What Is Nanotechnology?
Nanotechnology term refers to the branch of science and engineering dedicated to designing and producing structures, devices, and systems by operating atoms and molecules at the nanoscale, that is, having more than two dimensions of the order of 100 nanometres or less. Many examples of structures with more than two-nanometre dimensions and many innovations are included in such nanostructures.
How Does It Work?
Nanotechnology is the study and management of nanoparticles in a beneficial way. Nature contains nanomaterials such as haemoglobin, fire smoke, volcanic ash, and sea spray. Nanotechnology is the study of matter at the nanoscale scale, where unique events allow for creative uses. Observing, measuring, modelling, and controlling matter at this length scale is the scope of nanotechnology, which encompasses nanoscale science, engineering, and technology.
It includes the design, characterization, production, and application of nanoscale structures, gadgets, and systems that perform with at least one of these characteristics. One of the primary advantages of nanotechnology is that it increases the surface area of a material, allowing more atoms to combine with other materials. This application is responsible for nanoparticle strength, durability, and conductivity.
Features Of Nanotechnology
1. Electronics And IT
Nanotechnology has provided significant advances in computing and electronics, leading to faster, smaller, and more durable systems that can organize and save significant amounts of information. Transistors are the primary switches that allow all modern computing to get smaller and smaller in nanotechnology. A typical transistor was 130 to 250 nanometres in size. MRAM is allowed by nanometre-scale magnetic tunnel junctions and can randomly and efficiently save data during a system shutdown or allow-play benefits.
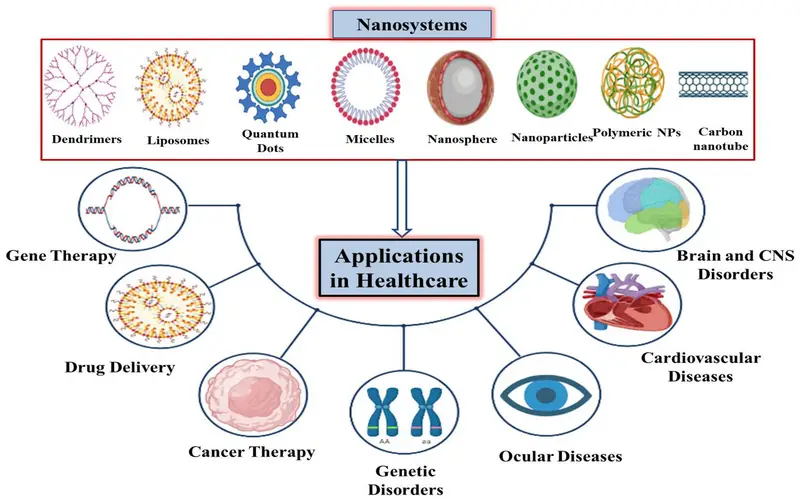
2. Healthcare And Medical
Nanotechnology is expanding the medical tools, knowledge, and therapies nowadays available to clinicians. Nanomedicine, the utilization of nanotechnology in medicine, draws on the natural scale of biological events to produce accurate solutions for disease prohibition, diagnosis, and treatment. Commercial applications have adopted gold nanoparticles as an examination for the detection of planned series of nucleic acids, and gold nanoparticles are seen as potential treatments for cancer and other diseases. Imaging and diagnostic tools allowed by nanotechnology concrete the way for previous diagnoses, more personalized treatment options, and the best therapeutic rates.
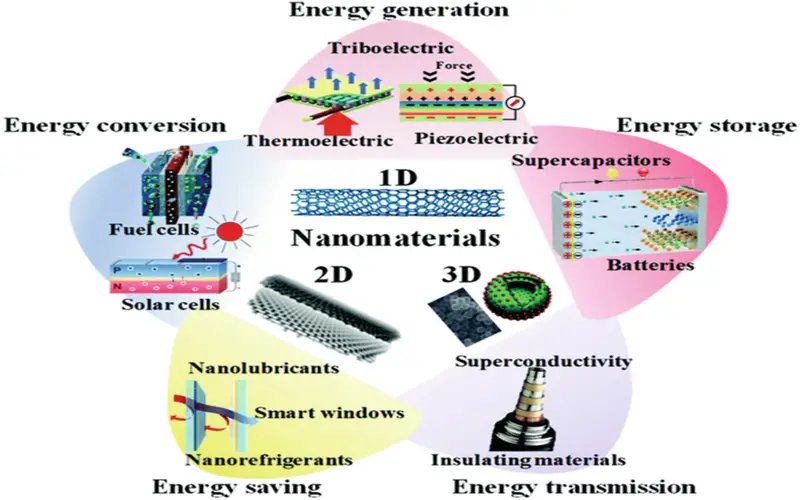
3. Energy Applications
Nanotechnology is application locating applications in traditional energy sources and is improving alternative energy access to help in increasing energy demands. Many scientists want to develop clean, affordable, and renewable sources, along with means to moderate energy consumption and toxicity load on the environment. Nanotechnology is the enhancement of the efficiency of fuel production from raw petroleum materials through best catalysis. It also reduces fuel use in vehicles and power plants by higher-efficiency combustion and decreases friction.
