Unified Messaging
The new Unified Messaging (UM) server role in Exchange Server 2007 extends the functionality of your Exchange messaging infrastructure, allowing it to transmit and store more than just traditional e-mail. As more established communication solutions
(Voice and fax) find a new life on IP networks, a new means of storing and facilitating access to the information is required. The Unified Messaging (UM) server role provides that capability natively in your Exchange 2007 organization. From a user’s perspective, Unified Messaging provides easy access to voice messages, faxes, and e-mail in way that was simply not possible before Unified Messaging.
The Unified Messaging server role provides the following functionality to an Exchange Server 2007 organization.
1. Fax reception and delivery to Exchange mailboxes
2. Voice call answering
3. Voicemail recording, and delivery of voicemail to Exchange
Mailboxes
4. Voicemail access via a phone connection
5. Message read back via a phone connection, including replying to the message or forwarding it to another recipient
6. Calendar access via a phone connection, including meeting request acceptance
Out-of-office messages in voicemail via a phone connection.
Unified Messaging servers are intended to be deployed only in the internal network and must be deployed in sites that contain at least one Hub Transport server. Additionally, the Unified Messaging server must have reliable, high-speed connectivity to the Mailbox servers, domain controllers, and global catalog servers in the organization. An IP PBX or VoIP gateway device is required to tie the Unified Messaging server to the phone system.
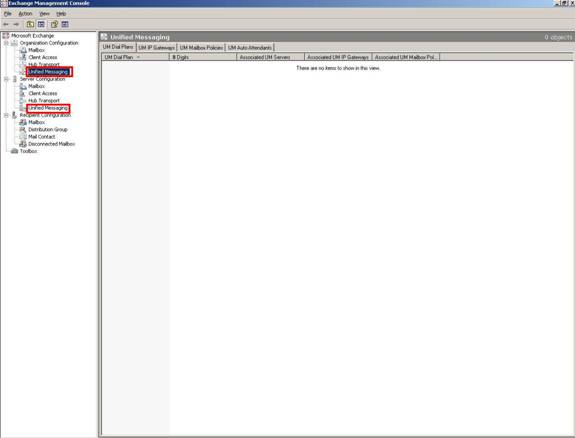
The Screenshot above is got when UM is configured at the organizational level.
Integrating Unified Messaging servers with a VoIP solution requires a minimum number of configurations performed in a specific order. These steps should be performed after the gateway and legacy PBX or IP PBX have been tested and are functioning:
1. Create a dial plan.
2. Create a UM IP gateway.
3. Create a UM mailbox plan.
4. Create a UM hunt.
5. Create UM dialing rules.
6. Assign UM dialing rules to the dial plan and to the mailbox policy.
7. Generate GAL Grammar.
We can see from the below screenshots that the new UM Dial Plan for the Exchange 2007 & Exchange 2007 SP1 differ. Exchange 2007 SP1 comes with the addition of URI type and VOIP Security.
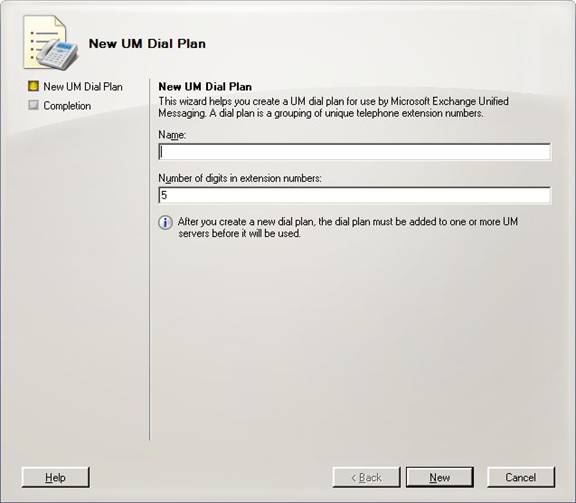
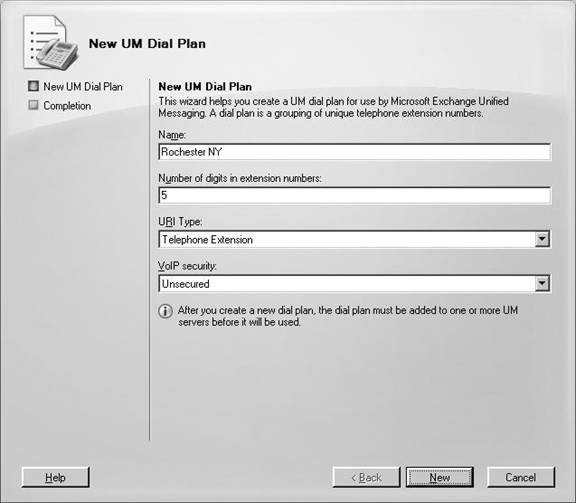
Creating a Dial Plan
Use the following steps to create a dial plan
1. Open the Exchange Management Console with an administrator account that has
The Exchange Organization Administrator role.
2. Expand Organization Configuration and select Unified Messaging.
3. Select New UM Dial Plan in the Actions pane.
4. Type the name of the dial plan in the Name field, as shown next.
5. Enter a value that matches the number of digits in your users’ extensions in the
field Number of digits in extension numbers. The default is 5.
6. Select the option in the URI Type drop-down list that is recommended by your
IP gateway or IP PBX vendor.
