Drought is the number one reason for agricultural loss globally and represents the greatest hazard to food security globally. Currently, plant biotechnology stands as one of the most promising fields with regards to growing plants that might be capable of producing excessive yields in water-restrained conditions. From research of Arabidopsis thaliana’s complete plant life, the primary reaction mechanisms to drought strain were uncovered, and more than one drought resistance gene has already been engineered into plants.
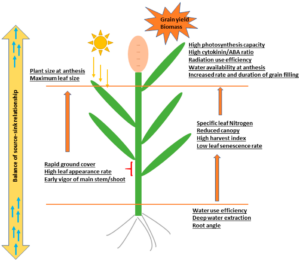
Major Traits Contributing To Drought Resistance
1. Early Flowering and Drought Escape
The molecular manipulate of flowering time is complex, and has been exceedingly studied in Arabidopsis in addition to in lots of different plant species. During the developmental transfer from the vegetative to the reproductive degree, the photoperiodic mild sign from the surroundings is perceived through leaves, wherein the FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) protein is synthesized.
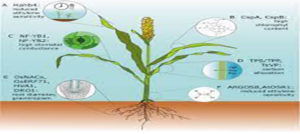
2. Leaf Traits: Senescence, Stay-Green, And Leaf Area
Senescence is a developmental degree of plant leaves that results in the arrest of photosynthesis, the degradation of chloroplasts and proteins, and the mobilization of nitrogen, carbon, and different nutrient assets from the leaves to different organs. As maximum cereals are monocarpic annual species, those assets are directed to growing seeds, and senescence consequently performs an applicable position in crop yield. Environmental stresses like temperature, loss of nutrients, and drought may provoke senescence prematurely, affecting seed dietary composition and crop yield.
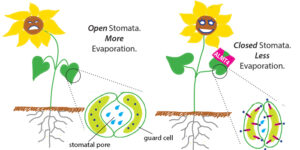
3. Stomatal-Mediated Drought Responses
Stomata, which might be openings at the floor of the aerial part of plant life, are enclosed through specialized protect cells that could open and near the pore through converting their turgor pressure. Stomata are essential for CO2 uptake in photosynthetic organs and are finely regulated through a molecular pathway that lets plant life accumulate CO2 at the same time as minimizing water loss. Manipulating stomatal quantity, size, and law became one of the earliest techniques followed by scientists in trying and producing resistant plant life, and the latest advances in Arabidopsis and plants to this impact are very well-reviewed in Bertolino et al., 2019.
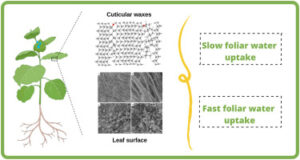
4. Cuticular Wax Production
Aerial plant organs have an outside cuticle layer of which waxes are a first-rate component. This hydrophobic barrier bodily protects the dermis towards a plethora of outside elements inclusive of UV mild, bloodless temperatures, fungal pathogens, and insects, and additionally regulates permeability and water loss.
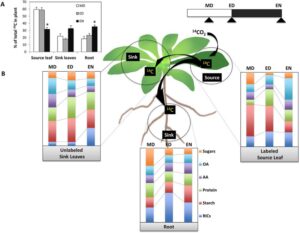
5. Carbon Allocation
Plants are photosynthetic organisms capable of restoring atmospheric carbon into macromolecules vital for boom and survival. Thus, it’s miles glaring that carbon metabolism and allocation are exceedingly regulated and this law has an essential position in plant resilience to stresses and crop yield. In cereals, carbon is the primary determinant of crop yield, and carbohydrates from cereals are the number one supply of energy within side the human diet.
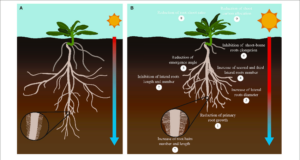
6. Root Traits
Roots are the primary plant organ devoted to the uptake of water and are the primary location wherein a loss of water is perceived. As such, an abundance of research has tested root responses to dehydration. The maximum applicable root developments able to enhance drought tolerance and their biotechnological programs have these days been reviewed through Koevoets et al. and Rogers and Benfey, respectively.
Challenges And Future Perspectives
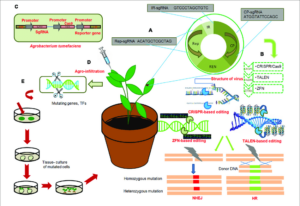
7. Genome Editing For Drought-Resistant Crops
During the beyond 10 years, genome modifying technology like zinc palms nucleases, transcription activator-like effectors nucleases, and homing mega nucleases have enabled scientists to supply focused genetic changes in organisms of choice. Innovative cloning procedures just like the Golden Gate machine made the meeting of those gear extra straightforward; however, genome modifying protocols had been nevertheless enormously time eating and exertions intensive.
8. Tissue-Specific Promoters To Drive Drought Tolerance
Basic plant technological know-how research, in addition to maximum conventional breeding and biotechnological procedures, are primarily based totally on loss-of-feature or gain-of-feature mutants, or at the constitutive expression of a gene conferring a sure trait. As an example, mutations within side the MILDEW RESISTANCE LOCUS O genes confer broad-spectrum resistance towards fungal pathogens to a big quantity of plant species inclusive of important cereals like wheat and barley. Similarly, Bt plants constitutively expressing bacterial pollutants from Bacillus thuringiensis are used international to guard plants against pathogens.
9. Cereal Transformation
With the extraordinary exceptions of rice and maize, for which transformation efficiencies can attain as much as 100% and 70%, respectively, plant transformation is notoriously tough in cereal plants and includes time-eating protocols that frequently want to be done through exceedingly professional technicians. Even while green protocols were advanced for the species of interest, excessive transformation performance is commonly restricted to only a few laboratory varieties.

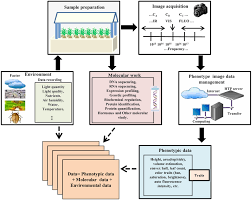
10. High-Throughput Plant Phenotyping For Drought Traits
Despite the sizeable quantity of facts that have been pronounced so far concerning drought in Arabidopsis, Bayer’s Drought Gard maize, Verdeca’s HB4 soybean and wheat, and Indonesian Perkebunan Nusantara’s NXI-4T sugarcane are the most effective biotechnologically advanced drought-resistant plants ever delivered onto the market.