With the advancement in technology storing, retrieving and sharing the data has become facile. One can communicate with other regardless the distance. But there are a number of attackers interested in stealing our data. So there are obvious reasons to secure our sensitive data from the attacks.
The most common way the internet users use to secure their data is transforming the original data into an unreadable form. This method of protecting the information is known as Cryptography.
CRYPTOGRAPHY: A technique used to secure the data from attackers that converts the plaintext into cipher text (unreadable form). This conversion is known as encryption. The decryption is performed to get back the plain text and done only by the legitimate receiver.
WHY STEGANOGRAPHY?
Yes, the data is encrypted and cannot be read by the attackers, but there is no guarantee that the data is safe. It is because the data is converted to unreadable form but still exists as data. The existence of data is not hidden. And techniques can be implemented to hack this encrypted form too. Steganography overcomes this problem by hiding the presence of data.
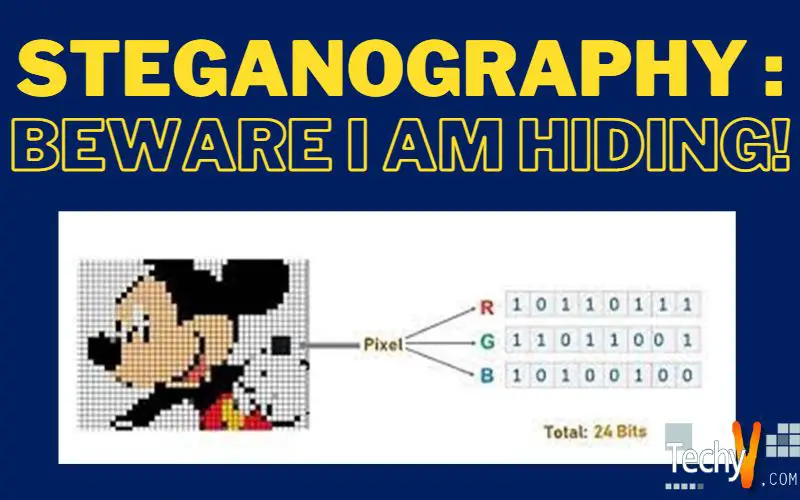
STEGANOGRAPHY: An art of hiding the information. Data of any form either an image, text file, audio or video clip conceals the data (plain text, image, audio, video or encrypted data). The attacker now does not know about the presence of data and is not easily hacked.
STEGANOGRAPHY à STEGANO means ‘concealed’ GRAPHEIN means ‘writing’.

HISTORY:
Steganography was first practiced during the Golden Age in Greece.
- According to the ancient records Greeks used to practice a method to communicate secretly about the rivals. It involves melting the wax on wax tablet and inscribing the message underneath the wax on the wood.
- Germans developed microdot technology in 1941. This technology doesn’t hide or encrypt the data, but the size of the message is so small that one cannot see.
- A very common and well-known form of invisible messages is writing a message using invisible inks and was in practice since World War-II.
STEGANOGRAPHY AND CRYPTOGRAPHY:
Steganography and cryptography can be combined to provide better security. A message can be encrypted using various techniques. In case if steganography fails and one found the hidden message, it is of no use as it is encrypted. The attacker must perform a number of different decryption techniques to retrieve the original information.
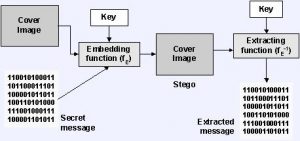
Cover Medium + hidden data + Stego key = Stego Medium
Cover Medium: Any form of data used to hide the data.
Hidden data: The data we are trying to hide
Stego Key: The key if the hidden data is encrypted
All the three combine to give the Stego Medium which looks like the cover medium itself.
STEGANOGRAPHY METHODS:
There are various methods used to perform steganography based on the type of hidden data.
- TEXT STEGANOGRAPHY: The text format is altered.
- Line shift coding: Vertically shifts the text lines of the document.
- Word shift coding: Shifts the text lines horizontally.
- Feature coding: Applied to either format file or bitmap image.
- IMAGE STEGANOGRAPHY:
The most common type of steganography performed is hiding the data in an image. The image may consist of noisy areas, and we hide the data in such parts without altering its properties.

- Least significant bits: A most common technique used.
Embeds the message in the least significant bits of the cover image. This method doesn’t result in any visual difference of the image because the amplitude of change is less (since, LSB).
Let us take an image of 24bit color (9 bytes of data with each bit of RGB components). Store 3 bits in each pixel.
10010101 00001101 11001001
10010110 00001111 11001010
10011111 00010000 11001011
Let us imagine that we want to embed ‘B’ in the image. The binary value of B is 10000010. After embedding, we can see the change in LSBs (can be seen in bold):
00100111 11101000 11001000
00100110 11001000 11101000
11001001 00100110 11101001
- Masking and filtering
- Transformations
- Audio Steganography: In this method, the message is embedded in an audio file that results in an audio file whose binary format is slightly varied.
- LSB coding
- Phase coding
- Spread spectrum
- Echo hiding
STEGANALYSIS: A process similar to cryptanalysis that detects the steganography by checking the changed bit patterns is known as Steganalysis.
APPLICATIONS:
- Digital Watermarking: The content owners wish to protect their content from piracy. This protection of identity is known as watermarking and can be done using Steganography. There are two types of watermarking, they are:

- Visible watermarking: As the name suggests the message is visible on the cover image ex: Logo, copyrights, etc.
- Invisible watermarking: Unlike the visible watermarking the embedded information is not visible.
- Confidential communication
- Secret data storage
CONCLUSION: Steganography is a technique used to protect our data from attackers and is neither good nor bad but depends on the way we use it.