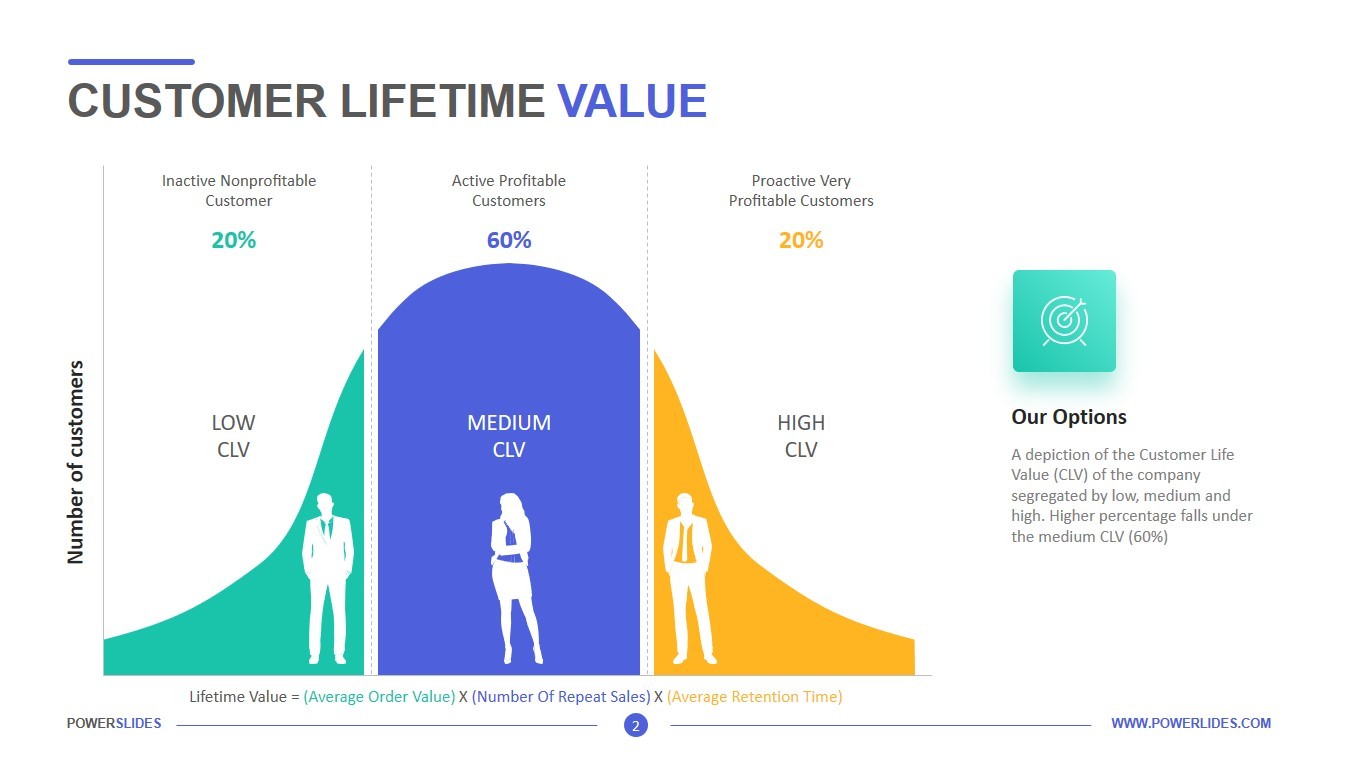
2. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is the average amount of money ideal customers pay during their engagement with your company. It helps to make business decisions about sales, marketing, product development, and customer support. Also, one can start thinking of ways to increase the customer lifetime value through new products, features, levels, or pricing changes. Each renewal yields another year of recurring revenue, increasing the lifetime value per customer.
