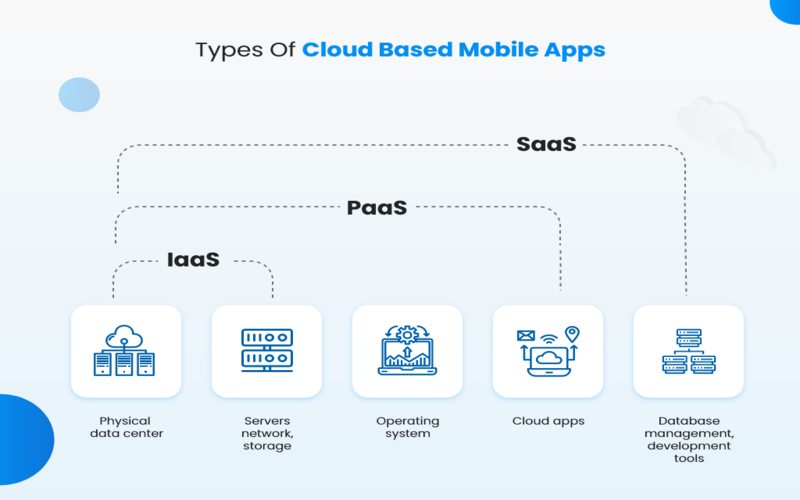
What Is Cloud Adoption?
Moving to or implementing cloud computing in an enterprise is referred to as cloud computing adoption. It can include transitioning from site infrastructure to the cloud or using it in addition to site infrastructure.
Features Of Cloud Adoption
Deploying Your First Workload
- Find your lighthouse application
- Include stakeholders
- Design right the first time
- Learn for free
- Flip back, automate, and evaluate.
Accelerate Your Cloud Adoption
- Look at a proof of concept
- Include a partner
Common Pitfalls
- People, Process, innovation
- Know your responsibilities
- Tag everything
- Transform as much as you can.
Network
- Don’t underestimate the potential complexity and time to execute
- Don’t estimate where the default VPC is located.
- Understand the mechanical limitations of Cloud networking, involving bandwidth and latency.
Performance And Cost
- Ensure you have cost control and governance decisions.
- Use tagging and cost organization mechanisms such as billing alerts.
- Turn off resources when not in use, such as development surroundings.
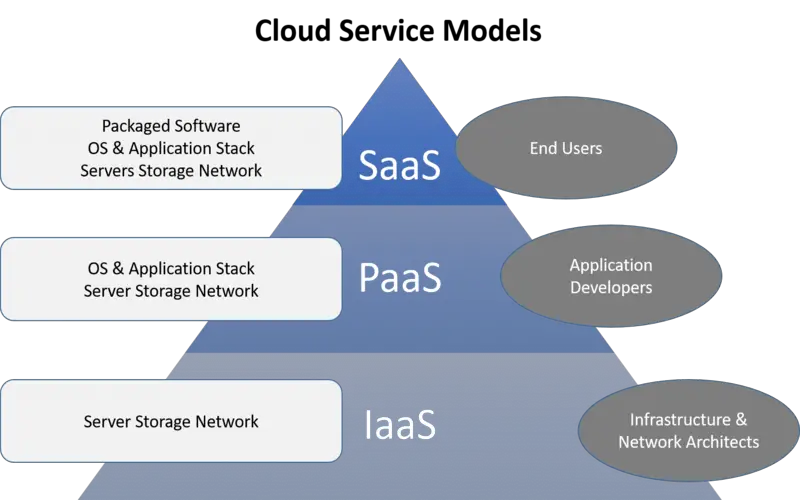
Shared Responsibility Model
- Where your responsibilities lie
- Be careful of dividing Controls.
- Don’t assume security
- Responsibilities are distinct for laaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Optimize Your Application
- Amaze Everyone
- Transfer something
- Avoid harm
- Ask for help
- Engage a partner
Practical market sentiment with stand-up competition and profit margins getting thinner, cloud computing has given a stream of hope to small-scale businesses. They can complete their more significant parallel by providing technology solutions based on the cloud. An expanding number of conferences by industry apartments and government have animated the reluctant small-scale companies’ owners to examine.
1. Efficient Communication
The end-user cloud applications were appropriate at a faster rate, The idea of operating organizations’ applications in the cloud had turned away many companies’ owners. Service offers security and privacy concerns continue, managing a clear understanding of the costs and benefits of operating applications in the cloud.

2. Size Of Small And Medium Organizations
India has the SME size in the Asia-Pacific region. SaaS has particular SMEs administer to innovation that has cut down the IT responsibilities of organizations—fast deployment, adaptability, and pay-as-you-go model outfit the needs of modern dealers in India. SaaS dealers entering this market space have a rare opportunity to tap both standard and start-up businesses.

