Secure identification technology is necessary in the current day to ensure the privacy and security of individuals, organizations, and sensitive data. Important findings in this field have changed how we authenticate identities. We’ll look at the top 10 developments in secure identification technology. These innovations, which include blockchain-based solutions and biometric authentication, are revolutionizing security standards and increasing trust in a variety of sectors, including banking, healthcare, and government.
1. Edge Computing
Recent developments in GPU processing technology have sparked the development of specialized computer systems that are very helpful for facial recognition. Without the need to send massive data streams to centralized servers, these systems can handle video data streams locally. The preprocessing of video streams can be done independently by edge devices like NVIDIA Jetson or Blaize. Only the findings, which are sent to a central server for comparison, are provided by the edge devices for face recognition, extraction, and template construction. By many orders of magnitude, this lowers the needed throughput of the local data link from as much as tens of megabits.

2. Biometrics In The Cloud
Processing-intensive jobs may now be transferred to the cloud instead of a dedicated local server with only a little performance penalty because of the decrease in necessary bandwidth, a task that was previously unimaginable for real-time facial recognition. This enormous advancement creates a host of fresh opportunities, including the simultaneous remote surveillance of many locations.

3. Accuracy In Image Fragments
Advances in reliably confirming fingerprints, even with minute fragments, were made possible by combining neural networks, high-resolution fingerprint sensors, and small-area detectors. Although this is crucial to enhancing criminal investigative understanding, there are many other possible applications for this technology. It works with tiny smartphone sensors and fingerprint readers for biometric payment cards. Because the technology is driven by a little current at a point-of-sale terminal, identification systems for credit cards will be able to validate the cardholder by just a small portion of a fingerprint.

4. Multifactor Authentication
MFA techniques employ multiple authentication factors, which a user must supply with each login attempt, adding an extra degree of protection. These elements are often things a user owns (a phone token or object like a USB key), something they are (biometric identification), or something they know (a code). The most desired component is evolving into biometric technology, taking the place of conventional single-factor authentication and easily cracked passwords.

5. Improving Accuracy In Specific Segments
With regards to children’s looks and fingerprints, for instance, biometrics still has challenges in delivering trustworthy findings. It is more challenging for computers to accurately recognize the nuances of tiny fingerprints. Today, several developing technologies concentrate on these particular use cases and work on accurate identification, which is a very useful tool in the battle against child abuse and trafficking situations.
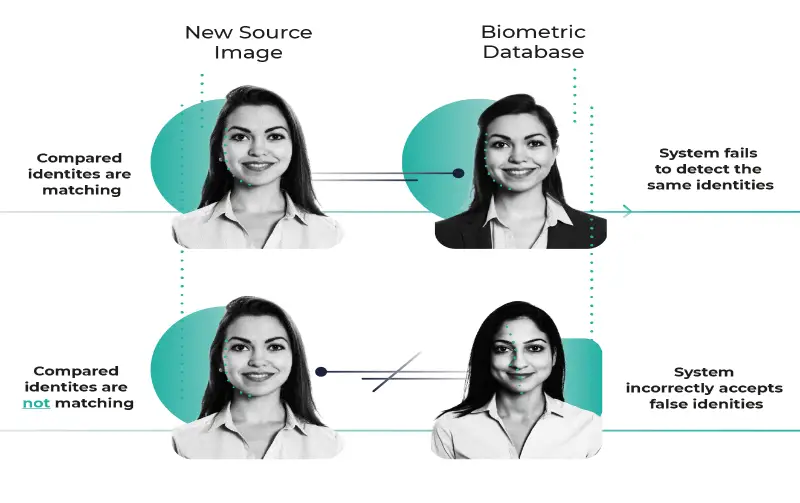
6. Seamless Biometrics
Recent developments in edge computing and novel identity detection techniques both contribute to the development of fresh ideas for seamless identification. For instance, modern algorithms may identify someone approaching a turnstile, provide entrance (if it’s a legitimate entry), summon a lift to the right floor, and only unlock the offices that the identified individual would use. There are still many application cases. In hospitals, biometrics can be used to recognize unconscious patients, alert medical staff about allergies, or reveal a patient’s insurance status.
7. Highlighting Ethics And Mitigating Bias
Companies will grow more concerned with the quality of biometric algorithms when choosing a supplier in light of recent dubious situations like ID.me, the IRS mess, or the Clearview issue. Finding business partners will be challenging for those perceived as biassed or unethically formed out of concern for a bad reputation blowback, particularly in industries where reputation is crucial for business (such as banking). This will lead to a good response against purported con artists or negligent service providers, raising industry standards overall.
8. Biometrics Beyond Identification And Verification
Although reliable identification and verification were at the forefront of biometric development, they may and will be used for a wide variety of other reasons as well. Consider age checks in supermarket self-checkout lanes or while purchasing alcoholic beverages online. All you need to do is scan an ID, compare the document photo to a selfie, and have the birthdate automatically read. Additionally, body language and motion detection are useful for immediately spotting suspicious behavior on public security cameras or risky mishaps, such as a person being struck by heavy gear in a workplace.

9. DNA Recognition
There is no biometric technology that always offers the best-identifying option. However, a certain biometric may stand out as the preferable way of identification based on the biological system. Undoubtedly, the most effective and trustworthy method for determining genetic features is DNA profiling. Numerous fields, including forensic science, environmental science, medical science, and history study, can benefit from the knowledge that DNA typing can give.
10. Behavioural Biometrics
The study of patterns in human behavior that are capable of being used for uniquely identifying and measuring purposes is known as behavioral biometrics. Physical biometrics, which uses natural human traits like fingerprints or iris patterns, is in contrast to the phrase.