How to Configure VMware Virtual Network
Configuring VMware Virtual Network
In this article, we will cover virtual networking components that VMware provides and explore how we will use various network configurations on VMware workstations.
Virtual Networks:
VMware workstation provides the following types of virtual networks:
- Bridged Network: This network model uses host computer physical adapter to connect the virtual machine to a network. Since it uses host computer adapter, the virtual machine can be visible to the other systems on the network and can communicate to other virtual machines.
- Network Address Translation (NAT): This model uses the host IP and MAC address to share with the virtual machine i.e. both the physical and virtual machine share a single network. This type of network setting is not visible outside of the network like the bridged network. NAT can be used with DSL, modems and Ethernet.
- Host-only Network: If you plan to use a network within the physical system then opt for host-only network. This type of network uses virtual network adapter within the host computer and is visible to the host system. This type of network is suitable for creating a QA and research the type of lab environment as this is an isolated virtual network.
- Custom Networking Configuration: This model uses a combination of the above other virtual network. Using this model, virtual network can be connected to an external network or can use the host system network. This option also allows you to create multiple virtual networks.
Virtual Network Components:
Most of the virtual networks consist of the following components:
- Virtual Switch: Virtual switch is used to connect other networking components in a network. We can create up to 10 virtual switches in Windows and up to 255 on Linux hosts. By default bridged network type uses VMnet0 switch, NAT uses VMnet8 and Host-only network uses VMnet1 switch.
- DHCP Server: DHCP server provides IP network addresses to the virtual machines. NAT and Host-only network which is not bridged to an external network uses DHCP server.
- Network Adapter: We can create and configure up to 10 network adapters in each virtual machine. It is used to set up the virtual machine and appear as Intel Pro/1000 MT Server Adapter on Windows Vista and Windows 7 operating guest.
Setting up Bridged Networking
To set up a bridged network on a new virtual machine use the following;
