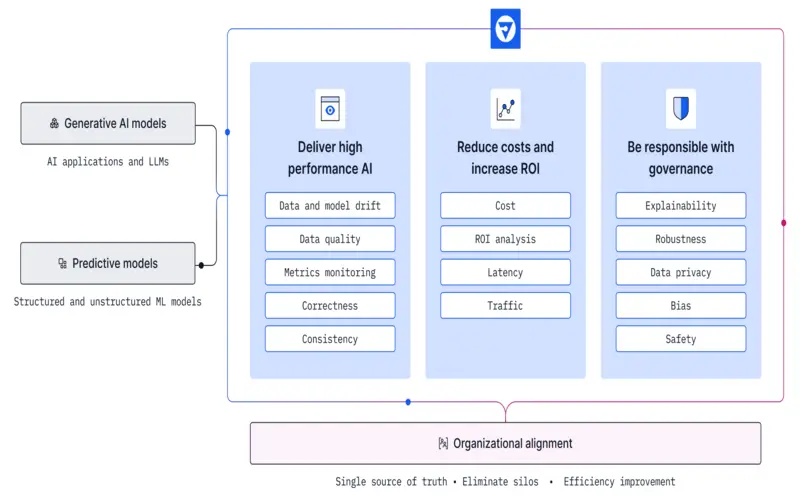
What Is AI Trust Risk And Security Management?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has experienced quick growth, allowing companies to forecast better, automate procedures, and make decisions more rapidly and correctly. This power of AI also prompts potential risks, such as data leakage, tampering, and malicious attacks. Businesses must go behind standard security measures and develop innovation and processes to secure AI applications and services and ensure AI usage securely and adequately. It is known as AI Trust, Risk, and Security Management. AI Trust, Risk, and Security Management is a shelter term that involves distinct elements of the AI lifecycle. These molecules are concerned with the creation, organisation, and continuing functioning of AI applications.
What Makes AI TRiSM Ao Famous?
Companies with operational AI transparency, trust, and security will have seen a 50% enhancement in the assumption, and company aim, and consumer suitability of their AI models. AI-powered robots will make up 20% of the universal workforce and 40% of economic output. AI models have been implemented without IT managers fully understanding or explaining them. The enterprises of AI trust, risk, and security cover many topics across the AI lifecycle. All the steps compulsory to create, release, and maintain an AI application are involved here.
1. AI System Development
AI system development entails creating procedures and processes to ensure that AI applications are made in a secure and accountable manner. It involves training development teams in good AI engineering practices, conducting security evaluation, and testing. It also needs procedures to ensure AI applications are planned with privacy and ethics in mind.
2. AI Model Testing
AI Model Testing is the procedure of testing AI models for precision and security loopholes. It entails the use of simulation and testing environments to replicate the conditions in which AI models may grow. It also includes recognizing potential malicious and accidental events and using attack surface evaluation to measure the loopholes of AI models.
3. AI Application Security
AI application Security is securing AI applications and services from potential risks. it includes executing protection mechanisms (such as recognize and access management, network security, and cryptography) and comprising security measures into deploying and updating AI applications and services.
4. AI Regulatory Observation
AI regulatory monitoring is the process of verifying that AI applications and services do not violate applicable laws and regulations. It entails creating applications and procedures to guarantee AI applications are compliant with data security and privacy legislation, as well as adhering to industry best practices. It also includes building methods to observe the ethical use of AI, such as ensuring data is composed and used ethically and responsibly.
5. AI Infrastructure Security
AI Infrastructure Security is the procedure protecting the infrastructure that holds up AI applications and services. It involves the physical and virtual parts (such as servers and cloud services), which must be retained and secure from potential threats. It includes observing and responding to responding to security events and executing measures to avoid them from occurring in the first place.
6. AI Security Auditing
AI Security Auditing is observing and assessing the security of AI applications and services. This includes transferring out regular security audits to locate and recognize potential loopholes and monitoring for attacks or breaches. It also needs processes for responding to security events and introducing measures to avoid them from reoccurring.
