Cloud storage and cloud security are two of the newest innovations in the world of new0 generations. Cloud services could prevent the potential benefits if there is insufficient and suitable security protection, which leads to higher costs and a possible loss of the firm. The controls, rules, technologies, processes, and services that supply hosted services over the Internet and safeguard cloud data and infrastructure collectively makeup cloud security, sometimes referred to as cloud computing. Many corporations have benefited from cloud computing due to its quick operations, adaptability, and scalability.
10. Internal Fraud
A security concern for organizations is malicious insider threats. These hostile internal users are more difficult to identify, especially with traditional cloud solutions, because they already have unauthorized access to the network and its sensitive resources.

9. Migration To Vendors
The threat of connections with a single provider is one of the biggest obstacles to cloud security. It can be very restrictive to use only one compatible security solution. That is due to the possibility of reworking security solutions to meet new business requirements. It is crucial to consider the ease of switching from one service to another when choosing cloud-based services.
8. Lack Of Cloud Security Architecture And Strategy
Many businesses adopt cloud computing without establishing the necessary architecture or plan. Customers must comprehend the risks they face, how to migrate securely to the cloud (remember that this is not a lift-and-shift procedure), and the details of the shared responsibility model before making the switch to the cloud. The customer is responsible for this danger, which is new to the list. Customers will be susceptible to cyberattacks without adequate preparedness, reputational harm, and legal and compliance problems.
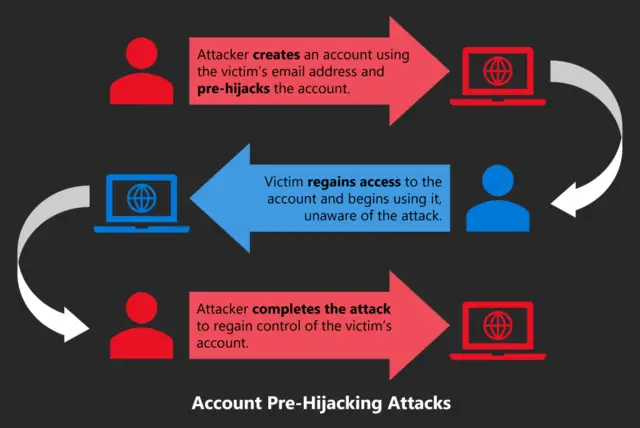
7. Account Hijacks
Other frequent problems with cloud security include employee passwords that are simple to guess and extremely lax password protection. Weak employee credentials—which allow one password to be used for several accounts—lead to data breaches and phishing attacks.
6. Non-compliance With The Regulatory Requirement
A company must follow and comply with several regulations. More specifically, these rules are sector-specific and differ from industry to industry. Any violation may result in additional fees, fines, condemnations, and other penalties, as well as the triggering of criminal provisions. The reputation of the firm suffers as a result of the market.
5. Misconfiguration And Inadequate Change Control
An improperly configured asset is vulnerable to attack. For instance, the Capital One hack was linked to a web application firewall error that made Amazon S3 buckets vulnerable. Other significant causes of vulnerabilities include using default credentials and having too many permissions, in addition to insecure storage.

4. Unauthorized Access
Any organization’s cloud-based operations and deployments are accessible over the open web and exist outside the network boundary. While this makes remote workers’ access easier, it also makes it simple for attackers to get unauthorized access to cloud resources. Ensure that cloud data access is secure by configuring security configurations and using reliable credentials.

