Formerly digital computers were large, expensive devices, now the size and shape of these machines are become different in past few years due to this new device “Microprocessor”. The microprocessor is an integrated circuit that contains processing capabilities of a big computer; it is a small programmable device. There are many companies which are manufacturing this microprocessor chips in different technologies and different world length. Some companies of the microprocessor are Intel, Motorola, Zilog, and Toshiba.
What is a Microprocessor?
The Microprocessor is a semiconductor, multipurpose, programmable logic device that reads binary instructions from a storage device known as a memory, accepts binary data as input and processes data according to the instructions and provides the result as output.

The electronic logic circuits are capable of performing various computing functions and making decisions to change the sequence of program execution. Microprocessors can also be present in a form of integrated circuit, which contains processing capabilities of large computers.
A microprocessor has three parts:
1. Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU) – A.L.U. is an arithmetic and logic unit, where arithmetical and logical operations are carried out.
2. Registers – They are primarily used to store data temporarily during execution of the program.
3. Control unit – It provides timing and control signals to the whole system. It also controls the flow of data.
The functions of microprocessors are as follows:
i. To fetch, decode and execute instructions.
ii. To distribute information from one block to another block or from one block to I/O lines.
iii. To give a proper response to different externally produced interrupts according to their priority.
iv. To provide control and timing signals to the whole system according to the instructions.
The evolution of microprocessor can explain by following five generations:
1. First generation:
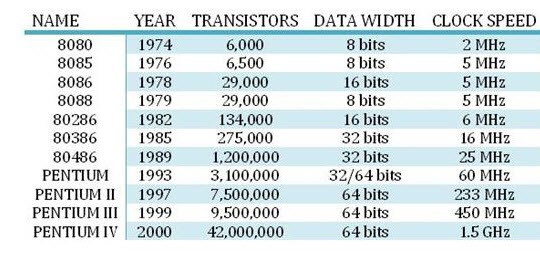
Intel’s 4004 was the first microprocessor available in the market. It was a four-bit
Microprocessor introduced in 1971, designed to be used in calculators. In 1972, Intel introduced first general-purpose 8-bit microprocessor Intel 8008.
E.g. Intel’s 4004 (4-bit)
Intel’s 8008 (8-bit)
Motorola’s 6800 (8-bit)
2. Second generation:
IN 1974, Intel’s 8080, Zilog’s Z-80, Motorola’s M6800 were introduced. All these were 8-bit microprocessors. During the second generation, the development of microprocessor has been in a direction of complete microprocessor system i.e. CPU, ROM, RAM, clock, ports all in a single package. In 1976, Intel’s 8085, 8-bit microprocessor was introduced.
E.g. Intel’s 8085 (8-bit)
Zilog’s z80 (8-bit)
3. Third generation:
Intel introduced first 16-bit microprocessor 8086 in 1978. The next versions of the microprocessor are Zilog’s z-8000 in 1979 and Motorola’s 68000 in 1980. In third generation memory space is 64 kb. The other features were full arithmetic execution and efficient higher level language addressing.
E.g. Intel’s 8086 (16-bit)
Zilog’s z-8000 (16-bit)
4. Fourth generation:
In 1981, Intel introduced first 32-bit microprocessor 80386. It includes physical memory of 4 GB. Other microprocessors Hewlett Packard’s HP-32 announced in 1982. In 1987, Motorola’s 68020, a 32-bit microprocessor introduced.
E.g. Intel 80386 (32-bit)
Intel 80486 (32-bit)
5. Fifth generation:
Intel made improvement in microprocessor design to provide the greatest speed. Also, the system can run on a new operating system like UNIX, Linux, etc. the processor in this generation is known as Pentium. It is a 64-bit microprocessor.
E.g. Intel 80586
Intel Pentium IV