1. Start VMware -> VMware workstation.
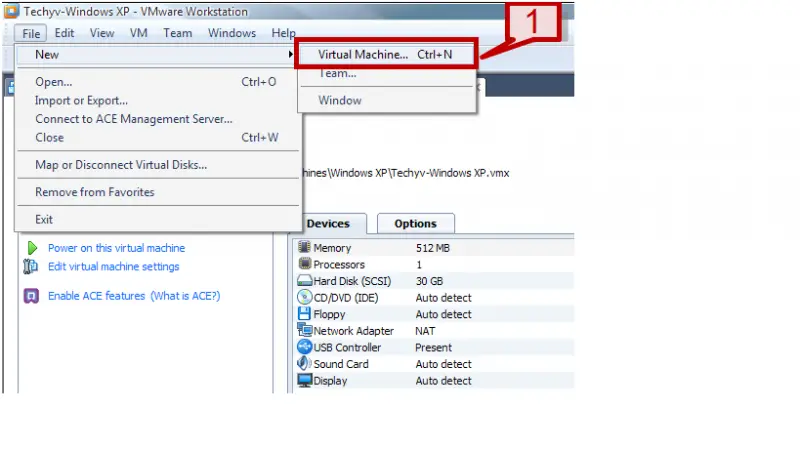
2. On the file menu select New -> Virtual Machine.
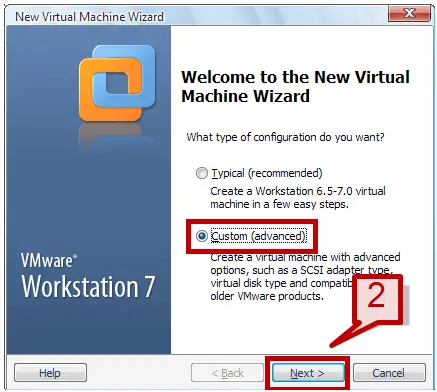
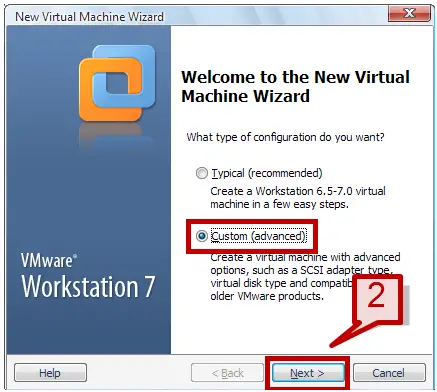
3. In the new VM wizard, select the Custom option and click next.
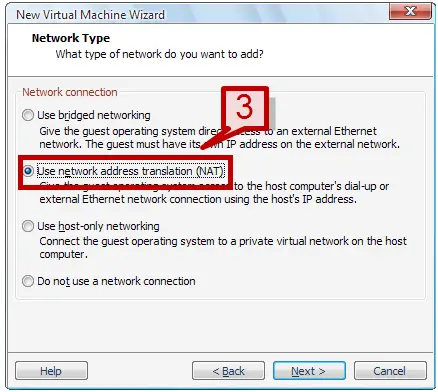
4. Select the different option on the wizard until the Network Type wizard appears. In this screen, select Use bridged networking option.
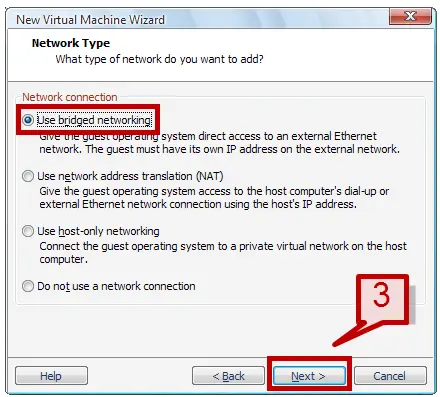
To set up bridged networking on the existing virtual machine, please follow these steps.
1. Go to VM tab and select settings.
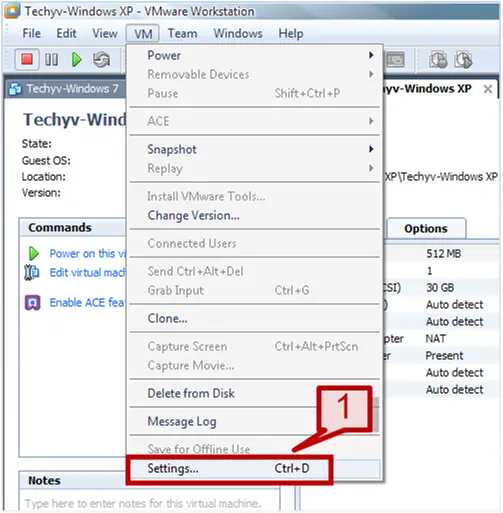
2. On the hardware tab select Network Adapter.
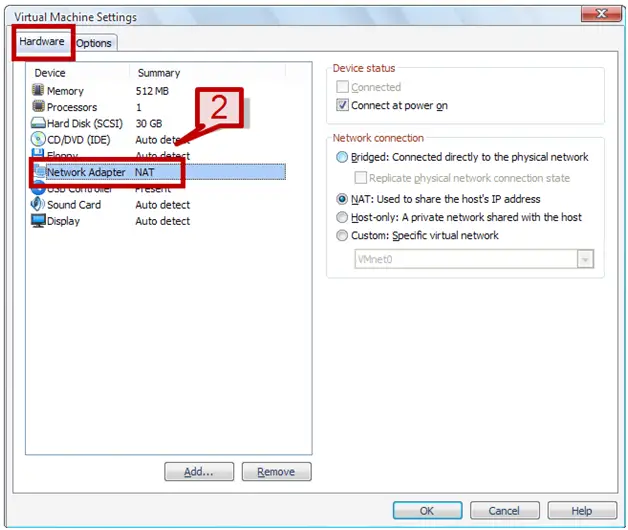
3. On the right hand side, select Bridged connected directly to the physical network option under network connection.
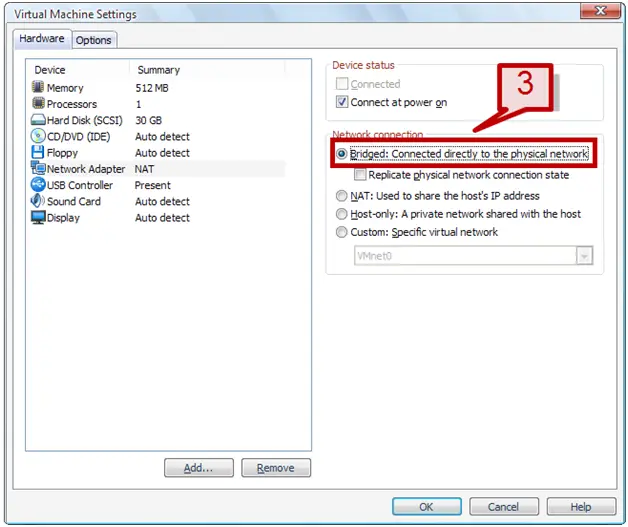
Note: The replicate physical network connection state can be used to virtual machine on mobile devices or on laptops.