The options are: • Telephone Extension (Default) • E.164 • SIP URI
7. Choose a security method from the VoIP security drop-down list.
The options are: • SIP secured • Unsecured (default) • Secured
8. Click New.
As an alternative to the EMC, you can also use the New-UMDialplan cmdlet in the
EMS, like in this example:
[PS]C:>New-UMDialplan -Name “Rochester NY” -NumberofDigits 5
If you do not choose a URI type or a VoIP security option,the default values will be used.
UM IP Gateway
The IP gateway must be identified in the UM IP gateway object configuration for the UM server to be able to communicate with it. It is possible to configure the UM IP gateway object in Active Directory to use an IP address or the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the physical IP gateway device. If you use the FQDN, there must be a corresponding DNS host (A) record so that the UM server can resolve the FQDN to an IP address. This address is used by the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) to establish each session between the IP gateway and the Unified Messaging server. Integrating voice with a data network does increase its exposure to data network vulnerabilities. After configuring the UM IP gateway object, you can associate it with the UM dial plan you created first. Be sure to verify that there is a UM server configured for the UM dial plan.
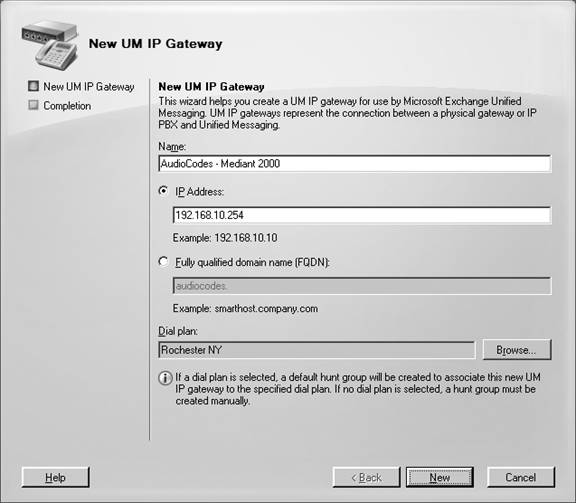
Creating a New UM IP Gateway
Use the following steps to create a new UM IP Gateway:
1.Open the EMC with an administrator account that has the Exchange or Administrator role.
2. Expand Organization Configuration and click Unified Messaging.
3. Click the UM IP Gateways tab.
4. Select New UM IP Gateway in the Actions pane.
5. Type the name of the UM IP gateway in the Name field, as shown next.
6. Type the IP address for the UM IP gateway in the IP Address field or in the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) field.
7. Click New.
8. Click Finish.
Using Powershell you can create IP Gateway plan
[PS]C:>New-UMHuntGroup -Name “ROC-HG” -PilotIdentifier 12700 -UMDialplan
“Rochester NY” -UMIPGateway “AudioCodes – Mediant 2000”
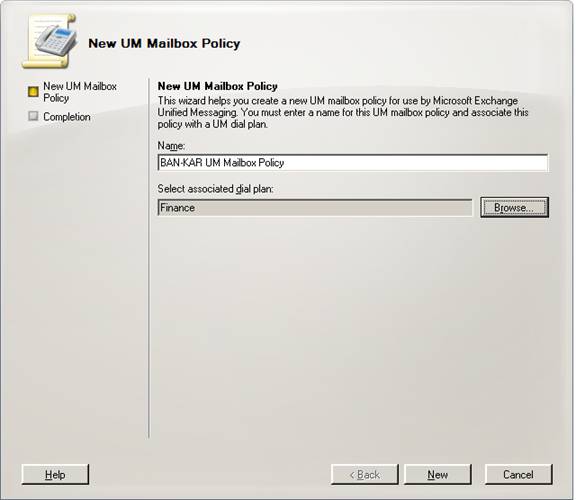
Creating a New UM Mailbox Policy
Use the following steps to create a new UM Mailbox Policy:
1. Open the EMC with an administrator account that has the Exchange Organization
Administrator role.
2. Expand Organization Configuration and click Unified Messaging.
3. Select the UM Mailbox Policies tab in the Work pane.
4. Select New UM Mailbox Policy in the Actions pane.
5. Type the name of the UM mailbox policy in the Name field, as shown next.
6. Click Browse, select a UM dial plan to associate with the mailbox policy click OK.
7. Click New
8. Click Finish.
As an alternative to the EMC, you can also use the New-UMMailboxPolicy cmdlet in the EMS, like in this example:
[PS]C:>New-UMMailboxPolicy -Name “BAN-KAR UM Mailbox Policy” -UMDialPlan “Finance”

The Screenshot above is creation of UM Auto Attendant Some Benefits of using UM
Ø You are traveling and your cell phone is the only way that you can connect to the network and you need to access your inbox to check for an important message—clearly, voicemail access can be a big Benefit in this situation. The benefit of being able to access your calendar via the phone is also obvious, especially as you can rearrange appointments via voice command!
Ø You are transiting between locations and need to check on your schedule for the rest of the day. You could look at your PDA, but this is hard to do (and illegal) if you’re driving, but you can use a hands free phone kit to call Exchange 2007 UM to check your calendar and find out where you are supposed to go. Along the same lines, if you discover that you are going to be late for your next meeting, you can ask Exchange to send a notice to meeting attendees to update them.
Ø You are on the road and do not want to spend time to listen to your voicemail messages on the phone before you leave the hotel. Because Outlook downloads your voicemail into the local cache along with your other email, you can listen to the messages through Outlook when you get a chance to later on, even if you do not have a network connection.
The full Value of UM can be fully realized only if it used in conjunction with Microsoft unified communication which includes otherassociated products such as (Office Communications Server 2007, Office Live Meeting, and the Office Communicator 2007 client.)