What Is Continuous Threat Exposure Management?
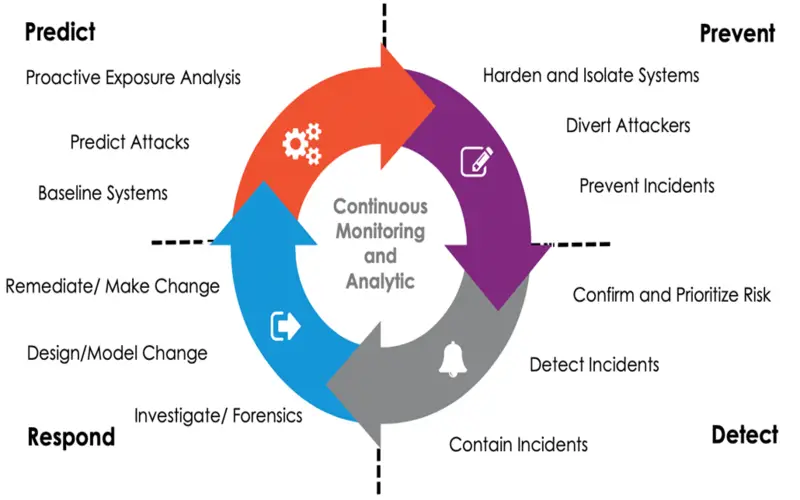
Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) is a cautious and ongoing five-stage program or system that assists organizations in monitoring, evaluating, and minimizing their level of exploitability and validating that their evaluation and curation processes are optimal. Organizations worldwide are manipulating CTEM to address exposures and enhance their security posture effectively. CTEM consistently assesses an organization’s whole ecosystem, involving networks, systems, assets, and more to recognize loopholes and weaknesses to reduce the likelihood of these weaknesses being maltreated. A CTEM program can allow continual improvement of security posture by recognizing and amending potentially problematic areas before intruders can purchase them.
The Five Stages Of CTEM Implementation
The five stages of the CTEM program – Scoping, Discovery, Prioritizing, Validation, and Mobilization complete the cycle and are required for its success.
Scoping
Scoping, the first stage of Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM), requires establishing the program’s scope, recognizing the most critical assets to secure, and determining the risk associated with those assets. This stage of the CTEM course is necessary for its overall success since it builds the framework for all that follows.
Discovery
The discovery stage of Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) includes recognizing and cataloguing all loopholes resources, such as hardware, software, databases, and network infrastructure. During this stage, businesses use various IT discovery tools and strategies to audit all their IT resources and find potential defects and dangers, which frequently involve conducting loopholes assessments, penetration testing, and other security examinations.
Prioritizing
After scoping and identifying broad flaws in the management’s digital infrastructure, the natural development leads us to devote. The prioritization stage of Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) analyzes the risk associated with each asset discovered in the discovery stage. It ranks them based on them crucially to the business operations.
Validation
In the phase of CTEM, security teams put their rules for addressing the loopholes and threats considered the most excellent order into action and test them. It could include introducing additional safeguards, updating software, or changing privacy settings. It also values nothing that it’s critical to include a vast range of stakeholders, including IT people, security personnel, and other workers who may have distinct viewpoints on potential loopholes.
Mobilization
The Mobilization phase, the final phase of the CTEM methods, includes defining the scope of the enterprise, setting aims and objectives, recognizing key stakeholders and resource requirements to support the effort, and, most efficiently, conducting an accessible assessment to determine the management’s current level of cybersecurity and exposure organization maturity.
1. Identify Scalability Issues
A scalable infrastructure needs to divide work across many threads to benefit all the CPUs of a physical or virtual machine. All CPUs would perform code all the time and never be idle. Locking is the weakness heel of any multi-threaded infrastructure. Many systems don’t scale in a direct trend because they need to collaborate work across many threads. More work means more integration and more locks, which means less code performed at any given time. Continuous thread evaluation enables you to recognize such behaviour automatically. Simply filter the thread group list by the locking thread state.
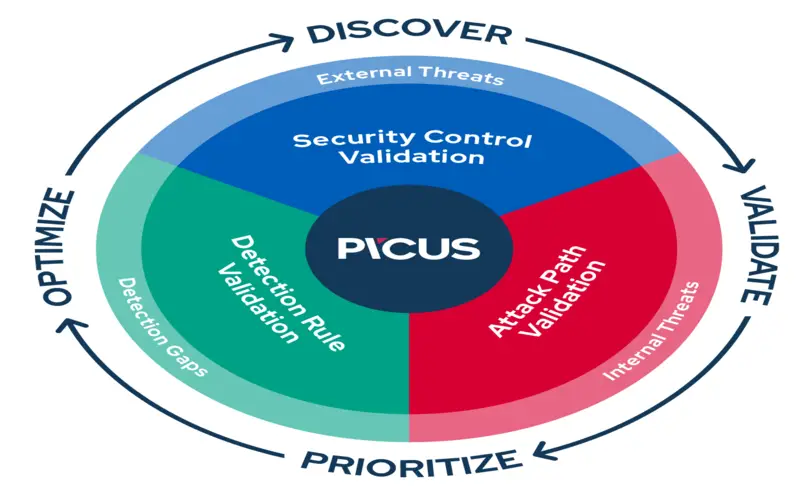
2. Prioritize Threats
CTEM helps organizations prioritize threats according to their potential companies’ effects. It enables organizations to analyze the severity and damage potential of every danger and then assign resources accordingly. It authorizes management security teams to not only prioritize more essential risks but also use resources more proficiently and respond more quickly to the most potential detective threats.

