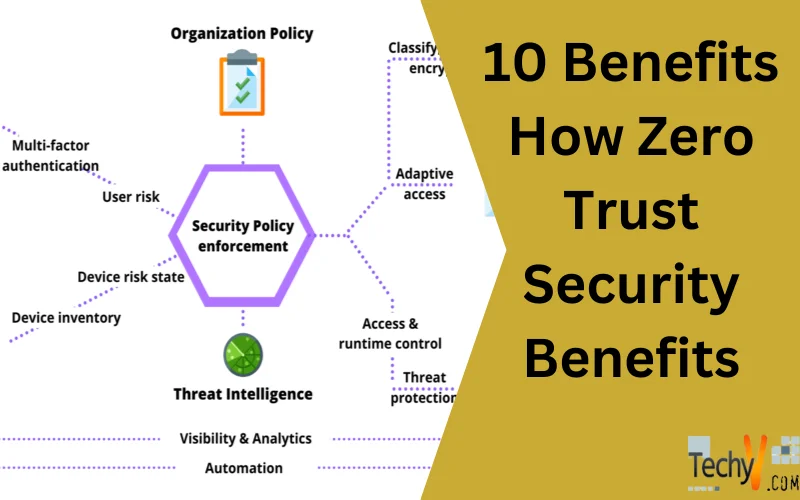
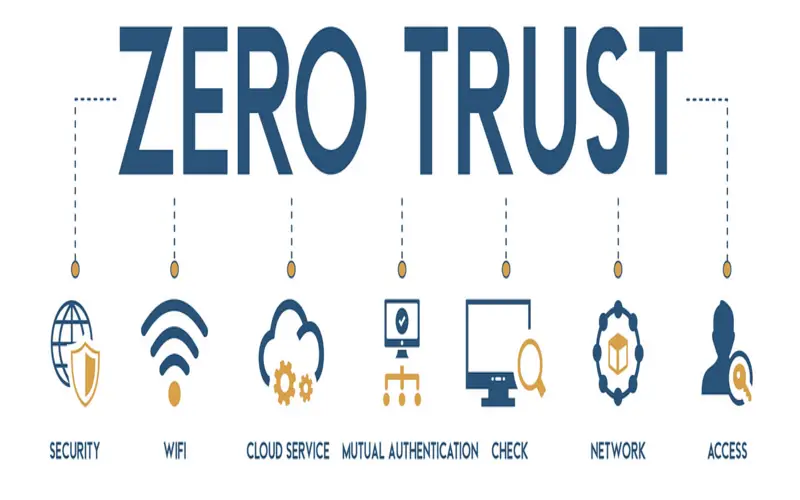
What Is Zero Trust Security?
All users, whether inside or outside the company’s network, must be vetted, approved, and continuously supported for security arrangement and posture before gaining or maintaining access to apps and data. Zero Trust supposes that there is no traditional edge; the network can be local, in the cloud, or gathering with sources anywhere as well as workers in any place.
1. More Extensive Visibility Across The Enterprise
The central concept of Zero Trust security is that organizations are required to be able to observe every action inside the network continuously. The Zero Trust Security reach and never expects anything to be reliable, enabling companies to across the whole surroundings. Most Zero Trust Security allows tools to help companies observe all things, people, and actions. It means management can see who or what accesses a network at any time. There are also real-time notifications available to highlight unusual conduct.
2. Easier It Management
Zero Trust solutions can decrease some of the work organized by IT leaders. The technique obtainable from Zero Trust vendors relies on a fundamental of continuous observing, which offers companies admin to salable data for automation. With automation workflows, organizations can set plans for which relations and actions are accepted according to particular needs. The capability to reduce the number of security professionals who need to observe an environment could be specifically beneficial to businesses trading with a growing cybersecurity knowledge deficiency. Zero Trust also offers a correct structures inventory for access to keep and manage.