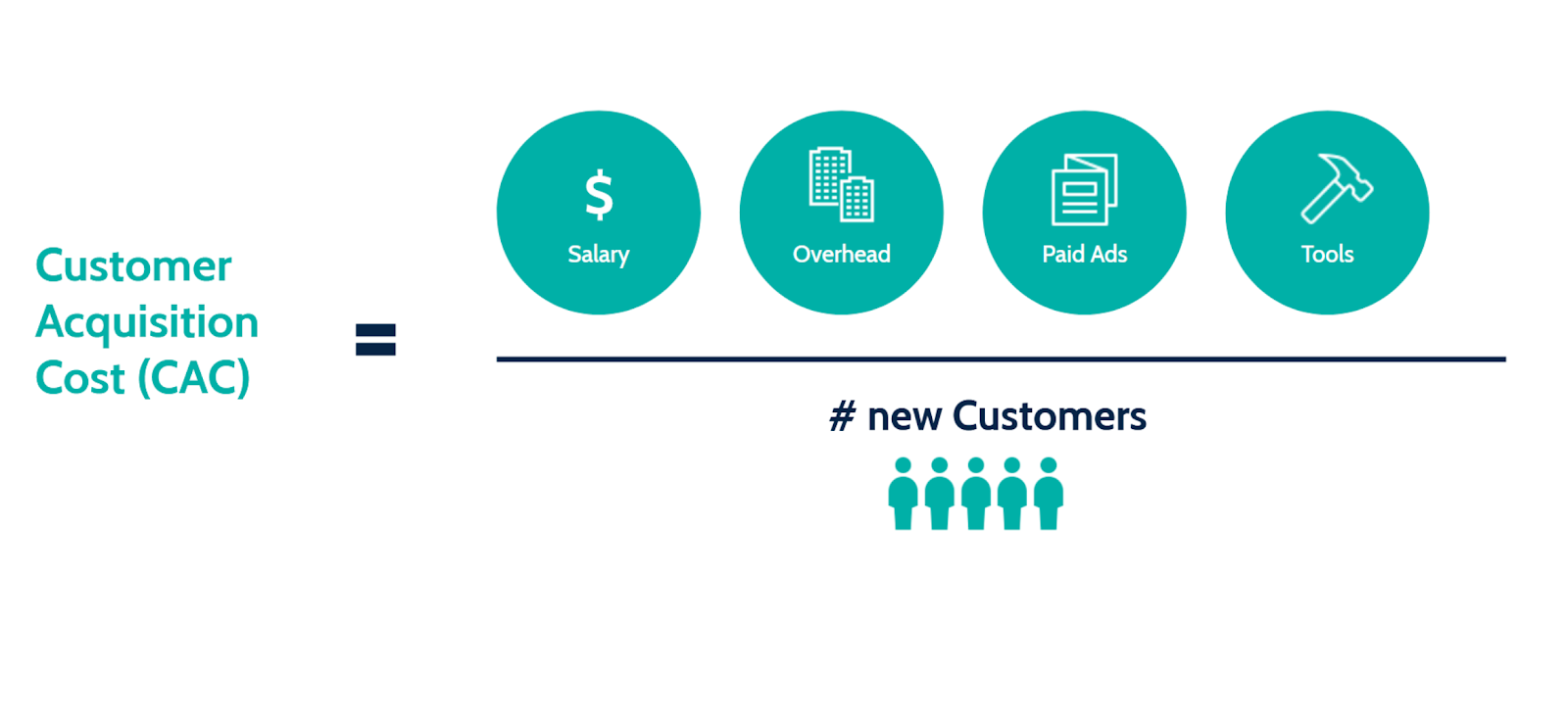
3. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is how much it costs to acquire new customers and the value they bring to your business. CAC rates fully quantified help companies manage their growth and accurately gauge the value of their acquisition process. The CAC of a SaaS company should be higher than its average CLV. The best way to reduce CAC is to get customer information when they first interact with your brand.
4. Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) is the predictable revenue that a company can expect to receive every month. In calculating MRR, multiply the total number of paying customers by the average revenue per user (ARR). Keeping these metrics healthy, you can retain potential customers by improving their engagement with your product and answering their needs with updates and new features. This metric is the lifeblood of any SaaS.
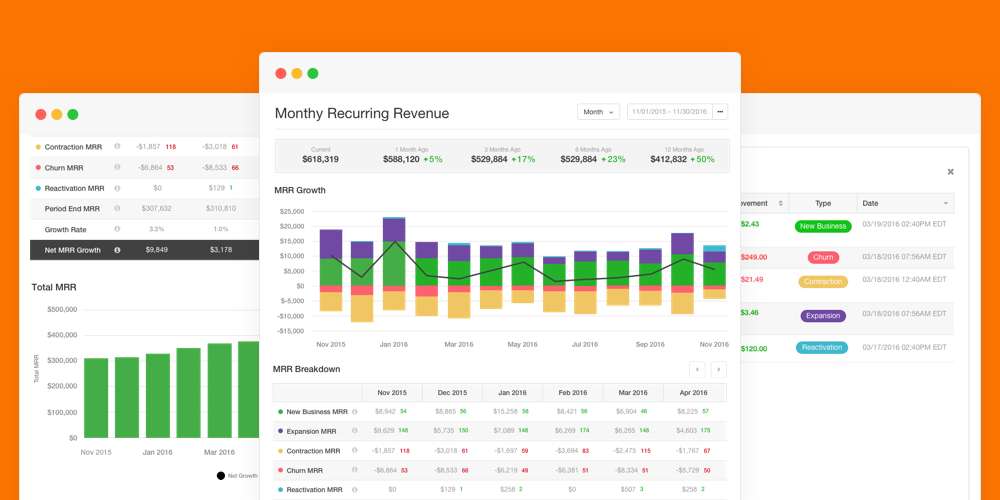
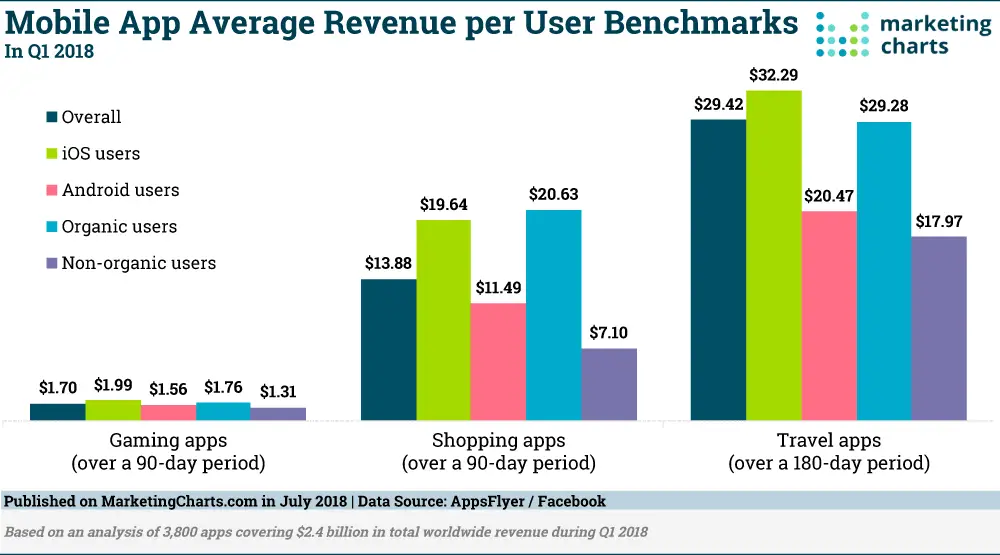
5. Average Revenue Per User (ARPU)
Average Revenue per User (ARPU) is also called average revenue per account (ARPA). It is a measure of the revenue generated per user. This metric allows you to identify trends and implement changes to shift the business towards a large pool of SaaS profits. Some best ways to increase ARPU are upgrades, premium features, etc. Increasing this metric will help you boost revenue and avoid acquiring the new-users costs.
