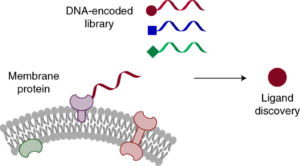
DNA-encoded libraries (DELs) are collections of small molecules covalently connected to amplifiable DNA tags sporting specific records approximately the shape of every library member. A combinatorial technique is used to assemble the libraries with iterative DNA encoding steps, facilitating monitoring of the artificial records of the connected compounds via way of means of DNA sequencing. Various screening protocols were evolved which permit protein goal binders to be decided on out of swimming pools containing as much as billions of various small molecules. The flexible technique has allowed the identity of several biologically energetic compounds and is now an increasing number of being followed as a device for lead discovery campaigns and identity of chemical probes.
What do you get from DNA encoded libraries ?
These DNA encoded libraries (DELs) are used to find moles, that are interact with pharmaceutically applicable . The chem. variety displayed via way of means of the library is fundamental to a successful discovery of potent, novel, and drug-like chem.
What are DNA encoded libraries used for ?
DNA-encoded chemical libraries (DEL) are a generation for the synthesis and screening on an exceptional scale of collections of small molecule compounds.
1. Building a library
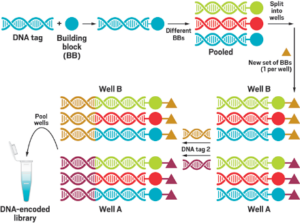
The maximum famous technique for developing a DNA-encoded library entails assembling DNA and a small natural constructing block. These additives are broken up into wells, and some other constructing block is added, alongside a 2nd piece of figuring out DNA. By repeating this technique with big numbers of constructing blocks, it’s far viable to create big libraries quickly.
2. Constructing and analyzing the library
The primary constructing block is broken up into wells in a plate, wherein it undergoes a chemical response with a one-of-a-kind constructing block in every nicely. Then researchers upload a unique little bit of DNA, everywhere from seven to fifteen base pairs long, to every nicely and connect, or legate, it to the prevailing DNA, developing a code for the response that simply took place. The contents of all of the wells are then pooled and broken up again.
3. DNA template strategy
One of the greater state-of-the-art techniques to construct libraries is to apply DNA code to decide the collection of chemical reactions. Templates are organized earlier than synthesis and include areas complementary to barcodes of BBs. When barcodes couple to the template, the relative satirical association of constructing blocks allows a chemical response among them. This technique is especially beneficial whilst assembling libraries of macrocycles and peptides.

4. DEL-well matched chemistry
The chemistry relevant to DEL generation is constrained to reactions well-matched with DNA. DNA is a water-soluble molecule; thereby conventional natural reactions have to be translated to corresponding conditions. In the beginning, only some reactions had been to be had withinside the toolbox of chemists, however, their range is extended, harnessing diverse synthesis approaches. One of the current thoughts became to hire photoredox catalysis for DNA‐Encoded Chemistry.

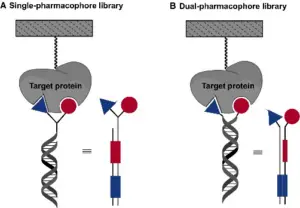
5. Dual-pharmacophore libraries
The gain of dual-pharmacophore libraries is that chemical moieties have the power to attain adjoining non-overlapping binding websites of a goal. Dual-pharmacophore libraries are assembled from sub-libraries, whilst blending collectively they shape heteroduplexes representing compounds. ESAC (Encoded Self Assembling Chemical) is the maximum famous technique.
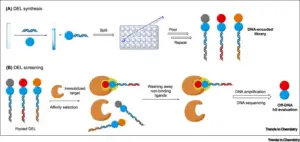
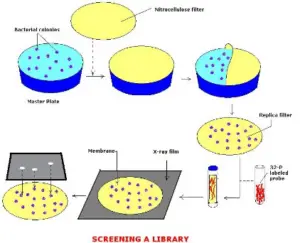
6. Library screening
Screening a DNA-encoded library entails exposing an organic goal or hobby to that library. Components that don’t bind are washed away, even as those who do are amplified and sequenced. Then records are replicated, and, added. “It’s a difficult task to do.
Advantages Of DNA-Encoded Library Technology
*Unprecedented get admission to big library drug discovery.
*Dynamic Library generation gives greater dependable outcomes than classical DEL approaches.
*Library individuals decided on for Medicine scheme relevance.
*High chemical variety, appropriate for some of the targets.

Challenges
Despite their innovative stature, DNA-encoded libraries aren’t without their challenges. Often chemists marvel if the big DNA bar code connected to a compound will intervene with the way it binds to a goal. Ideally, the DNA tag could face far from wherein the compound is binding to a goal explains GSK’s Davie. That’s continually located in crystal systems of library lagans which have correctly certain to their goal. Of course, that’s now no longer continually going to take place for unsuccessful logins, he says, however even as the DNA tag is a herbal constraint of DNA-encoded library generation, it’s now no longer a showstopper.