The convergence and interplay of several technology developments at the same time distinguish the fourth industrial revolution from earlier industrial revolutions. The 10 primary technological trends driving the fourth industrial revolution are discussed in this article — trends that will permanently change how we do business and live our lives.
1. Ubiquitous Computing
Computers are everywhere these days: in our pockets, on our wrists, in our automobiles, and even in our home appliances… We’ve become accustomed to computers and devices being smaller, lighter, cheaper, more powerful, and more widespread as processing power has improved and the size of computer microchips has dropped. (For example, today’s smartphones are more powerful than supercomputers from ten years ago.) Looking ahead, quantum computers are likely to be the next significant jump in computing power — machines that are so fast and powerful that they can do previously unthinkable jobs that ordinary computers can’t.

2. Everything Is Connected And Intelligent
You might have heard of the Internet of Things (IoT) from smart TVs, smartwatches, and smart thermostats. The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the growing number of intelligent, connected gadgets and items that can collect and transfer data. Anything that can be linked will be connected in the future. Not only in terms of gadgets and goods, though that is undoubtedly important for businesses, but also in terms of the environments in which we live and work. From smart, linked factories and offices to complete smart cities, the environments around us will increasingly be able to monitor and react to what is going on.
3. Our World’s Datafication
Ubiquitous computing & the Internet of Things are both major contributions to the massive amount of data collected daily. But, in addition to machine-generated data, we humans create massive amounts of data in our daily actions, and this trend shows no indications of slowing down. The good news is that organisations can utilise this information to improve product and service design, corporate operations, decision-making, and even generate new income streams. However, organisations must be mindful of the dangers that data poses, particularly in terms of data privacy and security.
4. Artificial Intelligence
Most of this data is a key facilitator for AI, which has advanced tremendously in recent years, notably in the area of “conversational AI.” Because of AI, smart speakers will respond to 100 billion voice requests in 2020, up from 75 billion in 2019. The implication for companies is that, as our interactions with machines grow more sophisticated, customers will anticipate AI capabilities across a wide range of products and services.

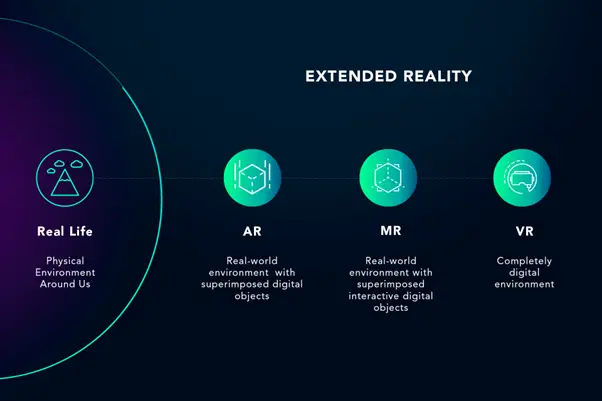
5. Extended Reality (XR)
Virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality are all included under the umbrella term “XR.” XR was first associated with immersive gaming, but it is now being employed in a variety of businesses to provide more immersive, individualised experiences for consumers and employees. Customers, for example, can now virtually test out things – for example, digitally placing a new couch in their living room to see how it looks – and staff may learn in immersive, engaging new ways. In the future, our perception of the world will increasingly occur in the liminal region between the physical and the virtual, and XR will further accelerate this trend.
6. Trustworthiness In The Digital World
Users’ trust in enterprises to construct a secure digital environment where transactions and interactions may take place safely, securely, and easily is known as digital trust. Many individuals feel that blockchain and distributed ledger technology will play a key role in increasing digital trust and secure transactions. However, the technology still has a long way to go before it is genuinely accessible to all sorts of businesses. Numerous firms may find success by collaborating with the many new blockchain inventors and entrepreneurs who are making significant progress.

7. 3D Printing
These days, 3D printing materials may be almost anything: plastic, metal, powder, concrete, liquid, and even chocolate. It is now possible to 3D print whole houses. This has the potential to revolutionise the industrial industry. In brief, 3D printing allows producers to make things that are difficult to construct using traditional methods, simplify the production process, and create highly individualised products (including one-of-a-kind items), all while lowering waste and expenses.

8. Synthetic Biology And Gene Editing
When “bad” genes are discovered – ones that might harm the health of an organism or its progeny – gene editing can be very beneficial. These negative features might theoretically be changed thanks to modern gene-editing technology. Gene editing might make significant advances in the battle against illness in humans, animals, and crops in this way. While gene-editing technologies may be used to make minor modifications to DNA, synthetic biology entails sewing vast strands of DNA together and putting them into an organism. As a result, the creature may exhibit novel behaviours or possess whole new skills. Synthetic biology and gene editing have the potential to transform the way we manufacture goods.
9. Materials Science And Nanotechnology
Materials science (the study and manipulation of materials) and nanotechnology (the science of regulating matter on a small scale, at the atomic and molecular level) have already made amazing advancements, from tiny computer chips to smartphone screens to stain-resistant textiles. Looking ahead, this trend might lead to huge breakthroughs in electric vehicle batteries, lower solar energy costs, and other advancements that will improve the planet.

10. Alternative Energy Sources
Nuclear fusion is frequently promoted as the future’s clean and possibly infinite energy source, but there’s a catch: sustaining a fusion reaction consumes more energy than it generates! However, because of advancements in magnet technology, a nuclear fusion reactor with a net power output might be operational by 2035. Green hydrogen is another intriguing zero-carbon energy alternative (which is different from traditional “grey hydrogen” production). Through an electrolysis process, water is divided into hydrogen and water without any by-products, resulting in green hydrogen. This procedure used so much power in the past that green hydrogen was practically impractical. However, renewable energy sources may change that.

The most important takeaway from all of these patterns is that we’re approaching an era of continuous and fast growth, in which several technological trends mix and feed into one another to produce massive changes. For enterprises, this implies that gradual technology improvements are no longer an option. The change will be constant in the future.


















