In an era of rapidly advancing technology, the field of healthcare is undergoing a notable transformation. The key driving force behind this shift is bioinformatics. It is a multidisciplinary field that merges biology, computer science, and information technology for the analyzation and interpretation of biological data. Bioinformatics is an immense promising and revolutionizing tool in the field of healthcare. It unlocks valuable insights into human health, disease mechanisms, treatment outcomes, challenges, and prospects.
Bioinformatics incorporates the application of computational tools and algorithms to analyze biological data, derived through genomics, proteomics, and other technologies. A wide range of techniques which includes sequence analysis, structural biology, data mining, and machine learning, to decipher complex biological processes and phenomena are used. Integration of diverse datasets and applied analytical methods, bioinformatics enables researchers and other experts to extract meaningful information from large-scale biological data.
1. Clinical Decision Support
In clinical arrangements, bioinformatics works as a functionary that provides valuable decision-making and supportive tools asissting healthcare professionals. Through this support, you can make evidence-based diagnoses and treatment decisions. Bioinformatics offers insights into disease mechanisms, treatment diagnosis, and patient outcomes by integrating a patient’s data, their genomic information, and clinical knowledge, which in turn enables personalized medicine approaches, helps in improvement of treatment efficacy, and enhances patient care delivery as per the requirement.
2. Genomic Medicine
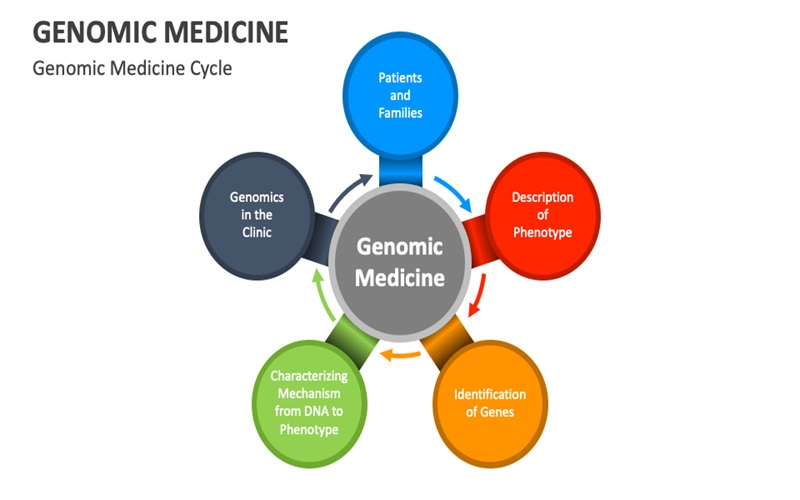
One of the most popular applications of bioinformatics in healthcare is genomic medicine. By integrating a patient’s genomic data, bioinformatics facilitates the identification of genetic variations associated with diseases. By acknowledging genetic variations, you can enable personalized medicine approaches. Various techniques, such as genome sequencing and variant analysis, help uncover genetic factors underlying diseases, predict disease risk, and tailor treatments based on genetic profiles of different individuals.
3. Embracing Data-driven Healthcare
D-driven healthcare has changed way we approach disease prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. With the discovery of advanced devices such as, remote monitoring technologies, and digital health platforms, a large amount of real-time health data is generated continuously. Bioinformatics plays a remarkable role in supporting this wealth of data to derive insights for customizable care and disease management. This is a remarkable approach towards healthcare in today’s time. It facilitates early detection of diseases, personalized risk assessments, and optimization of treatment strategies. Through bioinformatics we can empower patients to actively participate in their healthcare journey by providing them access to customized health insights, monitoring tools, and lifestyle recommendations as health is everyone’s topmost priority and the need for the everyone globally.

4. Proteomics
It is associated with studying proteins, their structures, functions, and interactions. Bioinformatics facilitates the analysis of proteomic data, along with protein-protein interactions, protein modifications, and pathways involved in diseases. This helps us comprehend the underlying mechanisms behind diseases and discover potential targets.

5. Disease Diagnosis And Biomarker Discovery
Through bioinformatic tools, we can quickly identify disease biomarkers, which are biological indicators associated with specific diseases. These biomarkers are utilized for detecting various diseases, monitoring the disease, treatment or other healthcare inventions.

6. Personalized Medicine
It is a tailor-made invention to each person’s unique genetic make-up. With the help of patient’s genetic profile, the doctor can quickly predict likeliness of certain diseases and likewise provide proper medication and proper dose to reduce side-effects of the disease. This application is already being used in the treatment of personalized cancer medicine, diabetes-related disease and HIV.

7. Preventive Medicine
Preventive medicine primarily focuses on the health of individuals. It makes use of various research techniques that includes biostatistics, bioinformatics and epidemiology to understand the patterns and the mechanisms of health and disease. Such information is transformed into programs to prevent disease, disability, and death. An illustration of preventive medicine is the screening of newborns immediately after birth for health disorders. These disorders include genetic diseases or metabolic disorders which are treatable, but are not clinically evident in the initial period. To develop such screening tests for the identification of the disease at an early stage, researchers make use of bioinformatic tools to analyze genomics, proteomics and metabolomics data for disease biomarker.

8. Gene Therapy
It is the method in which defective genes are replaced with a functional one in the cells of the patient. Gene therapy method is pretty complex and is not widely used as each person’s genetic profile is different. Applying bioinformatics helps to identify the best gene target site for each individual by looking at their genetic profile. This reduces the risk of side effects. In the field of medicine, the application of bioinformatics is unlimited. It is diverse and constantly evolving.

9. Drug discovery
Infectious diseases have taken over the lives of youth and children globally. World Health Organization (WHO) states that icommunicable diseases account for over 13 million deaths annually. Among all, the developing countries have recorded the-most number of deaths from the same. One of the main issues that has arisen and encountered is the manufacturing of cheap and efficient medicines. Moreover, the pharmaceutical industries have shifted from the trial-and-error process of drug invention to a rational and structure-based drug design. The time and cost of developing effective pharmacological agents can be mitigated through a successful and reliable drug design technique. The method of drug target identification and drug candidate screening can be fostered, and safer or more effective drugs can be invented based on molecular modelling and simulation.

10. Veterinary Sciences
With the use of Bioinformatics, the research in Veterinary Science has achieved an appreciable level. This field makes use of the application of Bioinformatics and focuses explicitly on sequencing projects of animals that includes cows, pigs, and sheep leading to the development in overall production as well as the health of livestock. Furthermore, bioinformatics has helped scientists discover new tools for identifying vaccine targets.

Conclusion
All in all, bioinformatics has come out as a powerful tool in unlocking health insights and bringing in diverse changes in healthcare delivery. By using data-driven approaches, fostering collaboration, and leveraging emerging technologies, bioinformatics has the potential to promote personalized medicine, improve patient outcomes, and address global health challenges. As we continue to support the power of biological data and computational analytics, bioinformatics will always remain at the forefront of innovation, shaping the future of healthcare in numerous ways.

