Configuring Bridged networking
By default VMnet0 is used for automatic bridging mode. To change and configure VMnet0 bridged networking use the below steps;
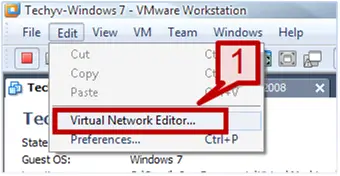
1. Go to edit tab -> Select Virtual Network editor.
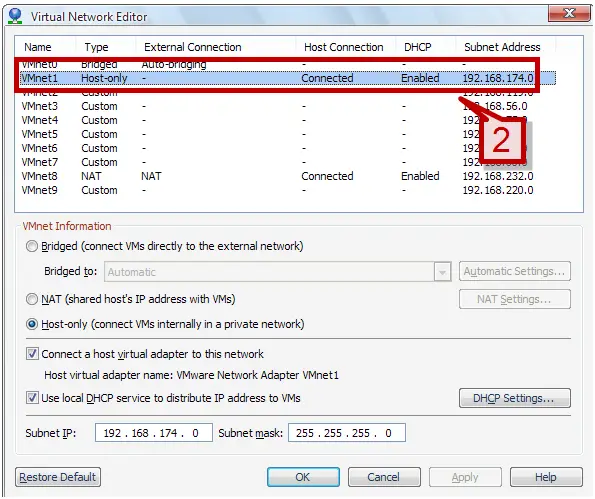
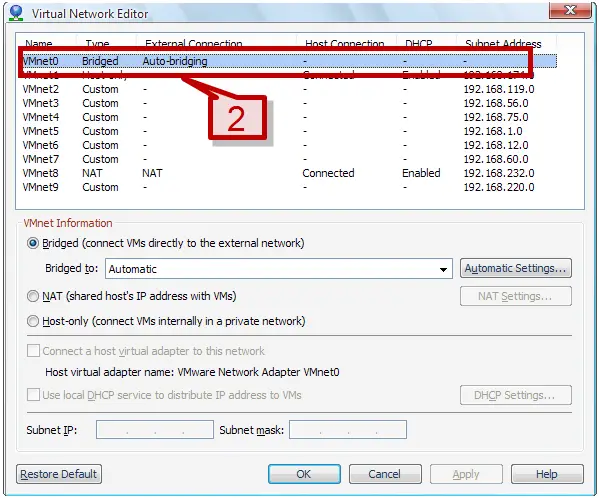
2. A Virtual network editor window will provide you the lists of the network adapter and their connection type. VMnet0 is default assigned to auto bridging connection mode.
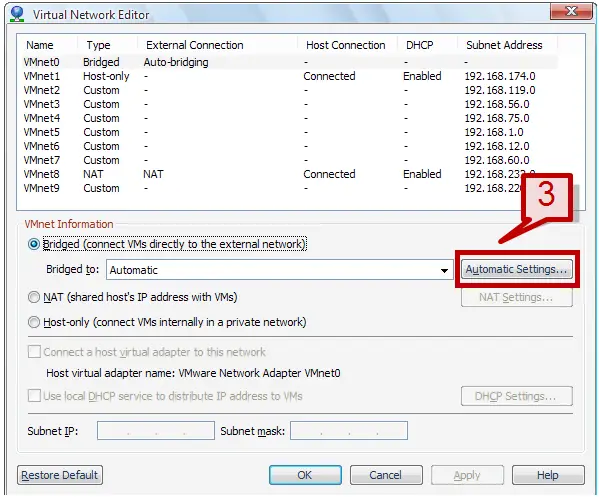
3. Select the automatic settings under VMnet information section.
4. Automatic settings would list the available physical network adapter. Select one of the adapters to automatically assign the bridge connection to VMnet0.
