Cloud computing is a form of IT infrastructure that delivers computing power and data processing resources, as well as related technology, to users through the internet. In contrast to traditional techniques in which all the responsibilities are of the individual users, cloud computing includes sharing a pool of customizable computing resources (e.g., servers) and data across numerous users for a continuous time (as long as the subscription payment is valid).
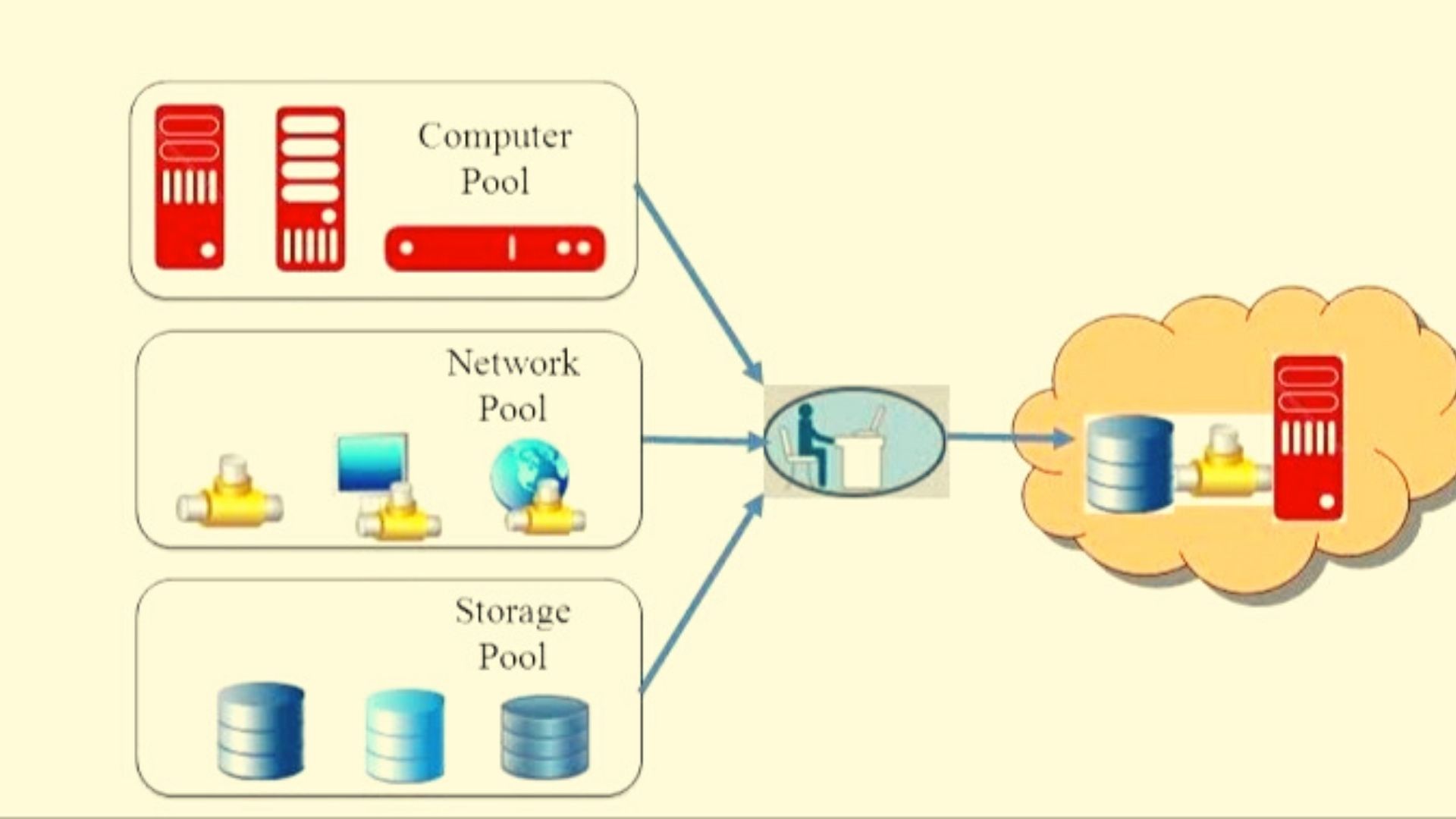
1. Resource Pooling
Resource pooling is a cloud computing service model in which the cloud provider aggregates hardware resources and makes them available to multiple consumers as a single pool of shared resources. In this way, users can leverage the benefits of virtualization without having to manage physical servers and operating systems.
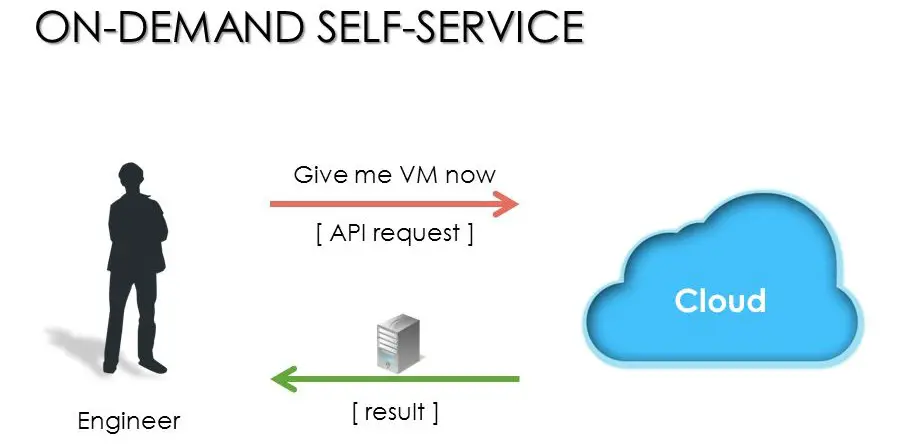
2. On-Demand Self-Service
On-demand self-service is a good thing. It means that you can get what you need, when and how you want it, without having to talk with a person about it. But there’s more to on-demand self-service than just being able to request things from the cloud. You also get control over your IT infrastructure via virtualization and automation tools—control that extends beyond managing servers or desktops to encompass applications like databases and storage systems that run across several servers in various locations. Allows companies like Google, Microsoft Azure, and Amazon Web Services (AWS) to access markets where they previously could not compete because they had no presence at all!
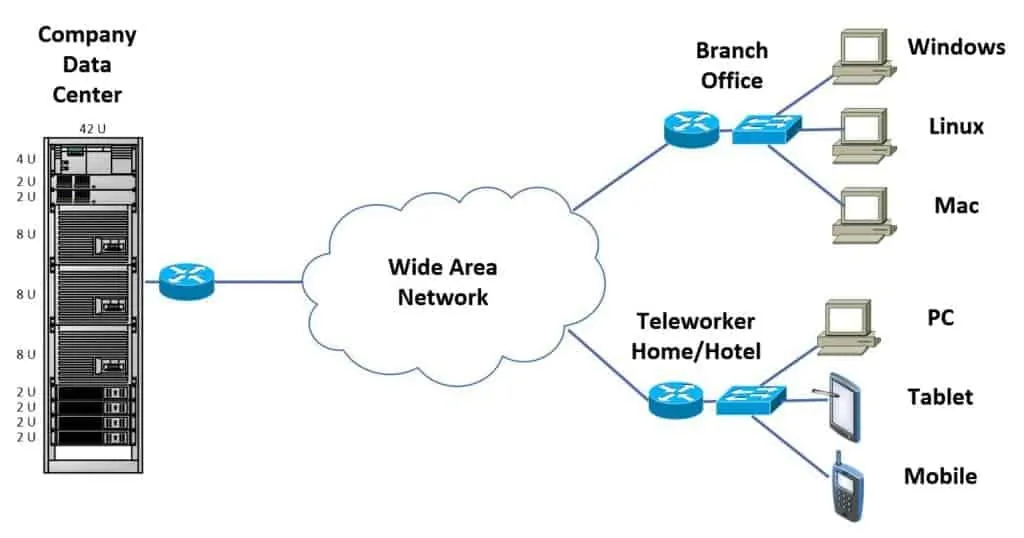
3. Broad Network Access
Cloud computing is a broad term for remote data storage and processing that does not require on-premises infrastructure and includes access from any location, including mobile devices; access from any device, including PCs, tablets, and phones; and over the internet (or another network).
4. Rapid Scalability And Elasticity
Cloud computing allows you to scale up or down automatically and manually. Still, it is much easier and faster when you permit your cloud provider to handle this task for you. Even if demand spikes unexpectedly, your cloud resources will be ready in seconds instead of minutes or hours. Cloud providers also offer rapid elasticity—the ability to add more servers as needed without having to wait until they become fully utilized before adding new ones. Businesses may scale up their infrastructure at any moment without suffering any downtime because of elasticity.
5. Economical
Cloud computing is economical. It reduces costs, meaning you pay for what you use and where you use it. There are no upfront costs for any cloud service.

