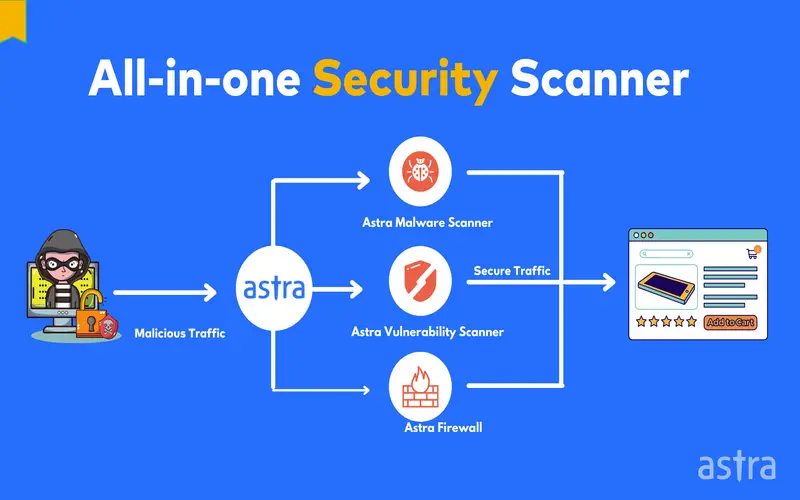
What Is Cyber Resilience?
Cyber Resilience encloses a set of enterprising cybersecurity strategies, practices, and innovations aimed at diminishing the impact of adverse cyber events and ensuring business continuity in the face of disruptions.
Security events are a major worry for firms of all sizes and across all organisations in an interconnected and innovation-driven world. These threats come in several forms, such as data breaches, ransomware attacks, network outages, or even natural disasters that impact digital structures. The consequences of these events can be severe, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, legal liabilities, and comprises of user data.
What Is A Cyber Resilience Strategy, And Why Do You Need One?
A Cyber resilience strategy is an extensive plan enclosing the essential measures to recognize, respond to, and recover from cyber threats. It examines the broader context of cybersecurity, aligning with your managing objectives, risk patience, and regulatory needs. It goes beyond a cyber resilience framework by offering a strategic reach to build resilience against cyberattacks.
Why do your enterprises require a cyber resilience strategy? The answer lies in the ever-evolving nature of the threat landscape. Cybercriminals are always discovering new methods to breach barriers, exploit weaknesses, and disrupt operations. A cyber resilience strategy allows you to confront these threats with caution, ensuring the seamless continuity of your companies and mitigating potential harm.
The Essential Components Of Cyber Resilience Are
Risk assessment and organization – it helps to recognize loopholes and threats and their potential effect on the organization and its companies’ processes.
Robust Cybersecurity measures – Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, safe network setups, encoding, and frequent security upgrades are examples of cyber resilience-enhancing technologies.
Events response planning—Including specific instructions on how to respond, who to notify, and what procedures to take during and after an occurrence to safeguard the company’s operations.
Business Continuity And Disaster Recovery Plans
It involves organizing backups of data, constructing redundant systems, and uniform testing of the recovery processes that maximize cyber resilience.
Employee education and awareness – it helps to reduce the likelihood of human issues leading to a prosperous cyber-attack.
Collaboration and Information sharing- It will enable the conversion of best practices and sessions taught for threat intelligence, resulting in the finest cyber resilience.
Continuous Evaluation And Assessment
Enabling management to detect and respond to potential threats in actual time and recognize loopholes to ensure the cyber resilience strategy and security solutions remain efficient.
Regular updates and patch management
It is vital to mitigate loopholes that may be exploited by cybercriminals.
Third-party risk management
It enables to administation and organize cybersecurity risks connected with third-party vendors or partners.
Governance and leadership – The senior management should vigorously support and forward a culture of cybersecurity and cyber resilience throughout the management.
The Goals Of A Cyber Resilience Strategy
An efficient cyber resilience strategy should be able to achieve most of these five goals.
Prevent Threats
Provident recognize and mitigate cyber threats before the loopholes in your system become compromised.
Develop An Events Response Plan
Initiate a clear plan to detect, accommodate, and organize cyber events swiftly and efficiently.
Maintain Companies Continently
Ensure daily operations continue constantly, even in the face of a cyberattack, by executing fast and efficient makeup and recovery measures.
Secure Stakeholder Confidence
Still trust and confidence in your users, partners, and stakeholders by justifying your commitment to cybersecurity and resilience.
Comply With Industry Regulations
The strategy should help you organize compliance with industry regulations and traditional to protect your stakeholder’s informative data and against lawful and financial consequences.
1. Reduced Financial Loses Linked To Attacks
Cyber attacks may be costly due to the costs of events response, recovery, and remediation. Being cyber flexible means managing can reduce the financial effect of attacks by executing preventive measures, having efficient response plans, and minimising any time.