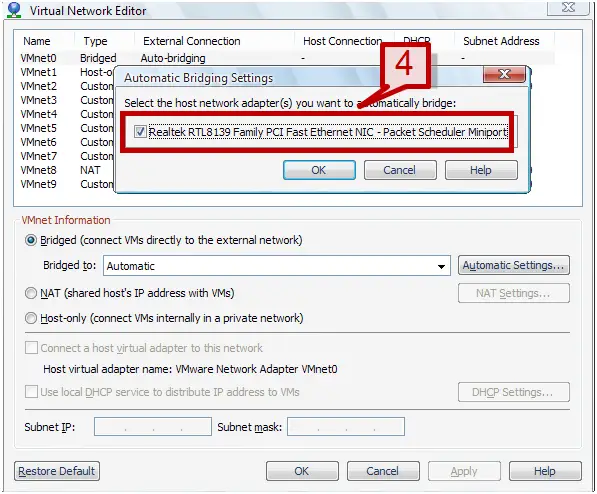
5. The bridged to option provides an option to designate a physical network adapter to bridged networking mapping. Under bridged to drop down menu, select an adapter to be assigned to the connection.
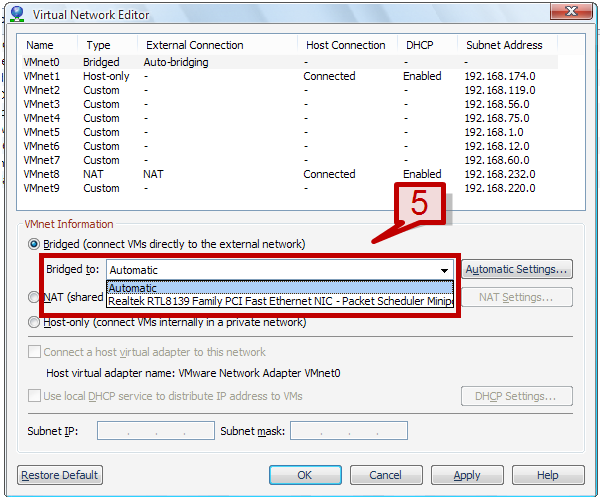
Note: If the physical host has two network adapters installed which are connected to two different networks then you can bridge the virtual machines to both network adapters. This result in the virtual machine can access any one or both the physical networks.
Setting up NAT Network
To set up a NAT network on a new virtual machine use the following:
1. Start VMware -> VMware workstation.
2. On the file menu select New -> Virtual Machine
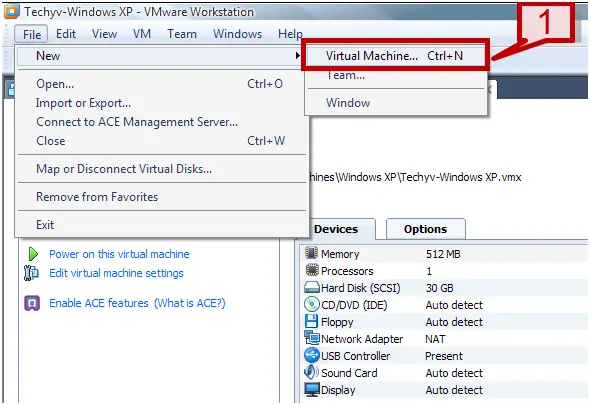
3. On the new VM wizard, select Custom option and click next.
4. Select the different option on the wizard till the Network type wizard appears. In this screen, select Use Network Address Translation option.
To set up NAT networking on the existing virtual machine, please follow these steps.
