What Is Hyperscale?
Hyperscaler is a large-scale data centre that is major in delivering vast amounts of computing power and storage volume to maintain individuals across the globe. These data centre is one of a kind to help the broad demands of millions and billions of consumers, ensuring seamless scalability. Unlike standard data centres, hyperscalers are outfitted to support massive workloads without accommodations on performance or effectiveness. Their structure is maximized for agility, adaptability, and scale, making them the backbone of modern cloud computing.
What Does A Hyperscaler Do?
A Hyperscaler’s primary function is to give scalable computing, storage, and network of servers, storage devices, and network parts that can be executed and scaled on demand to meet the needs of consumers worldwide.
How Do Hyperscalers Work?
Hyperscalers work by generating a massive hardware and software structure to enable a vast number of end consumers. One of the vital features of hyperscalers is the scale of their design. They have millions of physical servers distributed worldwide, each provided with high-speed network connections, powerful computing resources, and vast amounts of storage. It enables them to provide smooth and high-performance computing services to consumers.
Examples Of Hyperscalers
The digital landscape is marked with multiple prominent hyperscalers; each presents a unique suite of services customized to various needs. Here are some of the largest platforms:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)- Amazon’s cloud arm, AWS, provides many services, from computing power to storage solutions, making it a prime example of a hyperscale.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)- Google’s cloud services, enclosing everything from machine learning to data analytics, are powered by their hyperscale structure.
- Microsoft Azure- Microsoft’s cloud solution provides a variety of services, including computing, analytics, storage, and networking, all supported by hyperscale servers.
- Alibaba Cloud- As Alibaba Group’s cloud computing branch, it offers a comprehensive portfolio of worldwide cloud computing services.
How Hyperscaler Computing Works
Hyperscale computing enables for quick addition of resources without the requirement for more space, power, or cooling. Defining features of this computing group involve high availability and performance, standardization, automation, and redundancy. It’s generally associated with the broad data centres holding thousands of physical servers millions of virtual machines with structure specially designed servers and millions of virtual machines with structures for maximising hardware density and minimum spending. Hyperscalers are large cloud computing and data center solution providers who use this architecture. Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure are examples of well-known hyperscalers.
1. Limitless Resources
Hyperscalers provide users with virtually limitless computing, database, and storage volume. These services are easily reachable, highly available, and strongly focused on security and flexibility. Hyperscaler users gain agility via the quick on-demand entrance to technology that would ordinarily need a broad financial investment, as well as weeks or months to obtain build and operationalize. This on-demand model for structure also enhances cost-effectiveness for businesses of all sizes.

2. Migration Reach
Many adopters start their hyper scaler migration by selecting the software apps that are the most appropriate to run within a cloud environment. These organizations will resume migrating workloads to the cloud as their business goals expand, he adds. Many hyperscaler adopters, as they become progressively comfortable with the reach, are beginning to set up multi-cloud estates. The criteria are typically based on performance, cost, security, access to skills, and often and compliance factors.
3. Hyperscalers Outlook
It expects most hyperscalers to focus on enabling and supporting significant business transformations. Enterprises are trading with the entanglement of decades of innovation, modernizing offers by the hyperscalers, and the acceleration of decomposition and modernization offers a primary benefit for both business users and the hyperscale providers. It forecasts that hyper scalers will be required to become distributed to address the growing needs of increases digitally allowed and hyper-connected world. The processing power to shift closer to the user will enable businesses to contribute with users through advanced AI/ML ability in actual time, offloading complex observes to the existing centralized structure hyper-scalers have constructed.
4. Computer, Storage, Networking, And More
Hyperscalers provide more than just compute and storage power. They also offer various value-added services, such as database management, machine learning, big data analytics, and security. These services are united with core providing, allowing users to access an extensive suite Of It services from a single provider.
5. Hyperscalers Power Major Cloud Service Providers
Hyperscalers are the backbone behind significant cloud service providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These cloud platforms provide a vast range of computing, storage, and networking services, and software-as-a-service (SaaS) and platform-as-a-services (PaaS) services.

6. Services That Hyperscalers Can Provide
Hyperscalers provide a broad range of services that can assist businesses they’re IT aims. Some general services involve AI and machine learning, database management, storage, content delivery, and networking. These services can be deposited over the cloud or through assertion solutions and help reduce costs and complexity for consumers.
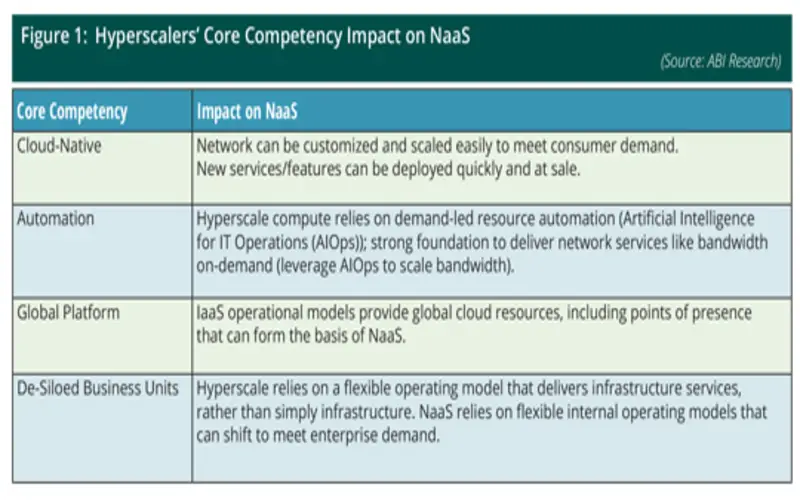
7. Hyperscaler Business Model
The organization’s model of hyperscalers is a blend of technology, innovation, and planned market positioning. At its core, the model offers 4broad computing resources on a scalable and on-demand premise, but there’s much more to the story.