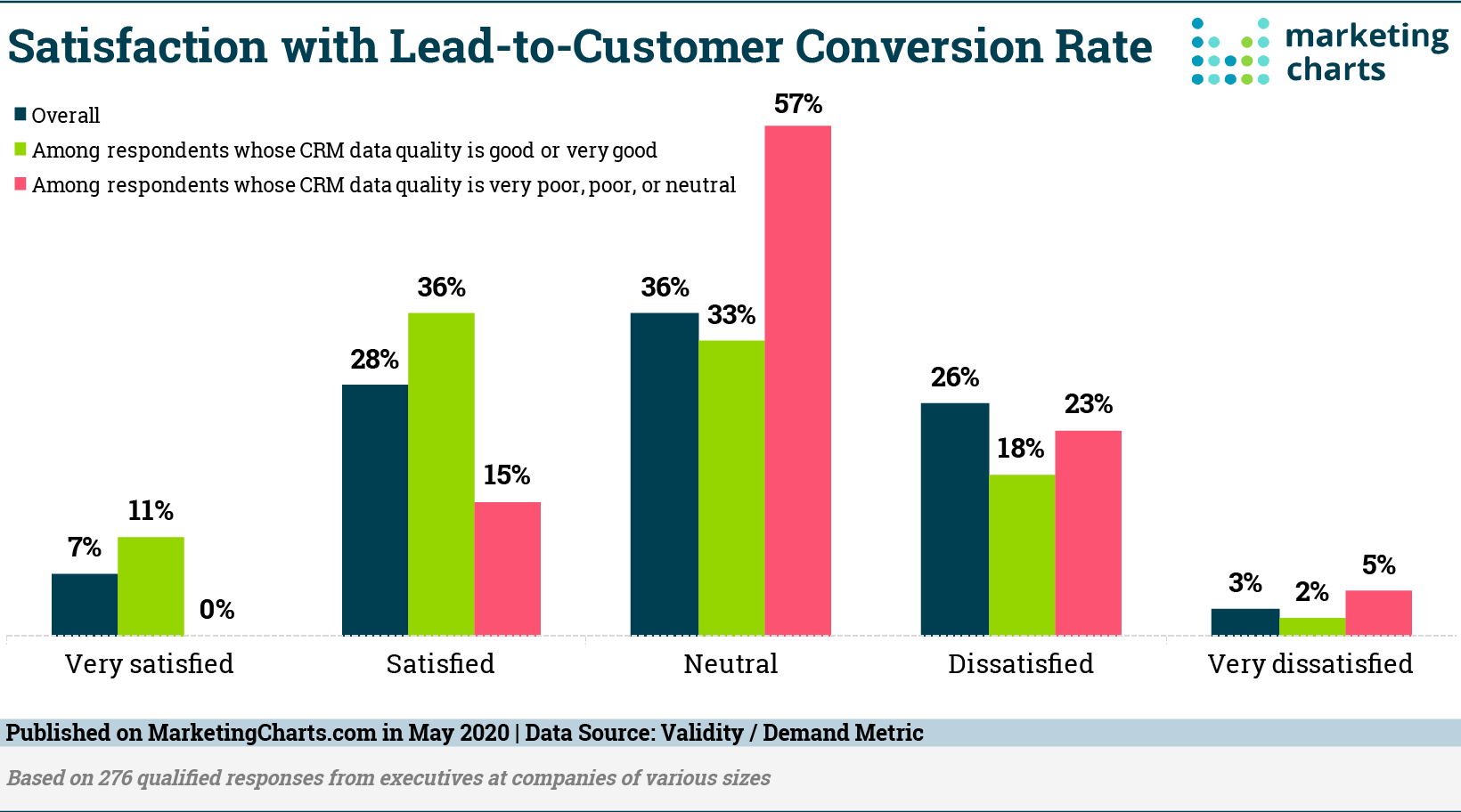
6. Lead-To-Customer Rate
The lead-to-customer rate is the proportion of qualified leads of a company that result in actual sales. This metric evaluates the performance of your organization’s sales funnel. Tracking the lead conversion rate gives you a proven plan for gaining future customers. It shows the status of the sales process and leads to nurturing methods, and helps shape new marketing campaigns throughout the year.
