The significant advantage of automating security functions is that it can manage and process many datasets, and manual security systems can be time-consuming. Organizations can collect and analyze the volume of data from multiple sources using automated technologies such as SIEM systems and threat intelligence platforms to uncover trends. It helps security teams respond quickly to potential breaches before they escalate into full-blown attacks. Another reason to automate security functions is that it allows security personnel to focus on more complex tasks that require human knowledge.
1. Defensive Actions
It is scanning the online resources from potential cyber threats to keep them safe. When danger is confirmed, it is processed manually to fix it. It is helpful for businesses to automate the steps combating security vulnerabilities, reduce downtime and save money.

2. Data Encryption
Companies use strong encryption to reduce the cost of data breaches because malicious actors read and use the data they have accessed. Organization encrypts their data, so it is difficult for cybercriminals to read. Companies never encrypt data and deploy other security technologies to prevent cybercriminals from accessing the data.

3. BOT Activity Monitoring
Monitoring robot activity should be part of the design of any automation program. Bot privilege is never tied to the end user account. The system credentials requested by the bot are encrypted and not accessible in plain text. Bot actions is centrally recorded at runtime. Bots run on their own VLAN to simplify network monitoring and risk management.

4. Compliance, Audit, And Incident Response
Automating compliance, auditing, and incident response process is beneficial for business. Companies ensure consistently to meet industry regulations and standards. It helps to identify potential compliance issues and address them before they become serious problems. The companies ensure that they are meeting internal and external audit requirements. Automation can provide real-time monitoring and reporting.

5. Threat Detection
Organizations prevent cybercriminals from accessing networks and stealing data by identifying and responding to potential threats. It uses machine learning, artificial intelligence to predict and stop cyberattacks. Automated tools detect threats more accurately than members of an organization’s security team.

6. Data Privacy
Automating data security ensure organization complies with the regulation. AI-powered tools navigate the environment of the organization and identify processes that is not complying with requirements. Ensuring companies meet regulatory compliance requirements to keep systems secure.

7. Vulnerability Scanning
Cybercriminals use system and software vulnerabilities to launch attacks against companies before vendors release security updates. Security analysts can’t identify and fix all vulnerabilities before a cyber attacker exploits them, Companies automate vulnerability scanning to identify and evaluate based on severity and potential impact.

8. Automation Of Data Management
Members of an organization’s security team spend most of the workday manually managing tools to ensure the security of sensitive company data. Spending many hours collecting data isn’t efficient. They are automating tasks such as logs, asset management, and data collection frees up time for skilled security team members to perform high-value tasks that require human intervention.
9. Application Security
It is no longer possible to rely solely on manual labor to guarantee application security. It is because the number of DevOps installations is increasing as more businesses use low-code, no-code, and application programming interfaces. A manual approach introduces human errors, increasing the risk of security breaches. Companies protect their applications using automated solutions that validate authentication, authorization, and encryption protocols. It can use automation to scan apps for known security flaws.

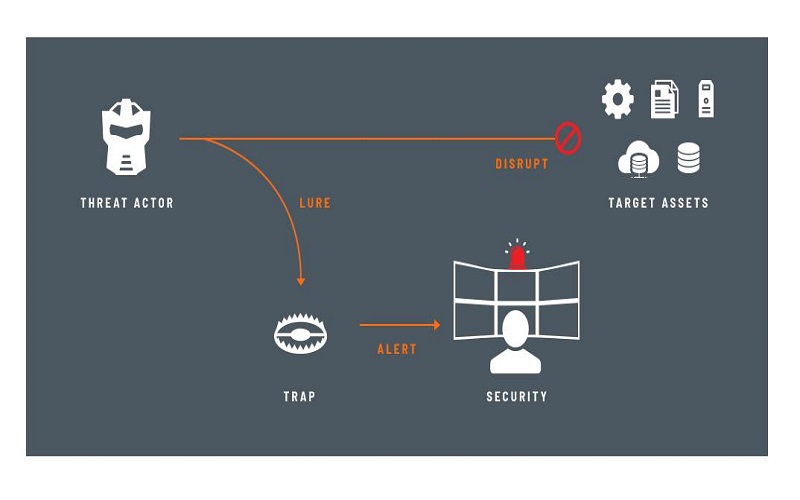
10. Automated Deception Technology
To convince cybercriminals, AI-powered deception technology deploys decoy assets in the network. If the attackers breach the networks searching for decoys, the tool gathers threat intelligence about them and issues a silent alert. The threat then be addressed by security teams taking appropriate action. All environments, including the perimeter, endpoints, Active Directory, IoT, and the cloud, can benefit from automated deception technology.