6. Performance
Performance is a crucial characteristic of cloud computing. Cloud-based services can improve performance by allowing users to offload tasks previously done on their hardware, such as data storage and processing. Speed, latency, and throughput are the metrics used to measure performance. Speed refers to how quickly a service responds; latency refers to how long it will take to complete your request; throughput refers specifically to the amount of information transferred at once (e.g., one gigabyte).

7. Reliability
Reliability. The cloud is reliable because it spreads widely, meaning that your data and applications are across multiple locations, providing greater redundancy and resilience. For example, if one server goes down, another will automatically take its place as soon as possible—no need for you to wait around until someone can fix it. You can scale up or down depending on what you need at any given time (e.g., when using Amazon Web Services).

8. Security
Cloud computing provides more security to consumers than traditional client-server networks. In transit, data is encrypted, and a firewall is responsible for preventing unauthorized access. Cloud services also include authentication, meaning only authorized individuals may access your data. The service provider implements access control policies to ensure that only authorized workers can access company information or apps on a desktop or mobile device. Cloud computing has many benefits for companies of all sizes. However, one thing that sets this technology apart from other IT solutions is privacy protection.

9. Work From Any Location
Cloud computing allows you to work from any location, not just your office or home. You can use the same tools and applications from anywhere, so there’s no need for a physical space. You can work from home or while traveling at your convenience.

10. Comfortable Payment Structure
Cloud computing refers to Internet-based services that provide shared pools of configurable, scalable, and available resources. These resources are virtualized on the cloud platform and are accessible online by users. Cloud computing enables businesses to build applications from scratch or modify existing applications in real time and deploy them as needed without worrying about hardware maintenance or security updates. Cloud providers such as AWS (Amazon Web Services), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform offer their services at various price points depending on how much you want to pay per month for your usage requirements. For example, if you need basic functionality like emailing documents between employees across different teams, then it would be more cost-effective than using SoftLayer, which offers dedicated servers only capable of handling basic webpages. At the same time, other platforms provide unlimited storage space, which can be used for anything from storing photos, videos, audio, etc., all at no extra cost!

Conclusion
Cloud computing is a great tool that you can use to make your business more efficient. With the correct configuration, the cloud can help reduce operational costs and increase productivity in both personal and professional life.

