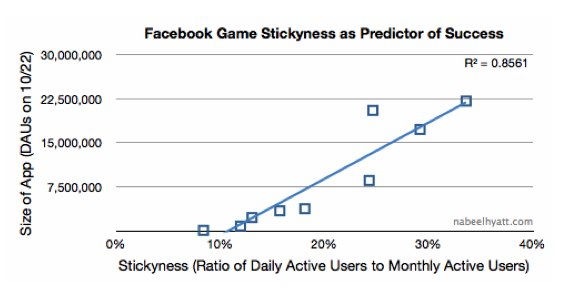
7. Product Stickiness
Product Stickiness is the ratio of Daily Active Users (DAU) and Monthly Active Users (MAU). It is a widely used metric for product engagement that tells how sticky a product is. Facebook popularized it to understand the stickiness of the Facebook app. This metric gives you insights on better onboarding, support users, and introduction of new features. Hence, users have a better sense of all features of the product.
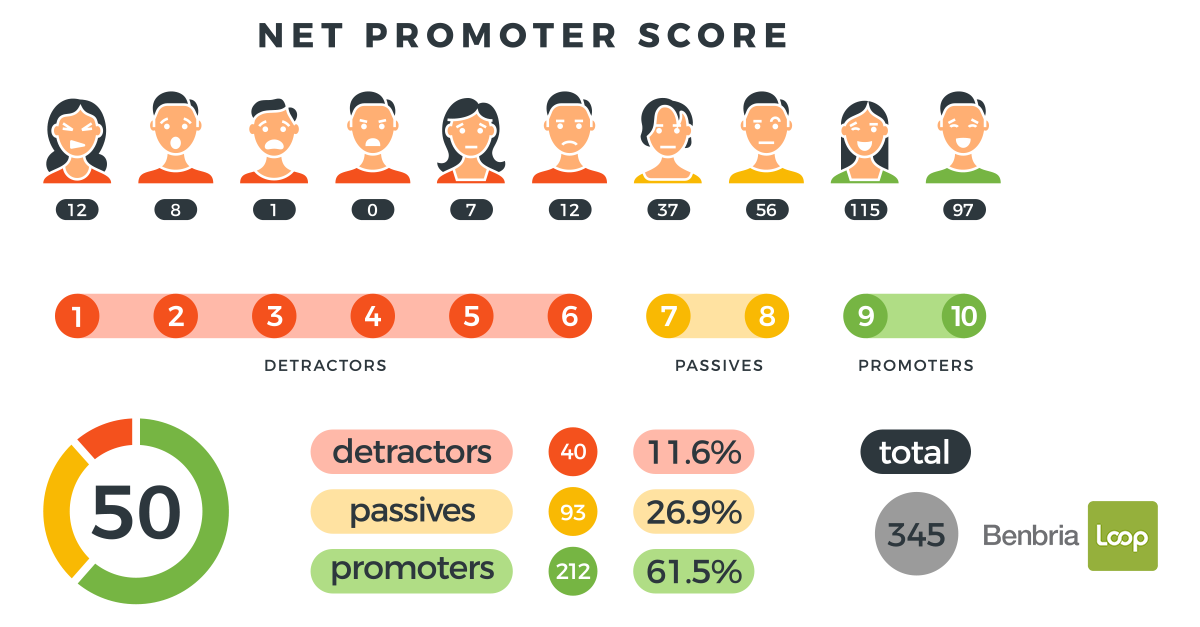
8. Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a customer satisfaction and loyalty measurement taken by asking customers how likely they are to recommend your product or service to others on a scale of 0-10. It is the difference between the percentage of promoters (who love and recommend the products) and detractors (who complain about the products). Having a high NPS leads to higher customer conversions and lower churn with less spent on advertising.