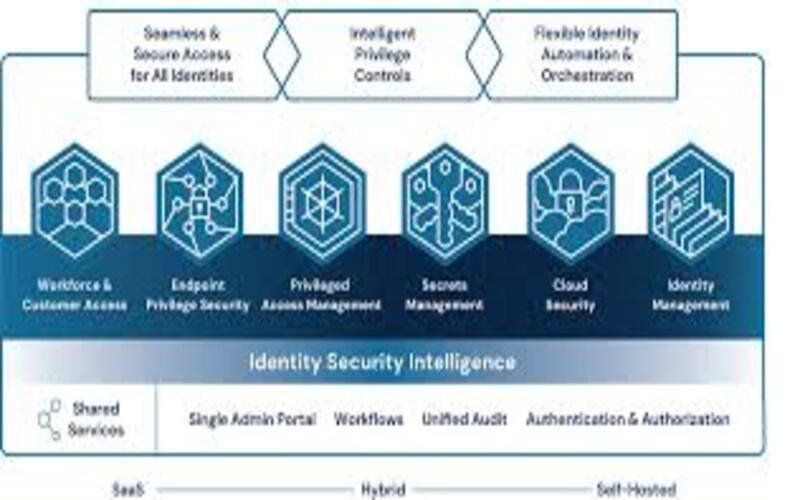
3. Enhanced End-user Experiences
Zero Trust Security may make connecting to sources more composite for end-users, but it can improve the user experience. Many customers try to remember the various passwords they need to administer projects and sources. Zero Trust Tools again came up with the answer to deploy certain sign-on (SSO) tools, which decreases this error. An SSO structure for access helps companies detect which consumers should have authentication plans that can manage to ensure the continuous safe of each source. Locating services for zero trust security near remote and local workers can improve all-over performance.
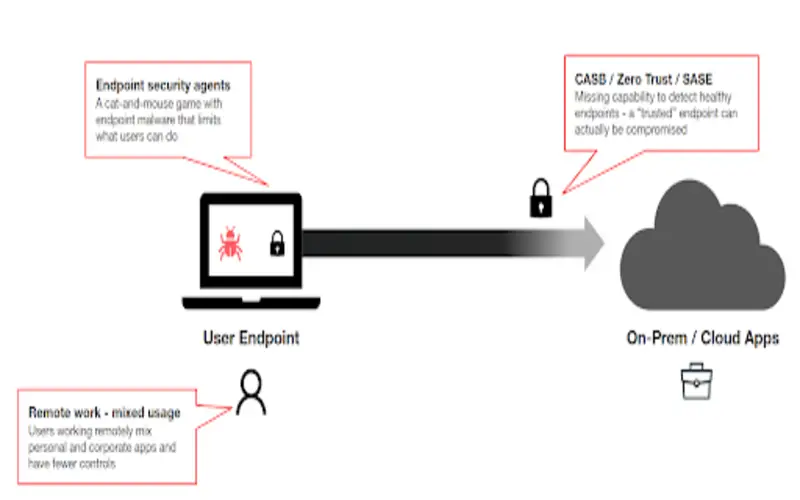
4. Streamlined Making Of Security Plans
Security plans are the primary terminology in any decision. Traditional security designs frequently depend on a siloed threat avoidance decision. It means multiple security tools are required to be arranged and operated individually, with their rare plans. It often led to components of the business that were more accessible than others. Companies can use Zero Trust to create a one-of-a-kind strategy and execute it from beginning to end of the management process. SSO can assist in organizing verification for all sources across the network. With Zero Trust, the arrangement and organization of security plans become more streamlined for executives and general gaps in the surroundings used.