1. Go to VM tab and select settings.
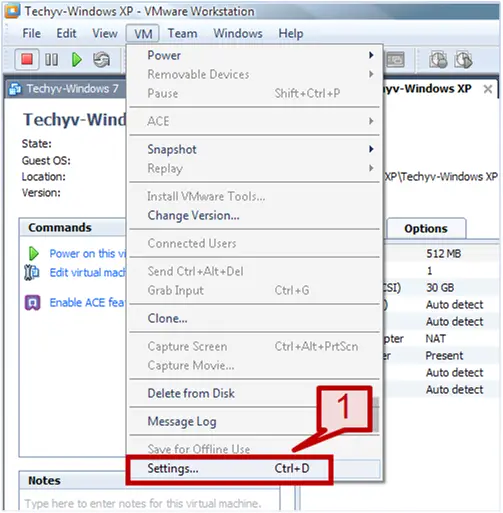
2. On the hardware tab select Network Adapter.
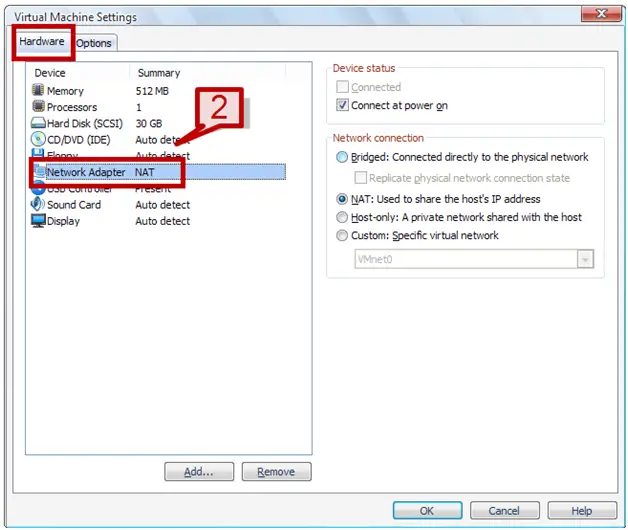
3. On right hand side, select NAT under network connection.
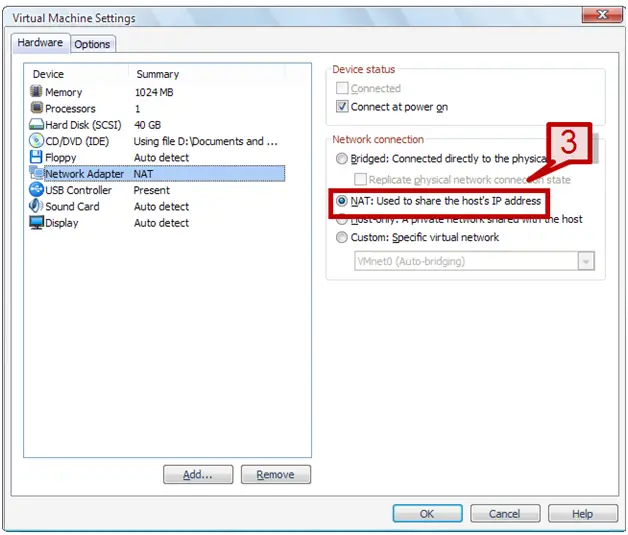
Configuring NAT networking
1. Go to edit tab -> Select Virtual Network editor.
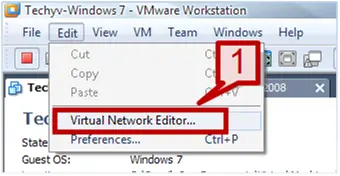
2. A Virtual network editor window will provide you the lists of the network adapter and their connection type.
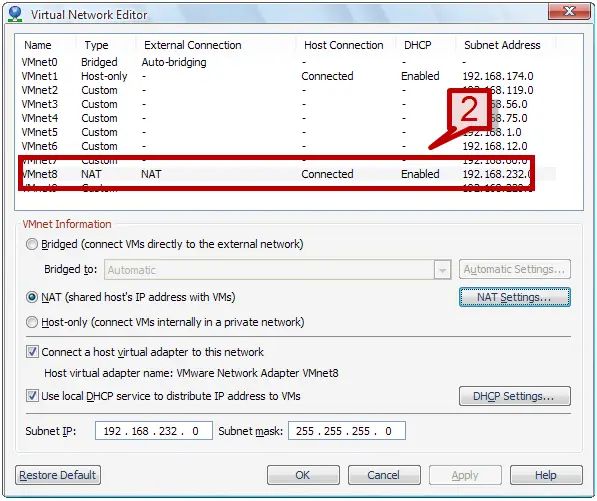
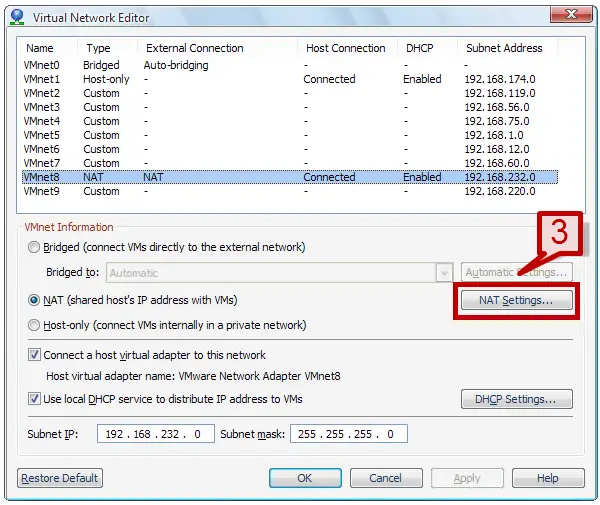
3. To configure NAT select the NAT settings tab.
4. Provide the various settings such as Gateway IP address, add a port forwarding address etc.
