What Is Applied Observability?
Applied observability is a globally popular business practice where you use several tools and methods to draw insights from the actions and performance of a given system. The subject of observation is frequently a complex operational system like business apps, IT networks, cloud infrastructure, or any other system that depends on correct data analytics. Applied Observability serves one precise aim: Collecting all the related data and metrics, classifying them, and processing them into actionable insights. The prepared information can be used for a broad collection of business objectives, and it helps engineers and developers recognize systemic dysfunctionalities and resolve errors rapidly.
Why Is Applied Observability Essential?
The most advantageous benefits you can expect from applied observability. This technique has become an essential part of organizational operations. Applied Observability also allows enterprises to uncover hidden designs in their data that can help them operational errors, identify trends, enhance process optimization, increase user satisfaction, make informed decisions regarding product launches, and realize cost savings.
What Are The Vital Elements Of Applied Observability?
It includes various key elements involving:
- Data Collection: Collecting data from several sources, such as logs, metrics, and tracks, to gain insights into system actions.
- Data evaluates: Using tools and methods to analyze data and understand what’s happening in the system.
- Instrumentation: Instrumenting the system to gather related data and offer visibility into system practices.
- Representation: Data representations, such as dashboards, alerts, and traces, to understand the system practiced.
- Hypothesis-driven Reach: Using a data-driven, hypothesis-driven reach to issues rather than depending on preconceived notions of how a system should be practised.
- Actual Time Visibility: Gaining actual-time visibility into system actions in the production to rapidly recognize and diagnose errors.
- Cooperation: Encourage teamwork and collaboration across management to ensure that everyone is working with the details and understands the system.
- Continually Enhancement: Continually enhancing system performance and reliability by applying data-driven insights.
Some Features Of Applied Observability:
- Serverless Observability: Developers can rapidly recognize and fix errors in applications.
- Cloud Observability: Management can get an actual-time view of how their systems are operating.
- Integrated Reach to cloud-native observability: Organizations’ observability solutions can combine into cloud-native application environments.
- Logging: A constant record of application events is generated.
- Observing: details from data, logs, metrics, events, and incidents are collected, transferred, and analyzed.
- Metrics – Numerical numbers that describe the conduct of a service or part over time.
1. Dark Mode
When you solve incidents in the middle of the night or want to keep away from straining your eyes, you can view New Relic dark mode. Dark mode is way more than just a fantastic, facility (though it still is that). It is essential for many industries.
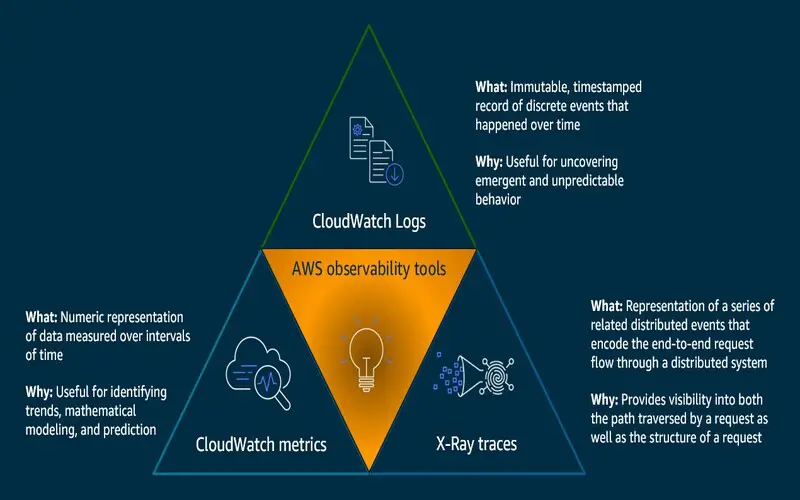
2. New AWS Integrations
- With costly new Integrations, you can have end-to-end access to your AWS cloud services and the rest of your stack:
- AWS Lambda Extensions – extensively ease your ability to send measure data from AWS Lambda to New Relic One.
- AWS Control Tower-Impulsively merges with New Relic One for single or multi-account environments registered in AWS Control Tower.
- AWS Distro for Open Measure – Uses the Open Measures collector and New Relic One.
- AWS X-Ray Integrations – Impulsively merge traces from AWS organized services with traces from New Relic for end-to-end observability imagined entirely within New Relic One. You can capture, filter, and query it all. No manual device is required.
3. Open Measures UI
New Relic One now has a UI that offers full APM functionality for your Open telemetry data. Send your Open telemetry data to New Relic using one of the Open telemetry exporters and rapidly discover and using one of seven main pages, examine your data to optimise the performance of your applications and services.
4. New Relic Edge With Infinite Tracing
New Relic consumers with Pro or organization Full-Stack Observability can now permit and benefit from New Relic Edge with a fully organized, cloud-native, tail-based distributed tracing service. This new service monitors 100% of all application traces across your distributed systems and provides imagination and storage for the most useful data, allowing you to explore and solve faults more quickly.
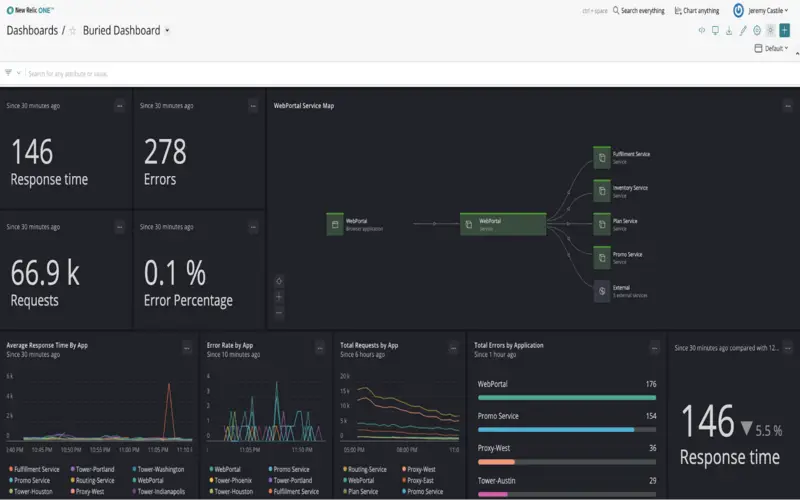
5. What’s New
When there are product updates, New Relic One notifies you and links you to the product end’s “what’s new” section to learn more about what we’ve released. There, you’ll discover blogs for each new feature, each with a summary description, resources, tips and tricks, and best practices to ensure you’re benefiting from the latest technology and making the most of New Relic One.

6. Anomalies Visible In The Activity Stream
Viewing abnormalities in the activity stream from the New Relic One homepage, APM summary page, and APM list page. The occupation stream displays recent incidents from alerts and deployments and offers a direct view of what is in your system so that you can fix disruption rapidly.
7. Kafka Connect
With Relic Connector for Kafka Connect, By consuming data from Apache Kafka topics into New Relic One without writing a single line of code, you can unlock open source and alternate device sources.
8. Windows Support For Logs
You can send all your logs to New Relic employing the structured agent in Windows. It uses the most recent filters to narrow down which log categories (application, security, or system) and messages to focus on, all the way down to the incident ID.
9. Share With Permalink
By clicking the permalink idol, you can quickly copy a short, permanent URL to the clipboard and share intuition, dashboards, and curated views from anywhere in New Relic One.
10. Scheduled Alert Muting
It schedules when you want to mute notifications to avoid messages during conservation or deployments.