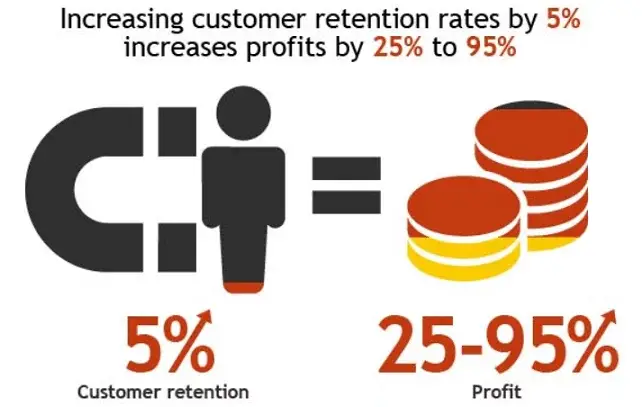
9. Customer Retention Rate
Customer Retention Rate (CRR) is the percentage of customers the company retains over a given period. The retention rate is an antonym of the churn rate. Keeping the existing customers is less expensive than trying to win new ones. Also, current customers often purchase more things and refer their families and friends at no cost. Hence, software companies should keep an eye on their customer retention rate.
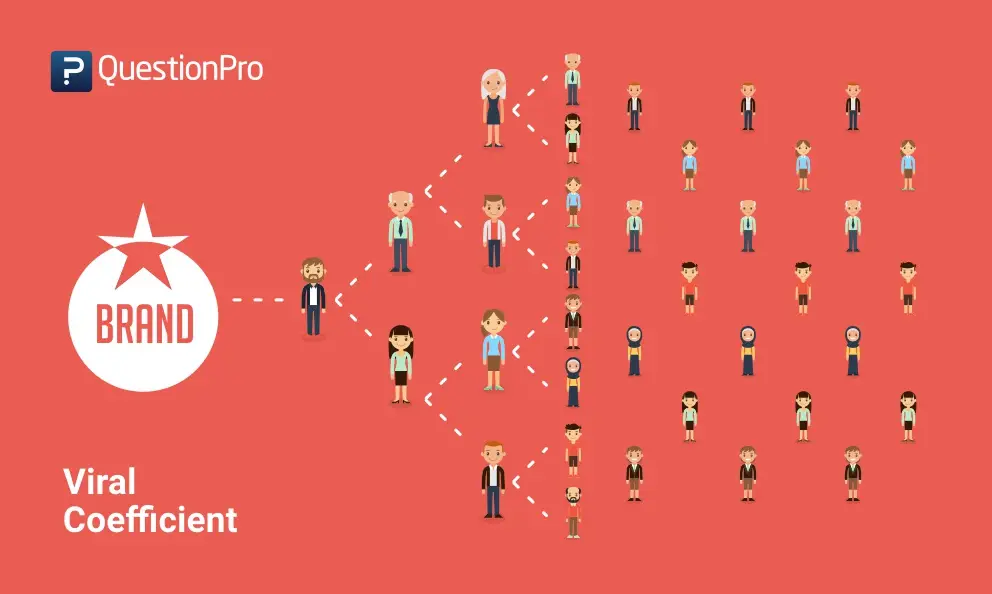
10. Viral Coefficient
The Viral Coefficient is the number of new customers generated by an existing customer. It displays how well your product customer base is organically growing. This metric saves time and money on marketing and sales. Customer success and satisfaction with the product also play a vital role. Ensure that the customers understand and use the product and its features. The greater the viral coefficient, the faster the company will grow.