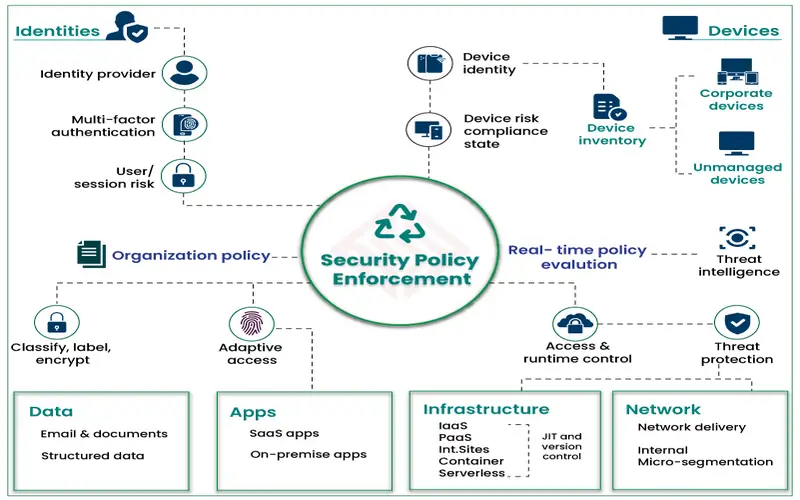
5. More Immense Flexibility With Services And Data
As Companies keep on innovating and developing with the latest technologies and answers, the technology needed to keep the companies managing efficiently also transfers. Applications, IT services, and data solutions are frequently transferred inside the company structure. With traditional security systems, moving data and apps need security operations to recreate the latest security plans generally. Zero Trust can assist in mitigating this time-compelling process while decreasing the risk of error and fault, which leads to more incredible security loopholes. App and data security plans can be properly handled within the cloud. Automation tools are available to help with transfer plans when needed.
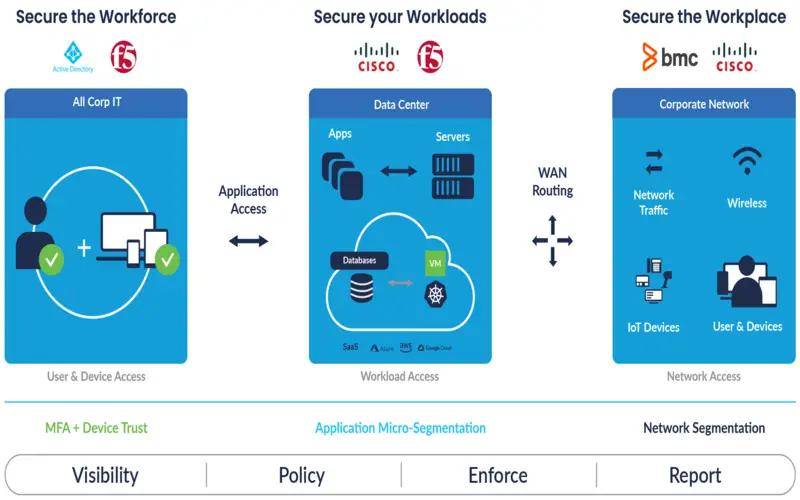
6. Extraordinary Assent And Protection
Zero Trust’s design quickly merges as an expensive insurance plan against stolen and lost data. It is critical when a particular data rupture can cost a company more than four million. Businesses can greatly repair and maintain their data using Zero Trust solutions. These tools can be modified to address distinct compliance, private, and security plans as they merge. In a Zero-trust design, whenever a movement occurs involving critical data, the payload and identity are both certified. It assists in preventing harm from proceeding early, and attackers gain access to necessary information.
7. Safe Cloud Adoption
The main reason Zero Trust security solutions have become so famous in recent years is that they are fabulous for organizing the evolving cloud landscape. Management is worried about the rise of cross and remote work and all the users own their single devices for work. Zero Trust solutions allow the quick classifying of all benefits in the cloud, so the correct protection and admin controls come at all stages. The solutions decrease the dependency on end-device security tools and enable companies to organize extensive visibility over the cloud surroundings as it expands, even in scattered landscapes.
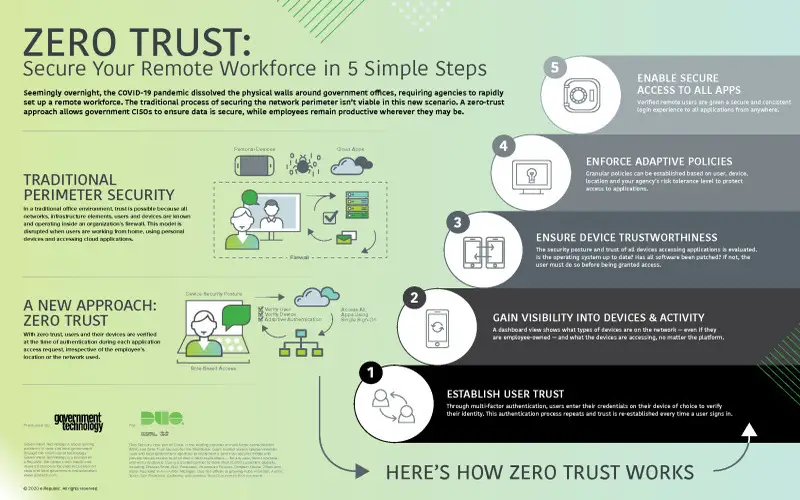
8. Permit And Secure A Remote Workforce
Traditional security improved around users relating to a secure business network, and any passage outside that outline was automatically treated as faithless. This reach is inconsistent with a workforce that is increasingly more remote and flexible.