2. Improved Business Continuity
Cyber flexibility ensures that enterprises can organize essential operations and services. By executing robust cybersecurity measures and having calamity recovery plans, organizations can reduce downtime, maximize users’ trust, and avoid main business interruptions.
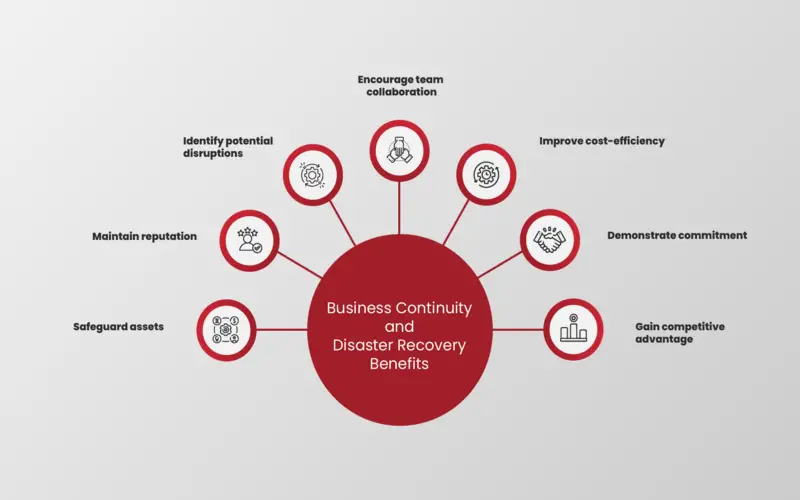
3. Protection Of Reputation And Trust
A cyber-attack can significantly damage an enterprise’s reputation and ruin user’s trust. By investing in cyber flexibility, organizations demonstrate their commitment to safeguarding information and maintaining the confidentially and availability of vital data.

4. Complained With Regulations
The industries become subject to strict data protection and privacy regulations, such as the Cyber above, Flexibility Act. Executing a cyber flexibility strategy helps businesses meet these regulatory needs, ensuring the protection of user data, avoiding lawful fines, and organizing compliance with ever-increasing cybersecurity while fulfilling its mission or company objectives.
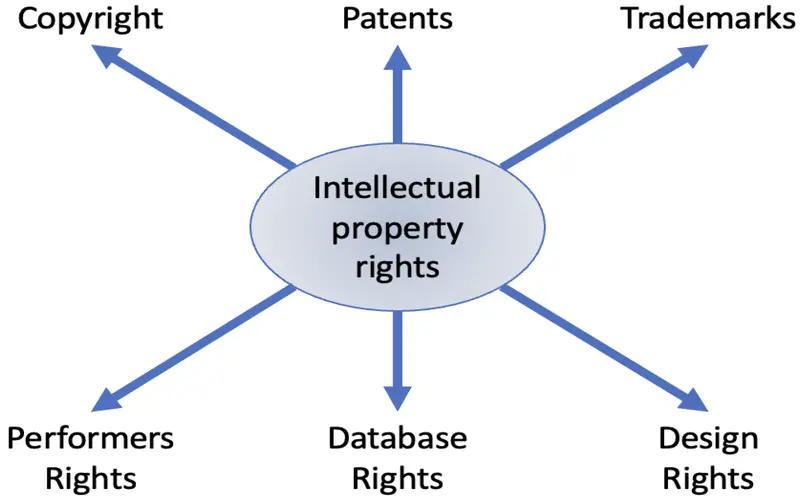
5. Securing Intellectual Property
Cyber attacks aimed at compromising intellectual property can have various consequences. Cyber flexibility quantity protects against denied access, theft, or manipulation of intellectual property, ensuring that managing can continue to initiate and maintain their competitive edge.
6. Enhanced Events Response And Recovery
By having well-defined processes, distinct roles and responsibilities, and efficient event response plans in place, managing can respond promptly to cyber events, mitigate their effects, and respond and recover vital systems and data more effectively.
7. Proactive Risk Organization System
By identifying and assessing potential loopholes, organizations can mitigate risks before bad can exploit them. Such a dynamic reach helps reduce the likelihood the effect of successful attacks or security breaches.
8. Stronger Suppliers And Users Relationship
Management that categorizes cybersecurity demonstrates their commitment to protecting divided data and information which can improve trust and foster stronger partnerships.
9. Competitive Benefits
Management that demonstrates a more robust cyber-flexibility posture is often viewed as more trustworthy by users, partners, and investors, giving them a competitive benefit.

10. Long-term Savings
While investing in cyber flexibility may mean some extra value, it will lead to long-term cost savings by reducing the likelihood and disruptive effect of future events.