7. AI Models And Apps Need Constant Observation
To keep AI protected, fair, and ethical, specialised risk management methods must be blended with AI model operations (Model Ops). There are few off-the-shelf devices, so you are likely required to develop traditional solutions, for your AI pipeline. Controls must be registered consistently across model and application creation, testing and organisation, and continuous operations, for example.
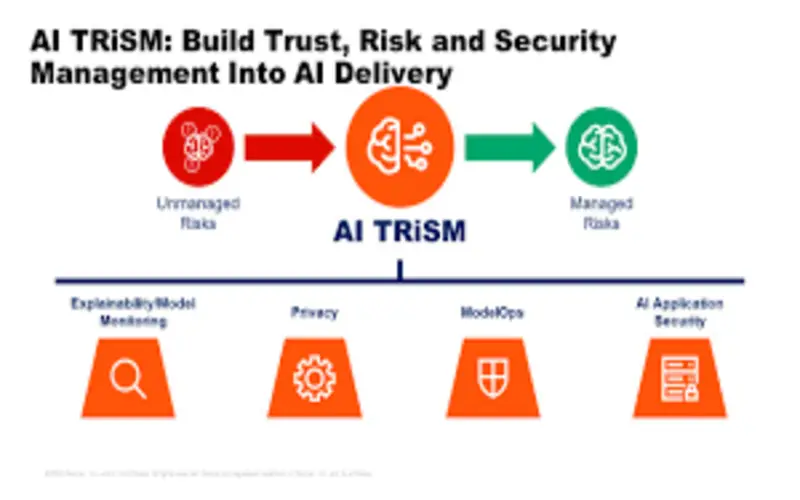
8. Security Of AI-Based Applications
The mean AI application security refers to keeping AI-powered schemes and services safe from harm. Combining defensive mechanisms (involving recognized and administered management, network security, and encoding) and security measures into the procedures of releasing and upgrading AI applications and services is essential.
9. The Compatibility Of AI With Laws
Regarding artificial intelligence (AI), it’s essential to follow the rules. Constructing AI applications and attaching them to the industry for data security and privacy requires building policies and processes. Structuring measures to ensure data is obtained and handled ethically and accountable is also part of complying with the moral use of AI.
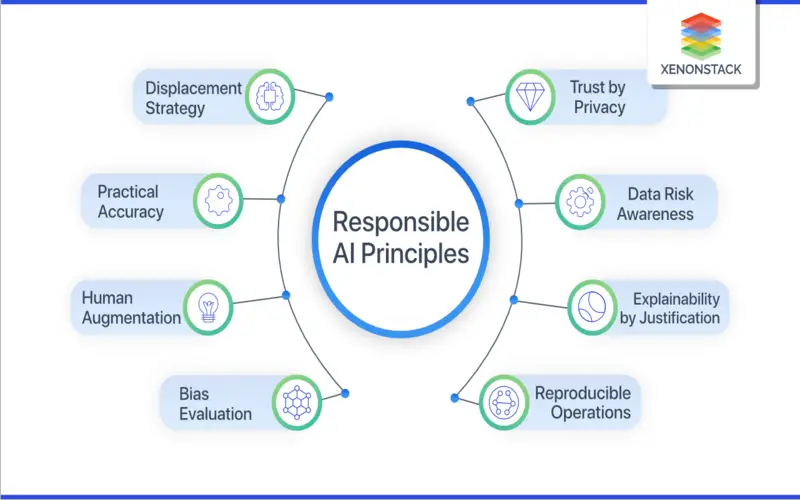
10. Evaluates Of Ethical Considerations In AI
The ethical assumptions of AI applications and services are known as AI ethics evaluates. Responsible and moral employment of AI needs setting up processes and rules to ensure it’s done right. It is also necessary to create processes to guarantee compliance with traditional practices, legislation, and regulations in the section. Companies must implement AI, Trust, Risk, and Security management to ensure the safe and ethical use of AI in operations. When executed correctly, AI, Trust, Risk, and security management may help companies safeguard their AI applications and services from harm and upgrade moral, lawful, and complaint AI deployment.