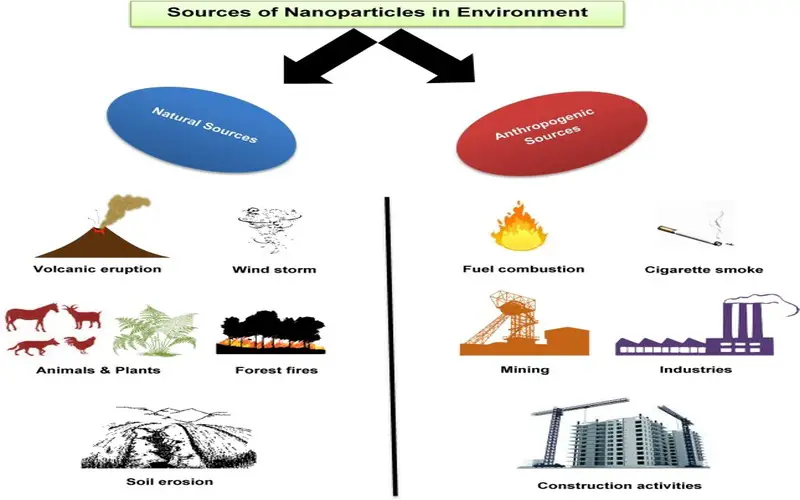
4. Environment Remediation
There are numerous ways that nanotechnology might help increase energy productivity and environmental circumstances. Nanotechnology helps to meet the requirement for economical, clean drinking water by quick, low-cost observation and treatment of impurities in water. This molybdenum disulphide (Mos2) membrane distilled two to five times more water than power ordinary filters.
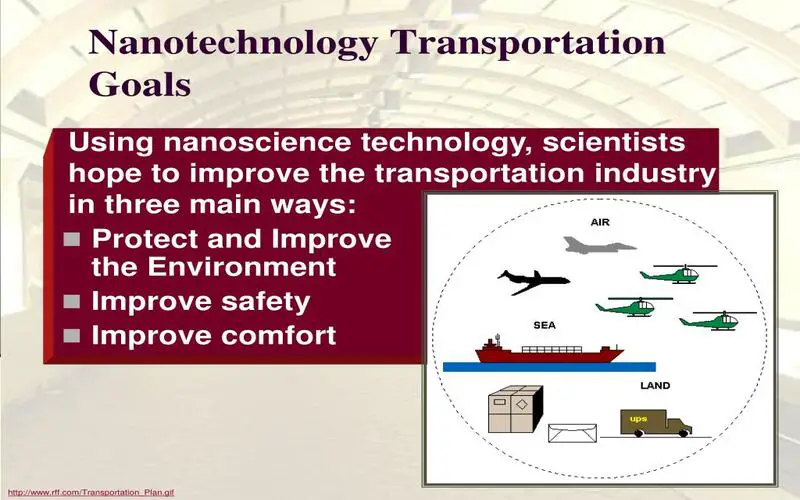
5. Future Transportation
Nanotechnology holds the promise of allowing the development of multifunctional materials that will help in the construction and maintenance of lighter, safer, brighter, and more efficient vehicles, planes, spacecraft, and ships. Nanotechnology provides a variety of ways to improve transportation infrastructure. Nano-engineered materials in automotive products include structural polymer nanocomposites, high-power rechargeable battery systems, thermoelectric materials for temperature control, lower rolling-resistance tires, high-efficiency/low-cost sensors and electronics, thin-film bright solar panels, and fuel additives and improved catalysts for cleaner exhaust and more extended range.
