10 MS Exchange 2003 Errors
Microsoft Exchange 2003 is an email storage client that runs on Windows Server. It is useful for businesses, as business email can make companies more productive in communications and worked. Below are 10 Microsoft Exchange 2003 errors that users may face, and their fix:
Error ID – c1030a8c
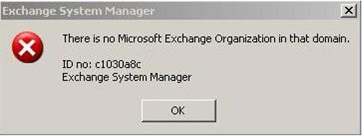
There is no Microsoft Exchange Organization in that domain.
ID no: c1030a8c
Exchange System Manager
A common error message that frustrates many MS Exchange Server administrators. As the administrator of Exchange, you’ll notice that despite the server functioning properly, you cannot access the Exchange System Manager.
This issue, however, can be simply solved by using the system as Local System instead of an administrator. This will give you the ability to open the Exchange System Manager via the command line or Start menu shortcut. You must now go to the Security tab in the ms exchange Properties, and adding the current user to the ACL and Enterprise and Schema Administrator groups. Following this, you will have logged out and log back on properly with the new user. Finally, give full rights to the proper administrator account (check all permission boxes).
The above fix may cause issues with the Exchange System Attendant. This, however, can be simply fixed by running setup.exe /forestprep and setup.exe /domainprep from the Exchange Server 2003 installation CD. Once complete, reboot the system and everything should be working correctly.
Error ID – 8063
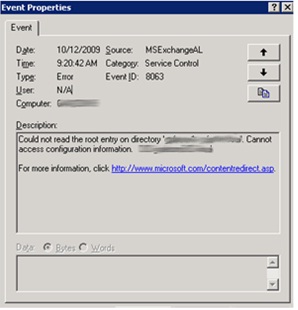
Could not read the root directory.
Sometimes, as an administrator, you may need to manually configure domain controllers for proper and fully functionality of your server or network. In turn, the manual configuration may also cause this error in MS Exchange. It is usually caused by the Recipient Update Service being unable to find the domain controller that may have been replaced.
The simple solution to this problem is to manually update the controller name for the Recipient Update Service. First, open your Exchange System Manager -> Recipients -> Recipient Update Services and right-click each RUS and select Properties. Choose Browse while under the Windows Domain Controller and select the new domain controller.
*This fix may take a few minutes to fully take effect.
Error ID – c1041739
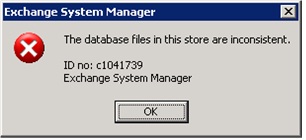
The database files in this store are inconsistent.
ID no: c1041739
Exchange System Manager
When receiving a Blue Screen of Death on the computer server you’re running Exchange on, the Exchange store may not mount, followed by giving the user the above pictured error. Given the error message, it is best to perform a clean backup to prevent potential data loss. This usually fixes the problem.
If, however, a clean backup is not possible or does not work, then you will want to run Eseutil.exe /p, the repair utility. Once this has finished, you’ll want to do an offline defragmentation, run Eseutil.exe /d and isinteg.exe -s servernsmr-fix -test alltests, tests that will give you information such as integrity weakness.
*It is to be noted that a repair may cause loss of data and should only be done under circumstances in which data loss is acceptable or a last resort.
Error ID – 2102
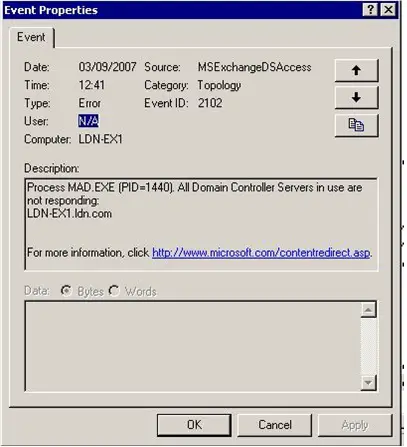
Process MAD.EXE (PPID=1440). All Domain Controllers Servers in use are not responding.
LDN-EX1.ldn.com
When rebooting a Domain Controller, a user may receive this error upon startup. This is caused from the Exchange Services starting before the Active Directory Services (process name: LSASS.exe) starts. Because Exchange has a total dependency on the Active Directory Services, the execution of Exchange before LSASS.exe creates a program malfunction, and therefore the error message.
Microsoft released a “fix” for this problem in either Service Pack 1 or 2 of Exchange 2003 that simply instructed the Exchange service to wait longer for the Active Directory Service to start. While it results in online functionality to the server, it does still log the error in the error report log. A custom made script to fully fix the issue and a guide to using it can be found on this web page.
Error ID – 1053
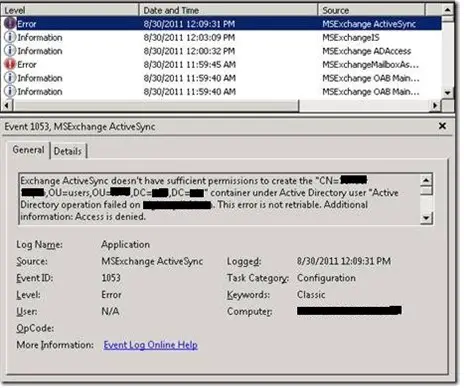
This error is basically caused by Exchange itself. When setting up ActiveSync, it tries to create a container named ExchangeActiveSyncDevices and store objects within the container, without having the proper permissions to do so. Luckily, fixing this is relatively easy.
First, ensure that the Advanced Features within the Active Directory Users and Computers is activated (by selecting the View menu option, and then clicking Advanced Features). Next, find the object(s) being created that causes the issue(s). Open Properties, select Security and click Advanced.Finally, check Include inheritable permissions from this object’s parent and click OK.
