Ever since there has been a need to store the data files like audio, video, images, etc., a number of storage-devices are evolved. Though there are various magnetic devices (tapes, floppy, hard drives) as well as optical devices (CD, DVD, Blu-ray discs), certain limitations bind them. All the above-mentioned storage media have readability and dependability concerns.
The challenge that we have to face is that maxing out under the existing technology. Holographic data storage comes into the picture to overcome these curbs. It is a prospective optical technology that can store data about 1 to 4 Terabytes in a cube sized crystal throughout the volume and not just on its surface. Not only recording the large amount of information, but the data transfer rate is also higher than the existing optical devices.

This holographic data storage system abbreviated as HDSS is a volumetric approach that reads the data bits in a parallel fashion. Unlike the regular hard disks (we write data in two-dimension) the data here is stored in the form of 3D holograms. The technology records multiple images at the same location by using the light in different angles.
The HDSS stores the data in the form of holograms. HOLOGRAM: A 3D image formed by the interference of two light rays.

Working:
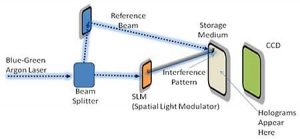
We make use of an SLM (Spatial Light Modulator) to create binary information out of a laser light. It acts as a shutter that allows the light to pass or blocks it corresponding to 0’s and 1’s.
Storing or recording:
Split the blue-green Argon laser into two signals:
- Reference beam
- Data carrying beam
Pass the second type of beam through the SLM, and the reference signal is reflected back to have an influence on the data carrying signal. These two beams intersect and form an interference pattern of dark and bright regions. A photo sensitive medium records this sequence and is known as a hologram.
Reading:
The light of reference beam on the hologram reconstructs the data.
The HDSS also store the data on circular discs similar to the conventional optical media. These are known as HVDs (Holographic Versatile Disc) that allows to read or write one million bits of data in a single flash of light.
This technology is a WORM technology which means Write Once Read More. It prevent the users from accidentally erasing the data recorded because it allows them to write data only once and read any number of times.
INTERESTING FACTS:
- According to an estimation, six HVDs have a capacity to store all the books of a largest library in the world (U.S. Library of Congress).
- Two HVDs are more than enough to record all the images of landmasses on the earth.
- A movie if continuously played for a year without a break (4,600-11,900 hours) can fit in one HVD.
How efficient is it compared to others?
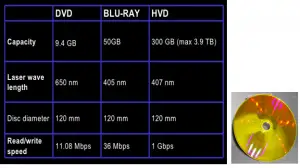
This HDSS is one of the better solutions for storage of increasing data, but the major drawback of this technology is its cost. But as a matter of fact with the progressing time, the cost of this system will also reduce to an acceptable amount similar to its ancestors or competitors.