3. Maintaining Business Data Core
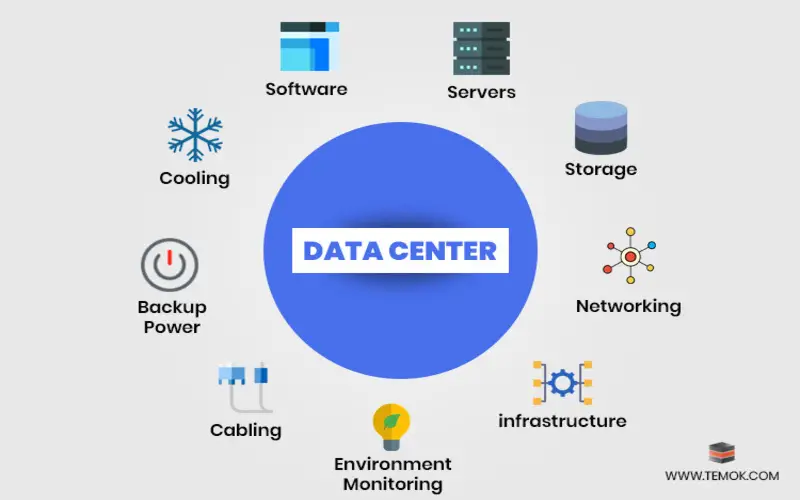
Maintaining a business data core is a costly affair. Organizations have to lavish significant amounts of money yearly to pay for power to run and cool the focus. A business data focus in India occupies an average space of 1000 to 1500 sq. ft, and buying or hiring this much space is nothing but the destruction of money and adds to the carbon footprint of the nation. Data focus security is vital for the organization. They must establish proper security precautions to avoid being refused admission to the institute. Data focus merging and virtualization is increasing the demand for public cloud.
4. Standard IT Models Are Becoming Unviable
Operating a business independently on a standard assumption system gives a chance to gain a competitive edge, and is the mark of inactive business. The growth rate of traditional IT systems has observed a significant decrease since 2008. Trader is maximizing adopting technology company’s models to overpower their rivals. The combination of the company’s model is finding united acceptance among businesses as it uses a mixture of standard IT systems and cloud services. While vital applications speed up on-premises systems, less critical applications are economical to run on the cloud.
5. Shortage Of Regulation Laws
Indian organizations don’t have to get approval from government authorities while moving data, services, or applications to the cloud. In Europe, for example, firms are expected to obtain government consent before storing data outside of the country’s physical borders. In India, there are no instructions for data security and privacy. Focused more on cloud innovation, Indian merchant is yet to understand the growing challenges of data security.
6. High Amount Of Independent Software Traders
Most individual traders have finite resources, but the cloud computing model has authorized them to use resources at reduced costs. As a result, traders have the development abilities to provide technological solutions to organizations of distinct sizes with different needs.
7. Difficulties Faced By Mobile Workforce
The number of mobile workforces is maximized at a quick pace. To remain alive in stiff competition, mobile workers must have administered actual time user information to analyze key performance metrics like bookings, revenue, and spending feedback, immediately assist with daily tasks, and gain awareness by creating evaluating reports. Cloud innovation offers actual time access to such data transport on mobile devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops through harmonious applications that are produced to enhance co-coordination, creativity, and responsiveness within the organization.

8. Quick Growth In Mobile Applications
With the increase in the number of smartphone consumers, there has been a quick growth in the demand for mobile apps. All the primary e-commerce stores have proceeded with a mobile application to make it convenient for users to buy from their stores. Many cloud storage, ERP, and CMR apps are accessible on mobiles. Thus, mobile apps are benefiting the consumers to share and have immediate access to content through cloud innovation.
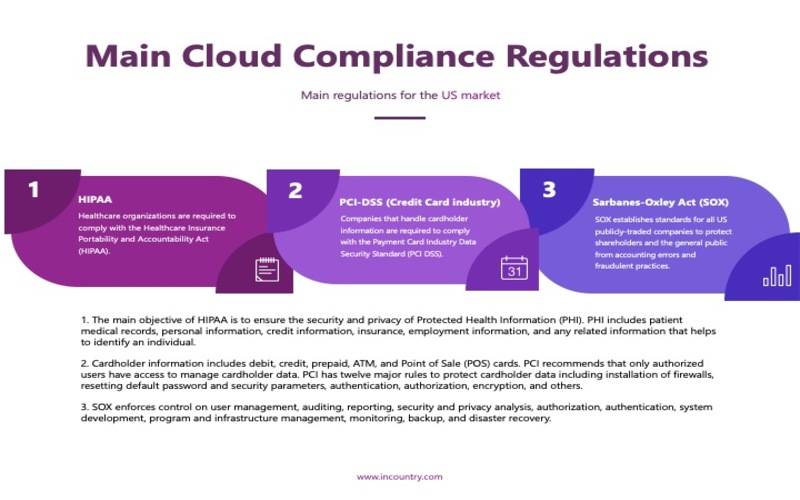
9. Regulatory Compliance
In cloud Computing, the geographical place of data storage and processing is not explained, unlike standard IT systems. These compliance difficulties were owing to data flow, companies’ continuity, and network scans on public cloud infrastructure. Security certifications of cloud infrastructure are a vital challenge for many companies as opposed to standard IT systems.
10. Shortage Of SaaS Integration
Cloud models provide significant benefits to business owners and several companies that expect seamless compatibility with in-house infrastructure and the cloud. Many clouds have platforms distinct innovations and configuring them with standard IT systems is complicated or impossible. SaaS inclusion is the best way forward to integrating several cloud applications with legacy systems. Still, to a shortage of awareness among both service offers and consumer organizations, SaaS implementation is going to take a long time before implementing several cloud application systems.