Error ID – 1009
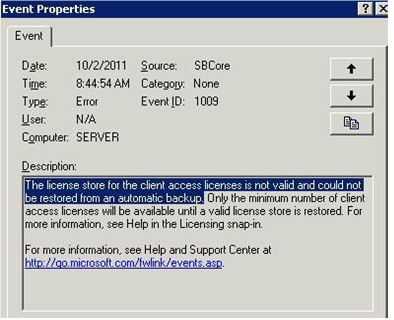
The license store for the client access licenses is not valid and could not ne restores an automatic backup.
When you reinstall Exchange but have your license number backed up, you may receive this error. However, this is easily fixed by first opening the SBS Server Management Console and clicking the Licensing tab. Click Restore Licenses, follow the wizard and when prompted to, point it at where you backed up license is located.
Error ID – c10308a2
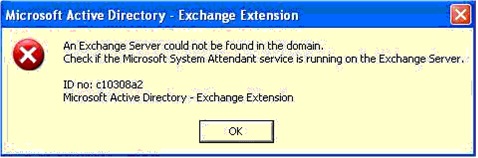
An Exchange Server could not be found in the domain.
Check if the Microsoft System Attendant service is running on the Exchange Server.
ID no: c10308a2
Microsoft Active directory – Exchange Extension
If you’ve ever tried to use the Active Directory Users and Computers MMC, then this may have come across or may eventually come across as a problem. When trying to add or change an e-mail address for a mail-enabled user from a remote computer, this error commonly occurs. This generally is caused by an improper delegation of a user to the server’s administrative group, attempted access from a non-administrative user, or have enabled Exchange’s hardening templates.
Fortunately, this problem comes with a simple solution. You must first determine the permissions required and then configure them on the Exchange Server to allow remote access to the Exchange System Attendant Service and SC Manager Database. A more in-depth look on this process can be found here.
Error ID – 9646
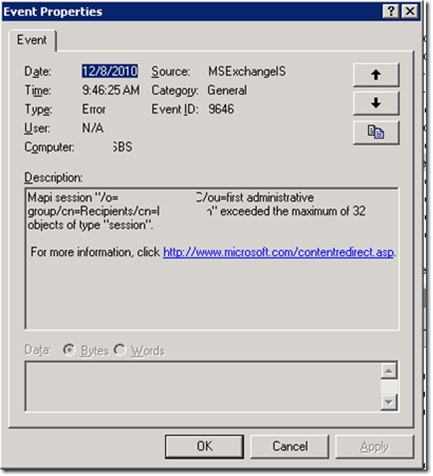
The following error is due to too many MAPI sessions being opened on the Exchange Server computer from another client on the network. It can also be the result of adding a large mailbox to a profile in Outlook 2007 if the profile uses the Cached Exchange Mode. In either case, the fix should be quick and simple. You’ll either want to increase the number of MAPI sessions allowed, or disable the default feature in Outlook 2007 that causes the issue. Both fixes with detailed instructions can be found here.
Error ID – 80090308
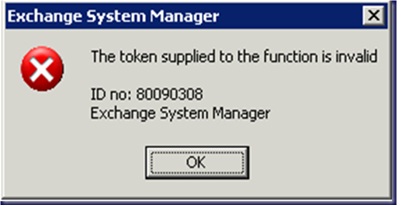
The token supplied to the function is invalid
ID no. 80090308
Exchange System Manager
When you do not have the SSL certificates required by the FQDN, you may receive this error. You may also receive this error when one of the SSL certificates is incorrectly published to the Exadmin root within the IIS. To correct this error, first try creating a new SSL certificate with the proper FQDN of the Exchange Server and publish the certificate. If you still experience errors, follow the instructions on removing the SSL from the Exadmin virtual root in the IIS
Uninstall Error – Insufficient Permission in the Domain
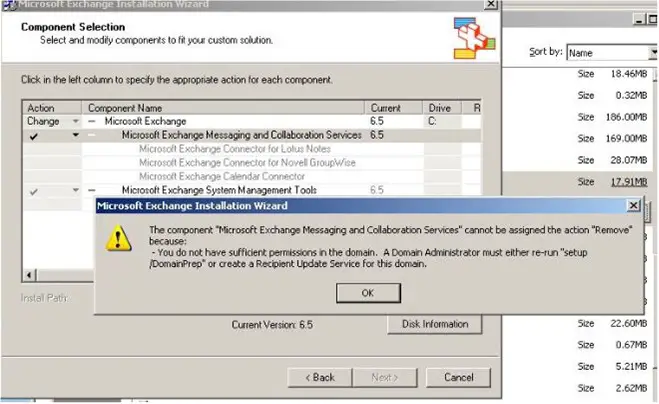
The component ‘Microsoft Exchange Messaging and Collaboration Services’ cannot be assigned the action ‘Remove’ because you do not have sufficient permissions in the domain. A domain Administrator must either re-run ‘setup/domainprep or create a recipient update service for this domain.
Some users may face this issue when uninstalling – some upgrading to Exchange 2010. The error message gives a pretty clear idea as to what the issue is at hand. First, make sure you’re attempting this while using an account with administrative rights. Next, ensure that your permissions to perform this action. If all else fails, and you can’t seem to successfully uninstall Exchange 2003, you may want to use IObit’s Uninstaller and perform a forced uninstall.
There you have it. The ten most common of many potential errors you may face while using Microsoft Exchange 2003. For additional information on fixes, first check above for your error, and if it’s not listed, visit the Microsoft website and download the Error Look-up Tool