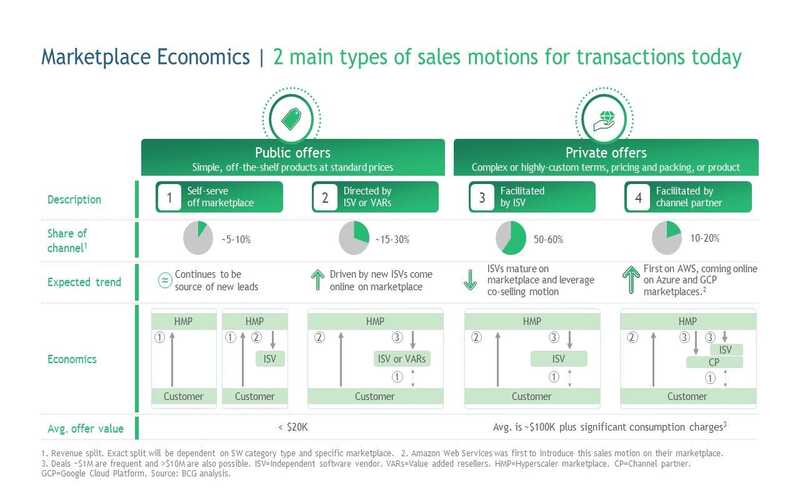
8. Pricing Schemes
Hyperscalers usually adopt a pay-as-you-go pricing scheme. Users are promoting their actual usage, enabling for cost-productive scaling. Some also provide tiered pricing, where businesses can choose from distinct packages based on their requirement, or even restored instances where they commit to enlarged terms for reduced rates.
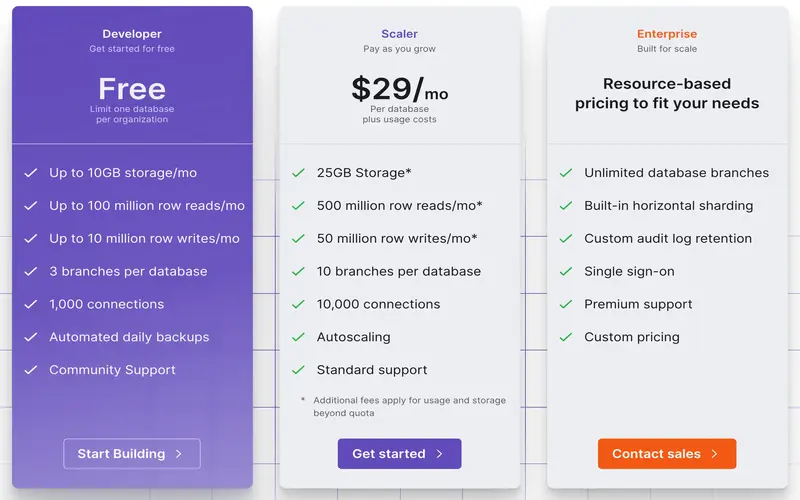
9. Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
To ensure credibility and trust, hyperscalers offer SLAs that contract certain levels of service uptime performance. These agreements involve compensation clauses for any downtime or service disturbance, ensuring businesses can handle it with confidence.
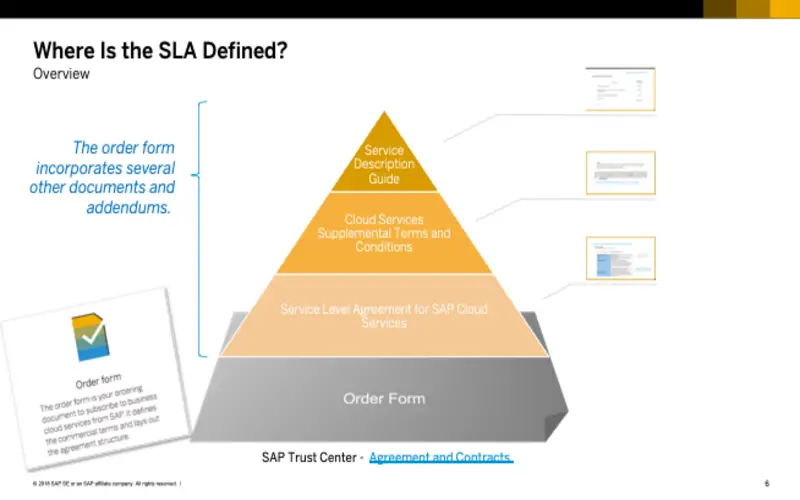
10. Infrastructure As A Service (IaaS)
IaaS is one of the critical services provided by hyperscalers. Instead of investing considerably in hardware, businesses can rent virtualized hardware resources from hyperscalers, such as servers and storage. This concept allows firms to grow up or down depending on their needs.