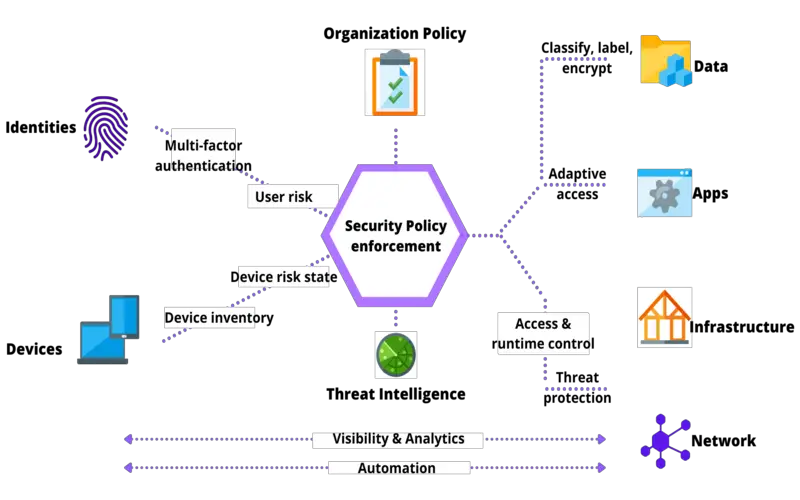
9. Reduce Your Attack Surface
When the more significant businesses or those with an essential online presence are at the most significant harm of a cyberattack, any organization can be interested in cyber criminals, so quickly decreasing their organization’s harm surfaces has become critical for IT managers. The Zero Trust frame has essential capabilities to decrease your organization’s harm surfaces due to how it sections users and applications aside from the internet. This partition decreases the offers attackers have to take unauthorized access to your structure.
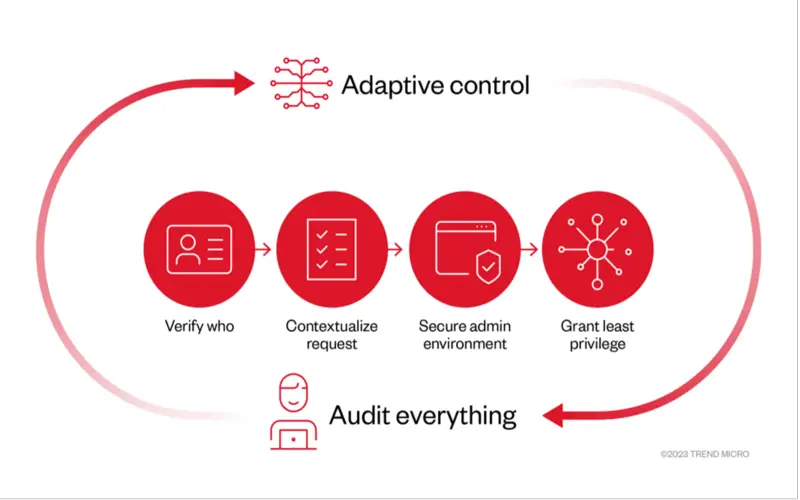
10. Continuous Validation
Maintaining an efficient security posture is a critical component of the Zero Trust Security model, which constantly verifies people and devices. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is one successful method for achieving this goal. It dramatically decreases the chances of unauthorized entry by requesting several parts of evidence during authorization. This trust model focuses on confirming identity and rights to protect sensitive data while allowing only authenticated users or devices access to systems – its crucial component.