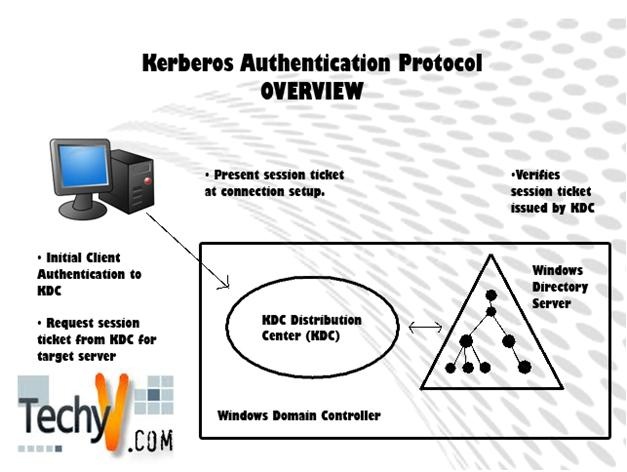
Zero Trust Security System is built on the idea of “no trust, always verification,” which seems to be favored by IT security specialists around the world. With the increasing number of endpoints due to remote work, most companies look for ways to implement this model.
However, one question comes to mind; how can companies create a Zero Trust model? This is one of the newest systems in cybersecurity, and its implementation can be tricky for most. That’s why we listed several steps of Zero Trust adoption that’ll help you out.
About Zero Trust Security System
Let’s define the general principles of the Zero Trust model to give you an overall idea. Zero Trust Security was first announced by John Kindervag in 2010 as a measure for the growing demand for cloud services and remote work.
In the Zero Trust model, authentication is mandated to every user whether they’re within or outside the network. In addition to the verification process before going into a private network in traditional security models, Zero Trust constantly monitors and asks for verification from the network users.
This verification-based approach is where the model takes its name from. Conventional security approaches believe the users inside the private network are trusted, but Zero Trust understands the insider threats and takes precautions.
The Zero Trust model can use several verification methods to validate users. One advantage of this model is the ability to verify remote users. Since this is mostly done via the cloud, locations and connections are not significant and the network can be protected no matter what.
Five Steps Create A Zero Trust Security System
1. Identify Allow Listed Users And Tools
Your employees are the ones who will be using this system. They’ll be asked for repetitious verification and you need to make sure it doesn’t interrupt their work.
That’s why you need to carefully assess the permissions of each user, and be more careful when preparing the system for remote users. You can use identity and access management tools to specify users and tools trying to access the network.
Whatever you do, guarantee a good user experience for the end-users and tools that will be included in the Zero Trust security model. If you assess the individual permissions by identifying the users, the rest will be much easier.
2. Specify Protection Policies And Segment Networks
Companies need to specify the protection surface in order to have a functioning Zero Trust model. The attack surface needs to be defined and certain policies have to be put in place. These may include layered access levels, network segmentation, or specific verification methods.
IT professionals believe that network segmentation is your first line of defense. This is the process where you can enable access levels for each employee and operate enhanced verification checkpoints. Segmenting networks also allow you to protect the most sensitive data from insider threats and data breaches.
3. Architect Your Zero Trust Model
After you identify the end-users and put in protection and access policies for each category of data, you need to design your Zero Trust model. Since Zero Trust is mostly operated on the cloud, VPN providers can take care of the architecture for you.
You can always design yours if you have a dedicated IT security team. But if you want to leave the job to the professionals, choose a reliable VPN provider. They are also able to provide the necessary security services so you don’t have to look for them in other places.
If you’re looking for a provider suggestion, check out NordLayer Zero Trust (https://nordlayer.com/zero-trust-security/). The best thing about NordLayer’s Zero Trust service is the experienced security team and continuous customer support throughout the service.
4. Monitor Your Network Frequently
Most of the maintenance will be taken care of if you get help from VPN providers, but you need to monitor your network. Zero Trust is already a great model to increase visibility, so it’ll be easy to track logins and data usage to gain insights.
Frequent monitoring will also help you understand the needs of the end-users, change architecture according to these needs, and ensure flawless security overall.
Don’t skip this important process before you have an up-and-running system, it’ll make sure the Zero Trust is functioning correctly.
Conclusion
It looks like Zero Trust will dominate other cybersecurity practices considering the significantly popular adoption of the model. You need to make sure you’re not left behind.
But creating a Zero Trust Security System might be more complicated than you think. Learning the right steps will both facilitate the process and guarantee a properly working Zero Trust model, so you must follow these steps.
We suggest you put great effort into these points so you can have peace of mind on cybersecurity afterward.