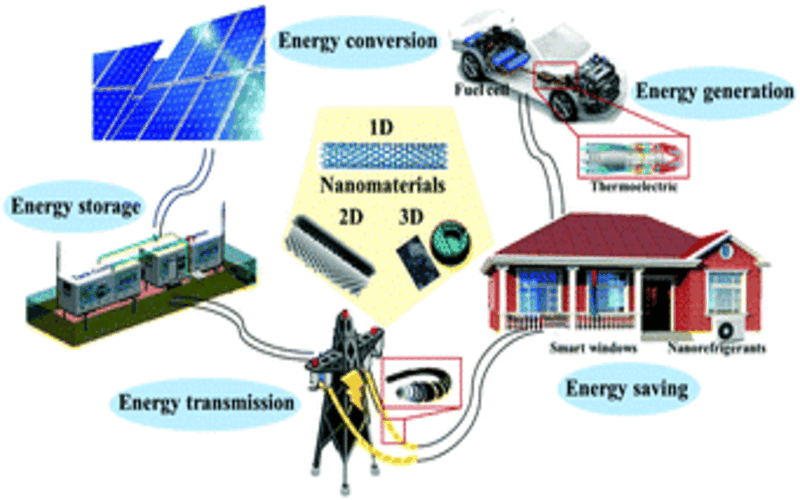
6. Energy And Electronic
Nanotechnology changes how we acquire and utilize energy. Nanotechnology will make solar energy cheaper by lowering the cost of creating solar panels and related devices. Energy depository equipment will become more productive as a result. It provides a new method of generating and storing energy.Nanotechnology will soon alter the world of electronics. Quantum dots, for example, are small light-creating cells that can be used in display screens.
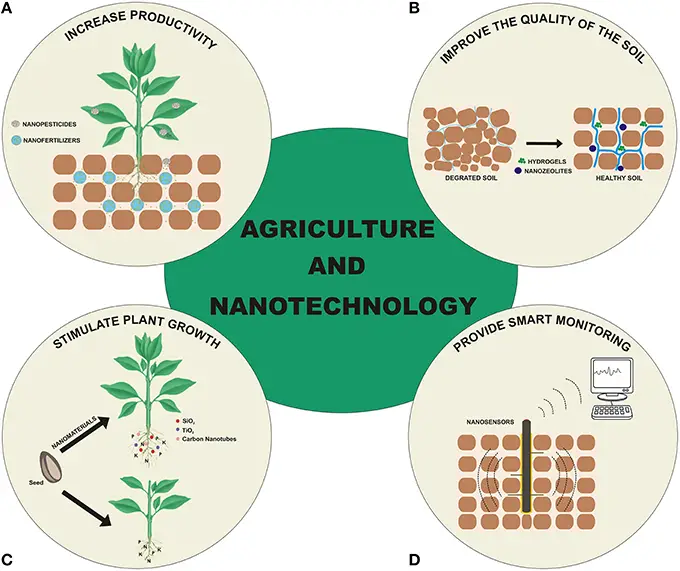
7. Agriculture Nanotechnology
The use of nanotechnology can undoubtedly extend the life of fruits and vegetables. For example, if we put a silver nanoparticle into foods, then it works as an antibacterial agent. The nanoparticles are large enough food components to have a harmful impact and alter the flavor. The elongation of the Food and Drug Administration doesn’t have a particular stance on nanotechnology. The organization suggested that companies using nanotechnology consult with it to discuss the product.
8. Reduced UV Exposure
The majority of sunscreens consist of nanoparticles that absorb sunlight, including the most dangerous UV range. They also apply more quickly over the skin. The same nanoparticles are utilized in food packaging to reduce UV exposure and increase shelf life.
9. Improved Security And Surveillance Systems
It allows a wide range of chemical sensors to be set up to expose a specific chemical at deficient levels, for example, a single molecule out of billions. This capacity is suitable for observing and security systems in laboratories, manufacturing plants, and airports. Nanosensors can be used in medicine to specify certain cells or chemicals in the body accurately.
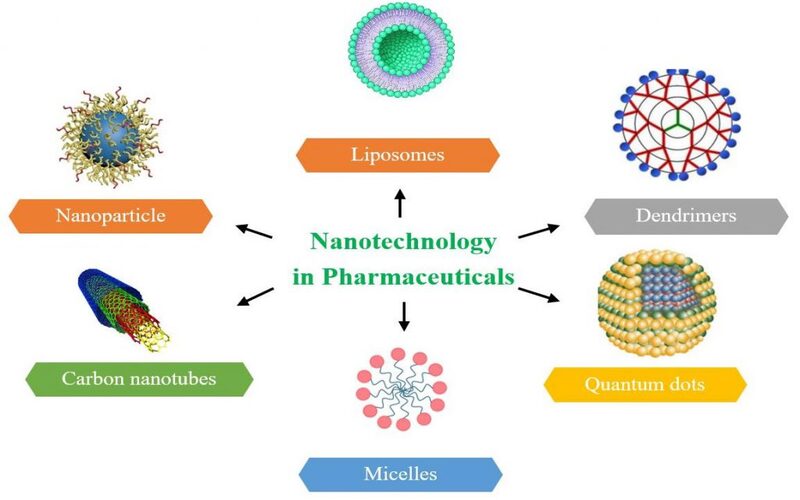
10. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
The Separate parts of nanomedicine, which may be incapable of therapeutic use on humans on their own, are combined to create a new tiny medicinal product with therapeutic enhancement. This new product surpasses its traditional equivalent in terms of absorption and administration. This production method, for example, is used to create several vaccinations.