In the socially growing world, smartphones are playing a vital role in human lives. For every month, we could see a new phone with advanced features release in the market. It is a common fact that one doesn’t like all the specifications of one particular phone. You may like the iPhone’s camera, Moto G4’s fingerprint sensor facility, the battery of Lenovo, etc. Google considering the above factors came up with this project ARA, named after one of its initiators. It is a project that allows users to build their own smartphone and customize it.

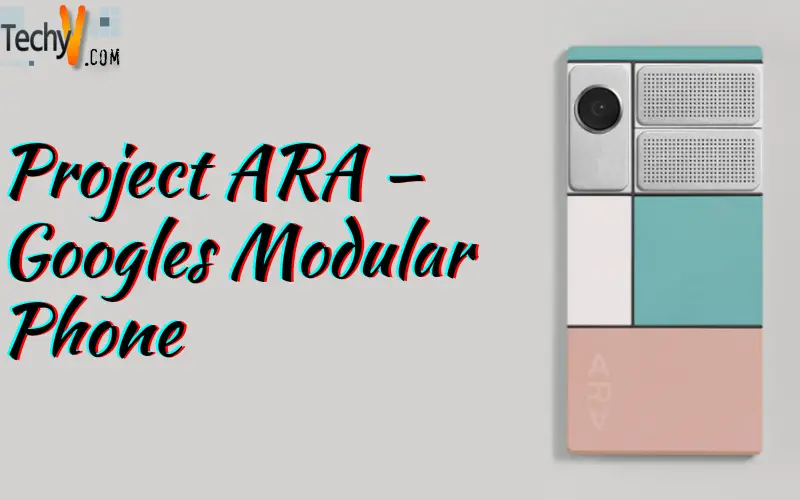
It was initially started in 2013 by the Advanced Technology and Projects (ATAP) group inside Motorola Mobility and aided by Google that was under the control of Regina Dugan (chief officer of the Project and former head of DARPA). The smartphone is a modular phone that consists of interconnecting parts called modules. A base frame (endoskeleton) has all these modules embedded in it that consists of slots for the modules with circuits and contacts. A Unified Protocol in short called UniPro technology interconnects the modules to each other that allows the faster communication with low power consumption between the blocks. There are six types of plug and play components as modules (processors, cameras, batteries, etc.). Each module slot is either in a rectangular shape (space for one module) or a square that allows two rectangular modules to fit in it.

HOW TO HANDLE MODULES?
The blocks are flexible to use, can add or remove them easily as you remove the SD card from the phone. An application helps the user in ejecting the module safely. The software called Greybus is used to swap and use the modules.
SECONDARY SCREEN:
One of the modules is a secondary screen, slotted at back of the phone. It is used as a display to possibly show the important information like weather or time or important dates. The technology behind this screen uses less energy and with greater visibility.

Battery Backup:
The framework provides the phone with a backup battery that will prevent the phone from dying while replacing the dead battery.
Toshiba and Miami-based phone maker Yezz are involved in this project in creating the modular components. The modules are of various types; the basic ones are a camera, battery, processor, etc. apart from these, can also design few specialized components that benefit gaming.
In the Google’s I/O conference 2016 (I/O stands for input and output and also represents a slogan ‘Innovative in the Open’), an announcement was made that a developer version of the ARA phone is released in the fall of 2016 and a commercial product in 2017. The curiosity of the users, as well as developers, had no bounds with that announcement, but it lasted no longer. The Reuters reported the suspension of Project ARA and Google did not want to comment about that. But there are few things that were the reasons probably for its suspension. Regina Dugan (chief officer of the project) left Google for Facebook. It was also not easy to produce the hardware. Since the actual reasons were not publicly stated, the death of the projects remains uncertain. It is also reported by the Reuters that Google may collaborate with other organizations or give the license to other third parties to work on a modular phone.
Coming to the concept of a customizable modular smartphone, the ARA is not the only project that worked on it but, a phone was released by LG (G5). It is also a modular phone with a battery as its module.

One must accept the fact that though the suspension of project ARA is done it gave rise to the conception of creating such customizable smartphones and there is no doubt that study was conducted to its fame and gave birth to a technology that one ever thought would be possible.