3. Less Visibility And Lack Of Control
With cloud-based solutions, the user can run the necessary servers without having to take direct control of them. One benefit of utilizing cloud-based technologies is this. However, daily maintenance of the server, software, or platform with little to no interaction may result in a loss of visibility and control over the specific resource.
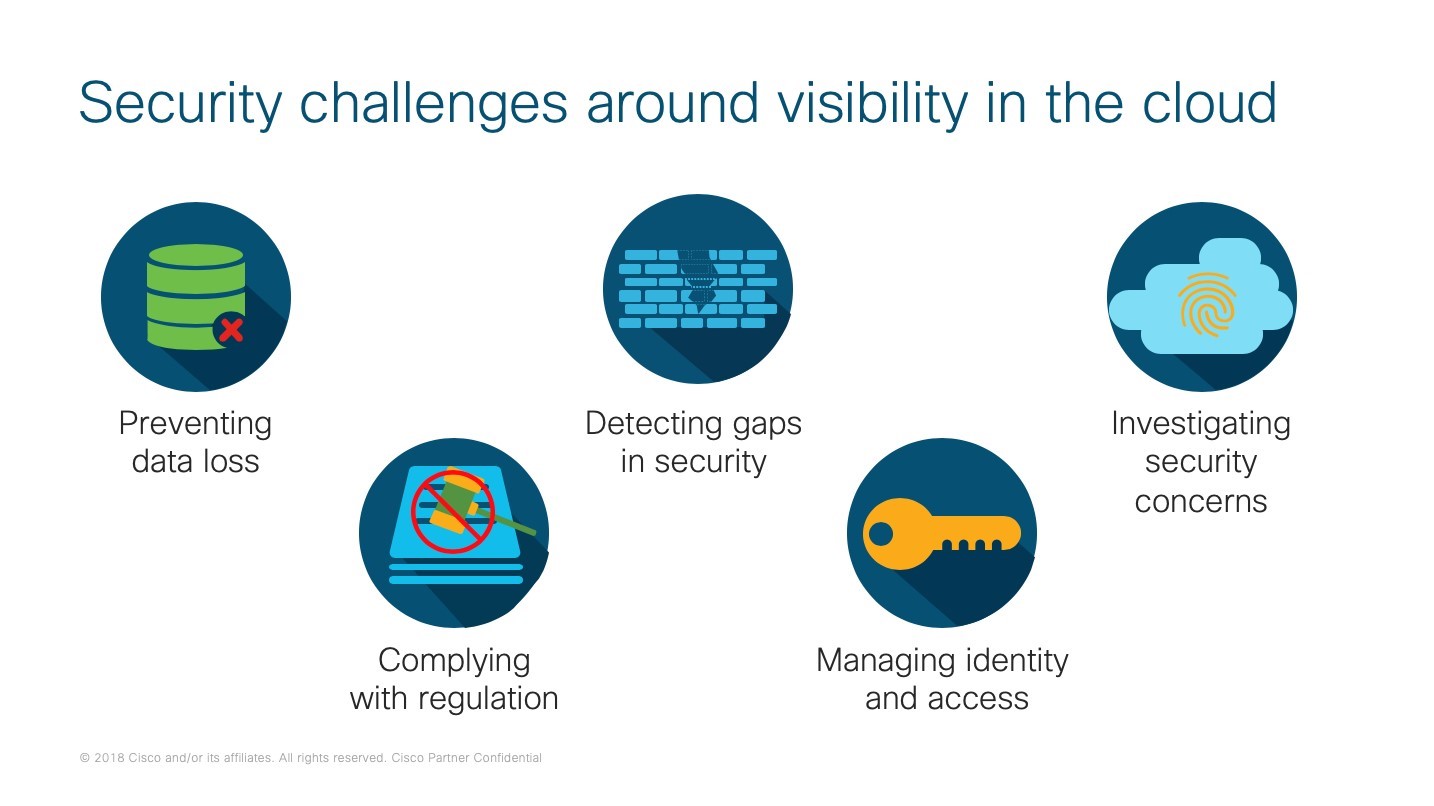
2. Data Breaches
Data breaches, which are the responsibility of CSPs and their customers, were again the danger to cloud security in CSA’s study this year. Over the past few years, the cloud has been blamed for several data breaches, Capital One’s cloud misconfigurations being one of the most notorious. A data breach can bankrupt a business, ruin its reputation permanently, and put it in financial trouble due to legal liabilities, regulatory repercussions, incident response expenses, and diminished market value.

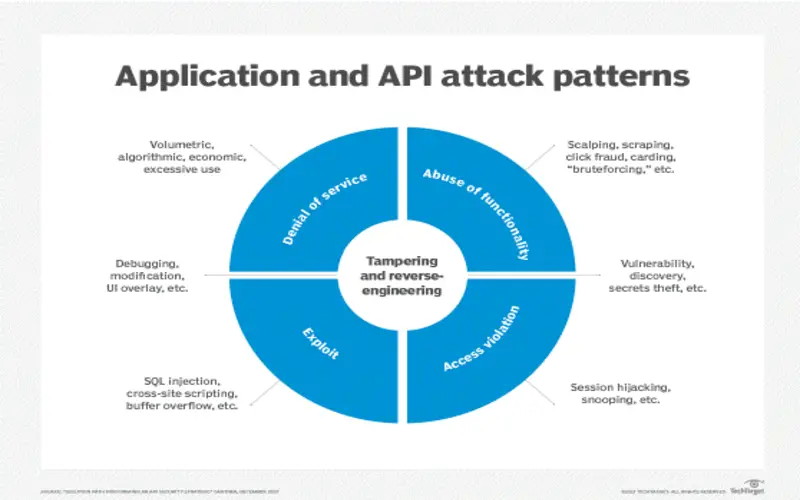
1. Insecure APIs/Interfaces
The multiple interfaces and APIs that cloud service providers offer to their clients’ organizations are well-documented, allowing for easy access and use by clients. As a result, if these interfaces aren’t appropriately protected, thieves might access and misuse critical data and information in the cloud environment by using the documentation the organizations have created.