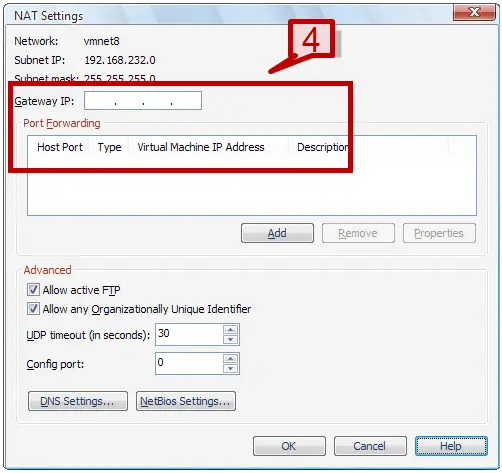
5. To change the DNS server addresses that the virtual NAT should use click on DNS settings.
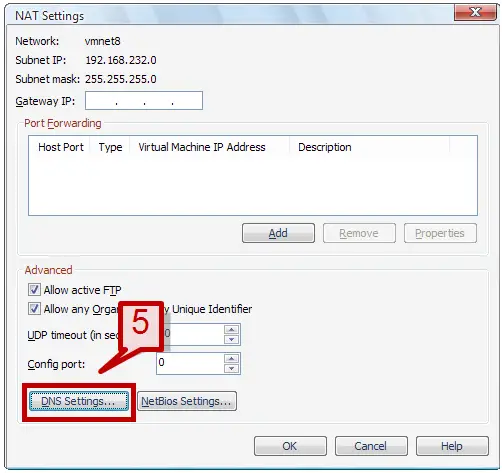
6. In the DNS window provide the preferred DNS server or the alternative DNS server IP address.
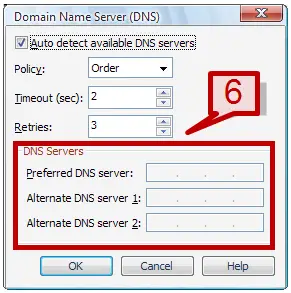
Setting up Host-only Networking
To set up host only network on a new virtual machine use the following;
1. Start VMware -> VMware workstation.
2. On the file menu select New -> Virtual Machine
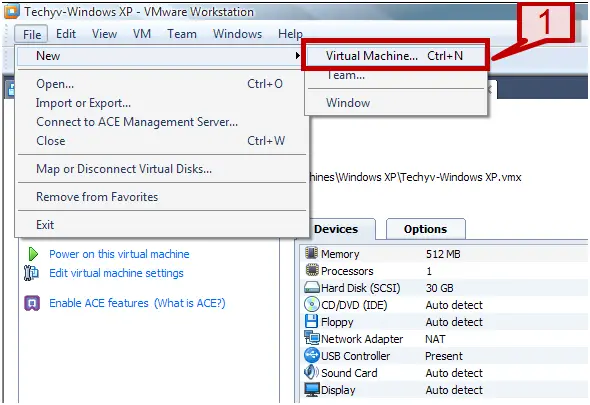
3. In the new VM wizard, select the Custom option and click next.

4. Select the different option on the wizard till the Network type wizard appears. In this screen, select Use Network Address Translation option.
