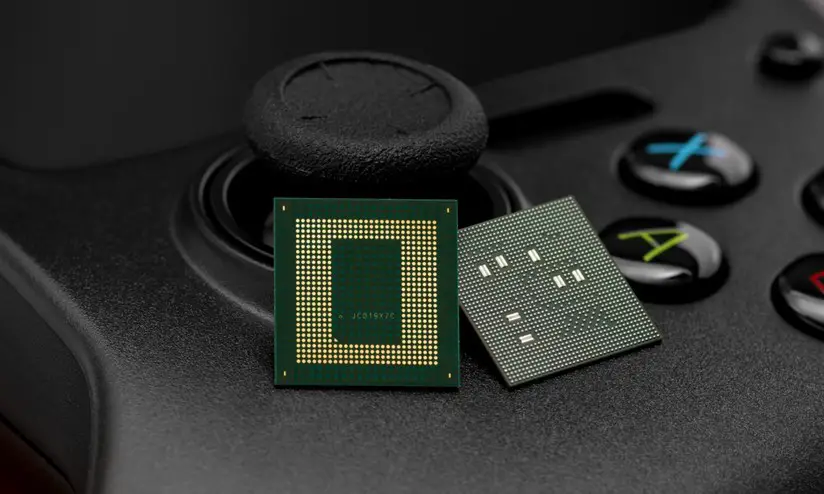
It is impossible to ignore Qualcomm’s new Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 chipset. The top-tier Android phones in the US, such as the upcoming Samsung Galaxy S22 and OnePlus 10, are certainly going to be powered by the mobile chip powerhouse in 2019. We first saw the Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 at Qualcomm’s Snapdragon Summit event. Since I have had time to reflect on yesterday’s announcements, Qualcomm’s presentation included several intriguing and peculiar features that I wanted to draw attention to. Some are fantastic, some could be frightening, and some are just strange. Not all of them might end up on your next phone. However, they are undoubtedly worth considering.
1. Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 Connectivity
Integrated FastConnect 6900 and Snapdragon X65 modem-RF system The Qualcomm Snapdragon X65 modem, unveiled earlier this year as the replacement for the X60, is integrated into the Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 processor. The X60 from last year had a top speed of 7.5Gbps, but this modem can reach 10 Gigabit speeds on both standalone and non-standalone 5G networks, making it the first modem-RF system to do so. Additionally, the Snapdragon X65 is the first modem to support 5G NR release 16 of the 3GPP, and the second set of requirements intended to accelerate the global rollout and adoption of 5G NR.

2. It Has An Always-On Camera. Qualcomm Insists It Is Safe
The chipset’s low-power sensing hub includes an always-on camera. The camera data remains on that portion of the chip and only provides metadata to the chip’s facial recognition system, according to Qualcomm. The design, according to the manufacturer, is safer than current smartphone cameras because data is kept on the sensing hub rather than being sent to the primary storage or CPU and because the central systems are essentially off when this camera is in use. The issue with this is that you not only need to believe Qualcomm on this, but you also need to believe phone manufacturers.

3. It Mints NFTs
The integrated security component of the Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 enables NFT minting apps to cryptographically ensure that tokens generated on the phone are unique, enabling proper delivery to NFT marketplaces. It is just horrifying buzzword pandering, in my opinion.

4. It Can Improve Call Quality. Call Quality Is Still A Thing
The noise cancellation technology from Qualcomm can cancel out all types of incoming noise during both regular phone calls and video calls.

5. Its Camera Will Consume Vast Quantities Of Data
If you are editing 8K videos to create 1080p video, the 8 Gen 1 camera can record 8K video in HDR, creating incredibly lifelike videos that you can pan or zoom around in. However, data from an actual video shot at the event indicates that this will use 790MB per minute. Ten minutes of video? Please, only 8GB. Naturally, Qualcomm does not mind too much because the company also wants to promote 5G, the only network system capable of handling that much data, thanks to its high-speed millimeter-wave technology.

6. It May Power The First Android Phones To Hold Your Driver’s License
The first Snapdragon to support Google’s Android Ready SE platform, which aims to make data secure enough so that you can store your driver’s license, passport, or car key on your phone, is the Snapdragon 8 Gen 1. In this regard, Apple is far ahead of Google, having already agreed to support digital driver’s licenses with eight states (Opens in a new window). The Samsung Galaxy S22 could overtake.
7. It May Finally Kill The SIM Card. That Is Good And Bad
The subscriber identification module, typically a tiny chip, is reduced to pure code thanks to the Snapdragon 8’s iSIM, or integrated SIM, feature. Most current phones have detachable SIM cards, though some have electronic SIM cards (eSIMs), which are chips soldered directly to the circuit board of the phone. The item allows for the removal of a component by manufacturers, resulting in smaller devices. It is also wholly reprogrammable, so your carrier will never advise you to get a new SIM for updated network features.

8. You Cannot Hold It Wrong
Based on where your hand is placed, the system’s AI-powered antenna tuner will be more adept at determining which antenna elements to turn on and off. On smartphones, hands-blocking antennas can be a severe issue, especially with 5G millimeter-wave because millimeter-wave is so brittle. However, due to excessive power consumption, phones cannot turn on all their antenna modules at once. Only the antennas not blocked are turned on by the 8 Gen 1’s tuner.

9. Spectra 680 And Snapdragon
Sight is the Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 ISPs Arguably, Qualcomm’s Spectra ISP has seen some of its most significant recent advancements. The Spectra 280 ISP introduced support for 10-bit color depth HDR video capture in the past, and the Spectra 380 ISP in the Snapdragon 855 was the first CV-ISP in the world. Then, the Spectra 480 ISP, with its impressive two gigapixels/second processing speed, and the Spectra 580 ISP, with its increased performance by 35%, support for staggered HDR sensors, new triple-ISP architecture, and other significant advancements came into view. As the Spectra 680 puts all those new additions into overdrive, things get even better.

10. It Is Going To Be This One Vs. Apple Next Year In The US
The US smartphone market’s premium segment is primarily a Samsung vs. Apple competition. Google receives more press than it sells, while Motorola and OnePlus wait in the wings. The premium smartphones from Samsung, Motorola, and OnePlus sold in the US will all be Snapdragon-powered. At a gathering last month, Qualcomm CEO Cristiano Amon discussed the company’s partnership with Samsung. Motorola committed to it yesterday, and I know OnePlus personally.



















