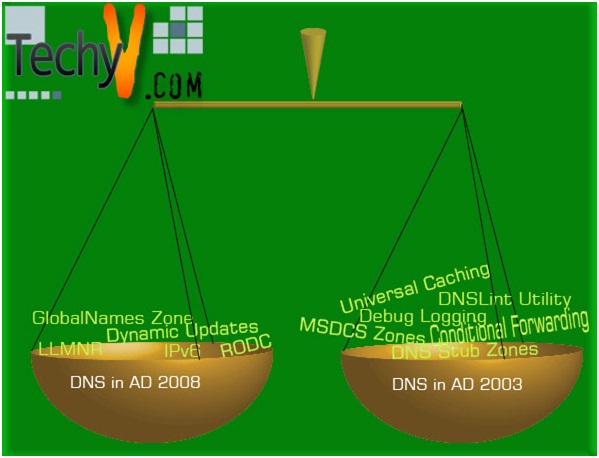
Differences between DNS in AD 2003 and Ad 2008
Active Directory (AD) is the nice addition to technology and it is the most talked about thing in Windows Literature. But to get full advantage of Active Directory, it needs a directory of servers and various workstations, which are commonly known as DNS. Active Directory cannot work properly with DNS.
DNS stands for domain name system, which is mainly used to translate the domain names to IP addresses. Basically it is structured in a hierarchical order, so that the users get easy access to the source. For instance, when a use enters the URL www.nro.dk into the browser, the query will be sent to his computer’s DNS. The DNS will further specify the IP address. If the query doesn’t match any results, it uses the advanced options.
Features of DNS in AD 2003
a. In Window 2003 server, the network needs DNS in three scenarios:
i. In the first place, to find AD resources such as Global Catalog Server
ii. Secondly, to trace pages on internet and
iii. Thirdly, connecting to a printer share
b. The network resources can be accessed via alphanumeric names instead of using IP addresses.
c. The hierarchical order of DNS makes it easy for users to update their server records themselves.
d. It also reduces the work load of administrator.
e. DNS practically adds a lot of value to the Active Directory (AD) as it helps in finding Kerberos, Global Catalog and Logon Servers throughout the globe.
Moreover, window Server 2003 is different from Window Server 2008 on account of its various features. The Window Server 2003 has DNS features such as:
1. DNS Stub Zones
2. MSDCS Zones
3. Conditional Forwarding
4. Debug Logging
5. DNSLint Utility
6. Universal Caching
DNS in AD 2008
The main definition of Domain Name System (DNS) holds the same in Active Directory 2008. Quite similarly it is used in TCP and IP networks to manage the network services. Users get access to the shared source of information on network with ease. However, Windows Server 2008 has some improved DNS features than the older versions. It works with more efficiency and better performance. The new features of DNS in AD 2008 are as followed:
- The New Background zone loading: this the new feature in which zone data keeps loading in the background. This is how the stored DNS zones on the DNS servers quickly response to users’ queries and save the time.
- Support of long IP address: It offers support to the longer IP addresses in the IPv6 specification.
- Read-only Domain Controllers’ support: It provides primary read-only zone on RODCs in the Windows Server 2008.
- Support of Single names: The large enterprises and business networks can use small and convenient names. It is also helpful while using DNS name suffixes.
- Block list for Global query: Some of the protocols which rely on DNS name resolution i.e. Intra-site Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol (ISATAP) & Web Proxy Auto Discovery Protocol (WPAD) raise the potential security risks for servers. The DNS in Windows Server 2008 has this special feature of global query block list which reduces such vulnerability of mal-functioning.