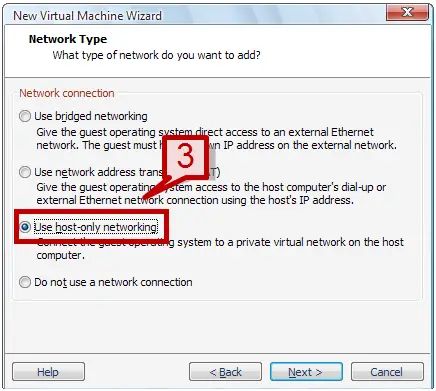
To set up host only networking on the existing virtual machine, please follow these steps.
1. Go to VM tab and select settings.
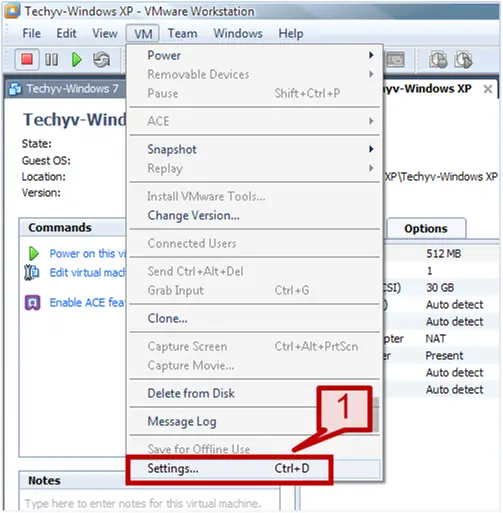
2. On the hardware tab select Network Adapter.
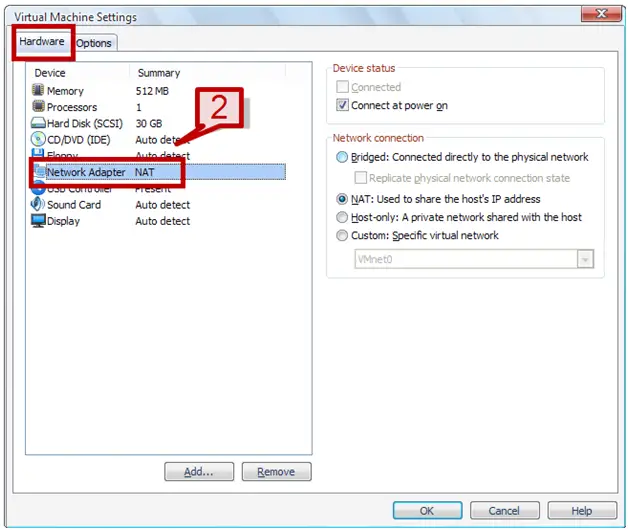
3. On right hand side, select Host-only option under network connection.
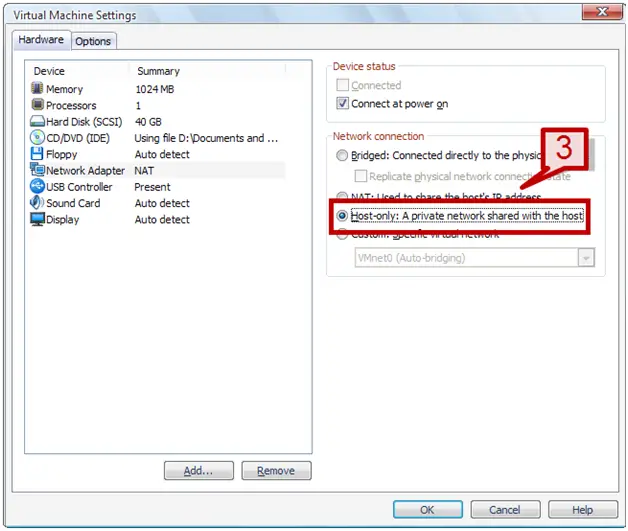
Configuring Host-only networking
1. Go to edit tab -> Select Virtual Network editor.
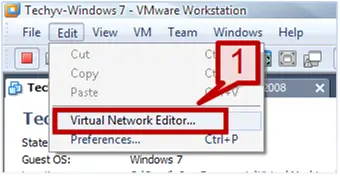
2. A Virtual network editor window will provide you the lists of the network adapter and their connection type.