What Is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication refers to strategies of using biology like fingerprints, eyes, voice, and even interior features to confirm the recognition of individuals. Biometrics are better than standard passwords used for authentication because they verify exactly what you recognize through inherent biological features. Password theft methods such as keylogging can easily compromise passwords.
The most general biometrics used for authentication involve fingerprints, facial recognition, or retina scans. Many distinct biological phenomena can be used to assist in authenticating access to systems, services, and networks.
They remember an account number, password, or PIN or answer a secure question. By utilising two-factor authentication, biometric authentication aims to make these operations faster, smoother, and more secure.
Why Is Biometrics Used?
Using biometrics is longer science fiction. The period of Minority Report is here. We probably use biometric recognition every day on our smartphones, for example—the first mobile phone featuring fingerprint-identical dates. High-end smartphones can be unclosed by reading your face. Observing access to critical areas, tracking employee bearing, combating fraud in central banking enterprises, fingerprints as a payment strategy replaying typical PoS, or even authentication in call centers.
How Biometrics Work In Tech
- Biometric software like face identification grabs the biological input that a consumer offers.
- The software quantity that grabs to generate a baseline data point template or the “Lock” that will regulate data point for future uses.
- The biometrics that are quantity and captured are changed and stored as data in internal hardware on the tool used or on the cloud platform during the enrolment stage.
1. High Security And Assurance
Biometrics offers maximized stages of assurance to offer that a person is exact by confirming tangible, actual world attributes as both something the consumer has and something the consumer is. Most consumers’ passwords PINs and personal identifying information have likely been endangered by a data breach, meaning, billions of accounts can be acquired by fraudsters that only an actual. They can’t use their fingerprint to unlock an account if they can’t offer it on the spot.

2. The Consumer Is Convenient And Fast
The internal process for biometric authentication is strategies, from a consumer point of view its credibility is simple and quick. Situating a finger on a scanner and unclosing an account in seconds is faster than typing out a long password with various special characters. Forgetting a password is a general mistake of most consumers.

3. Non-Transferable
Biometric authentication needs its input to be current upon authorization. You can’t transform or share a physical biometric virtually. The only way to employ most biometric authentication systems is with a physical application.
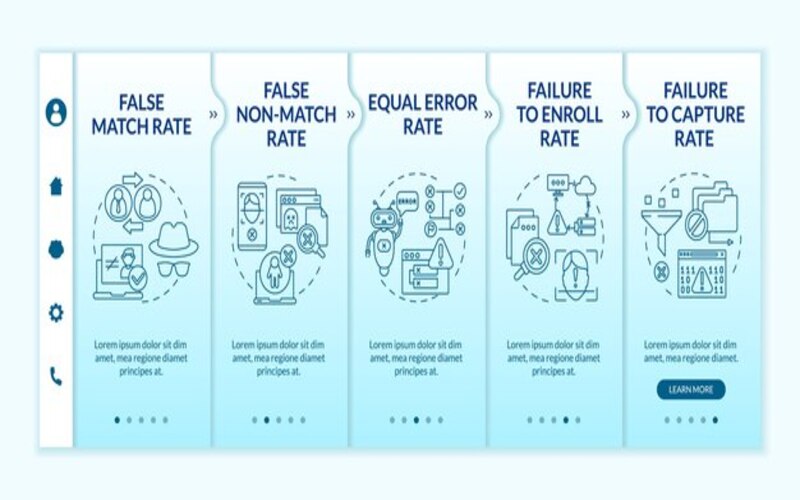
4. Near Spoof-Proof
Biometrics like designs, fingerprints, iris scanning, and others are unlikely to duplicate with present technology. There is one in 64 billion. You have a better probability of winning the lottery than having the same fingerprint as a hacker trying to get into your account that’s protected by biometrics.
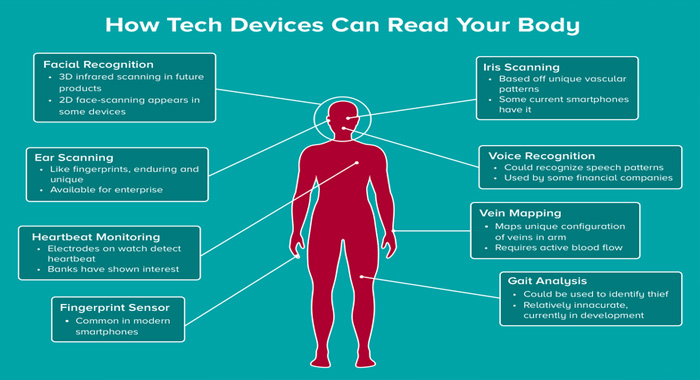
5. Minimizes Exposure
Fingerprinting individuals is the most general means of authentication at the moment. Many companies depend on this innovation. Requiring a fingerprint scan on a public surface could discourage users from using your services. Using contactless innovation lessens the probability of people spreading the virus to one another in your office by touching a general interface.