3. Augment Cyber Resilience
Management implanting a CTEM program consistently evaluates and enhances their defense. This type of repetitive refinement results in more robust cyber resilience since management can draw resolution from every assessment and then accommodate the military accordingly.
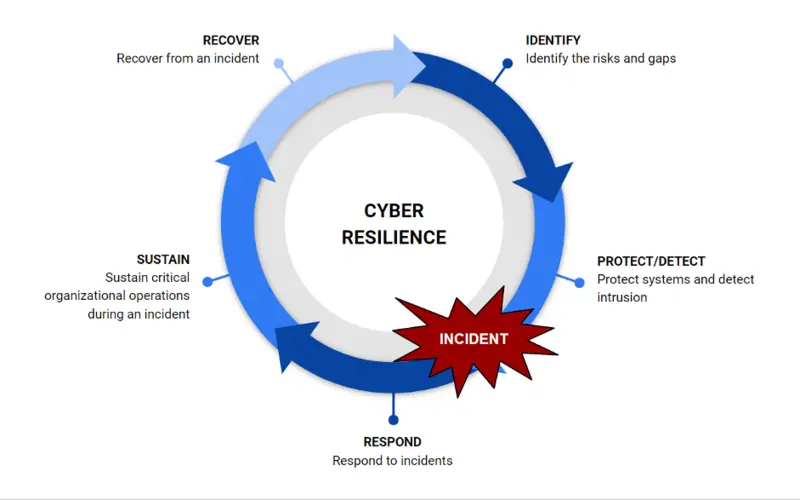
4. Improved Adaptability
CTEM programs are naturally adaptive, helping companies respond to occurring or evolving technology and cyber threats. It ensures that security is continuous and relevant, which is crucial in a quickly changing digital landscape.
5. Detection Perspective
It frequently degrades itself to a minor role, presuming attacks are approaching and formulating methods for countering them during or after attacks. Resisting is a monumental challenge, given the fantastic diversity in attack strategies, resulting in an almost certain oversight. Detection is minor, while the whole industry is focusing on detection.
6. Encrypt Your Data
Encrypting your data can be an efficient security strategy in case of data leaks. For example, a hacker holds the company’s data but it’s encrypted. Unless the attackers get encryption access from you, they cannot authorize your company’s data. It adds an extra layer of security in addition to the everyday cybersecurity best practices that you should obey in your business. Make an essential point to encrypt all your data, in a crucial case.
7. Limit Authorizes To Critical Data
Try to limit authorization for critical and sensitive data to lesser workers by basing access on job duties or needing approval for access, making it various steps to process it. Frequently review who has granted what data to ensure no overinvestment of access.
8. Analyze Your Security Posture
Organizations can efficiently organize their protection posture and minimize the likelihood of a violation by consistently observing and enhancing the security posture around quickly reacting to potential threats after they have occurred. Executing a CTEM program needs a dedicated team of security experts with the skills and professionals to manage the program effectively. Management running a CTEM program should also have the required tools and technologies to support the program. It may involve network scanning tools, penetration testing tools, and loopholes management tools.

9. Proactive Risk Organization
CTEM program assists management in proactively addressing loopholes and threats by consistently observing and evaluating their digital structure. Overall, cybersecurity shifts the focus from reactive to proactive, dominating a more robust military against cyber threats.

10. Actionable Perception
CTEM programs create actionable perceptions from actual time threat data. This perception can assist organizations in implementing efficient curation measures. CTEM’s data-driven strategy ensures that strategies are based on the new threat intelligence, dominating more efficient and intended curation efforts.