Deep Neural Nets: Advanced Machine Learning
Machine learning is a part of computer science that makes the computer capable, to learn without actual programming. The machine learning technique emerged from the applications of computational learning theory and pattern recognition that comes from artificial intelligence.
It deals with the study of algorithm construction that makes data predictions or decisions, over constructing a model from sample inputs. Machine learning engages with computing tasks where programming and designing explicit algorithms is unimaginable; some of the example applications consist of spam filtering, computer vision, optical character recognition (OCR), detection of network intruders and search engines.


Machine learning relates to the computational statistics, which also targets in prediction-making with the help of computers. Machine learning fuses with mining of data, where the latest subfield targets more on exploratory data analysis known as unsupervised learning.
Deep Learning:
Deep learning goes down the stream of machine learning based on a set of algorithms that tries to design data having a high-level abstraction. There are two types of neurons: input signal that receives and output signal that sends. As soon as the input signal receives from the internal layer, it passes on an altered version. Between the input and output, many layers are hidden in a deep network, letting the algorithm to use multiple processing layers, poised of non-linear and multiple linear transformations.

Deep learning is a part of a large group of machine learning methods based on learning representations of data.
Neural Network Definition:
Neural networks are a set of algorithms, constructed for pattern recognition. They model in such a way that they work on the human brains. They depict sensory data over a kind of machine concept, defining or gathering raw input. They recognize patterns that are numerical, which consists of vectors that contain, all data in reality like images, time series, sound, text that translates.
Neural networks help us to gather and categories. They extract the features from other algorithms to cluster and segregate. Deep neural networks are components of advanced machine learning the applications involve algorithms for learning of reinforcement, regression, and classification.
Deep learning is also called “stacked neural networks”; that is, networks poised of various layers.
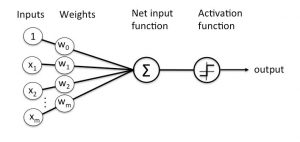
Each layer composes of nodes. A node is just a place where computation happens, loosely patterned on a neuron, which acts similarly like the human brain and gets fired when it undergoes stimuli.
The below diagram represent’s the structure of one single node.
Neural Networks & Artificial Intelligence:
In some circumstances, neural network reflects as “brute force” Artificial Intelligence, because they start their design with a blank slate and batter their way to create an exact model. There are two types of artificial neural networks Feed Forward ANN, and Feed Back ANN. The ANN’s make use of the idea based on the conclusion that human brain works by right connections, restricted from making use of wires and silicones, as living limits with dendrites and neurons.
The human brain consists of 100 billion nerve cells known as neurons. They further connect with thousand other cells by Axons. The dendrites accept the sensory organs input or the external agent’s provocation and the electric impulses creates, which quickly travels through the neural network. The neuron sends the message to another neuron for handling issues or remains without forwarding.


