6. Speed And Efficiency
If you have employees, clients, and visitors using a touchscreen surface, you will most likely need to have someone wipe and disinfect that surface after each usage. It shows a lack of productivity for the person allocated to clean the screen and line buildup if various people sing in at once. It’s just an ineffective system. Contactless innovation needs no touching, therefore reducing cleaning. The system individuals the user faces, and then they are done. It’s rapid, simple, and highly effective.

7. Cost Reduction
Implementing a technology but mature innovation, such as biometric multi-factor consumer recognition, in the distinct stages of the relationship with the company creates vast savings in the company’s running costs. These savings can significantly impact the profitability and effectiveness of the company’s model.

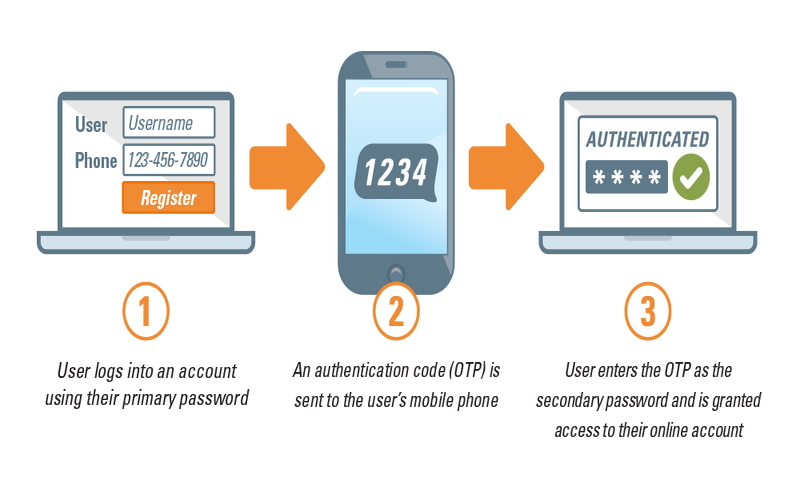
8. Reduced OTP Message Costs
Standard authentication frequently includes using text messages, also known as OTP or One Time Password, to confirm consumers’ identity. These messages, while efficient, have a cost. Biometric authentication removes the need for these codes, as consumers are verified by their rare biometric facilities. Another benefit of biometric authentication is the verification process simplification.
9. Productivity In Internal Processes And Access Control
Adopting biometric authentication can maximize the productivity of an organization’s internal procedures. Biometric systems can combine into various applications and systems, from manufacturing access to time record organization. Waiting times and delays are decreased by simplifying authentication, increasing staff productivity, and lowering access control operating expenses.
10. Decreases Security Costs
The first installation of biometrics may necessitate significant conjecture due to integration expenses; however, with actual long-term support, this innovation can help minimise security-related expenditures. Biometrics is hugely effective in preventing undefined access, which reduces the likelihood of costly security events such as data loss or sensitive information theft.