What is Telnet?
To better understand Telnet, it is a client program that enables the programs to be run remotely as well as facilitate remote administration. This is found in almost all operating systems such as Telnet for Windows XP and even in Macintosh operating system. Telnet helps the integration of many computers and applications in a certain networking environment.
Just like TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), Telnet is also one of the protocols used to let users connect to the Internet so that network of computers can be utilized. Telnet is important in networking as it serves as the medium in the utilization of online applications such as yahoo messaging, Skype video chatting, and a number of programs on the Internet.
Note, Telnet server is able to pass the data on to several processes which includes the log-on server. These data may refer to files or information that came from or received from client programs.
On the part of the client, communication is made possible via TCP/IP and based upon the NVT of Network virtual terminal. The program called Telnet translates the codes of Network Virtual Terminal into a set of codes that it can be understood by the client program. The telnet also converts the keyboard codes produced by client programs into NVT outgoing codes.
The NVT is using 7-bit codes for all characters. The Telnet as well uses RFC in displaying the standard ASCII characters. These characters are represented by 7-bit codes. The RFC is also used to process and recognize control codes. Note, NTV is used by several Internet protocols such as SMTP and FTP.
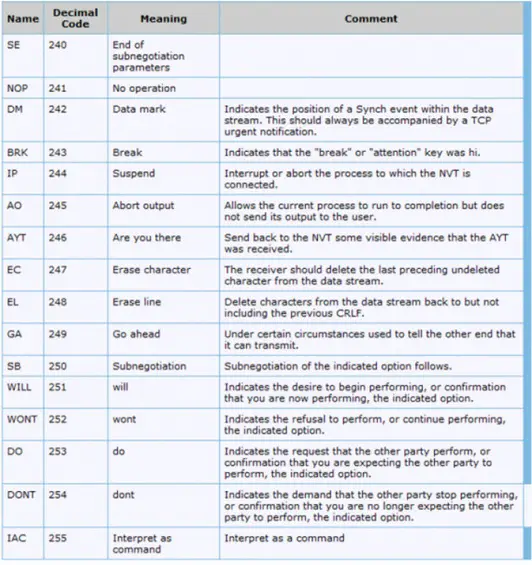
Important codes required to be interpreted by NVT are NULL, CR, LF. NULL means ‘no operation’, CR means that printer is moved to left of margin of current line, and the LF means printer has to be moved to next line but keeping the horizontal position. NULL stands for NULL, LF stands for Line Feed, and CR stands for Carriage Return.
In order to control the connections between server and client, there is a need for telnet command to be used by Telnet protocol such as the following:
History
In March of 1973, Telnet used to be an ad-hoc protocol without an official name or meaning. It used to be an 8 bits channel in exchange of 7 bits ASCII codes. Any higher bytes are considered special telnet characters. In the same year, the UCLA defined the Telnet Protocol and published two documents: Telnet Option Specifications (NIC # 15373) and Telnet Protocol Specifications (NIC # 15372).
How to activate Telnet?
In order to use the Telnet, there important data that needs to be secured such as the password, username, and IP address. For users of Windows PC, telnet can be run by first clicking on the windows start button, then choose the ‘run’ window, key in the word ‘Telnet’, and the particular window will pop up. Then, ‘Remote System’ option must be selected from a drop down menu and key in the address of all remote computers. Note, Telnet can only be accessed if Internet is available. You will then be asked to supply your username and password. Log-in and the computer being used becomes the terminal machine and online resources can now be accessed. The ability of the terminal machine to access information and other online resources is due to the optimal characteristic Telnet to locate information from the Internet.
For those users of Windows XP, there is a slight difference in activating telnet. This is done primarily by hitting the windows start button, when a window pops up, type is the word ‘run’ and this shows the window for Telnet. Following the steps mentioned, this should give you a prompt such as: Microsoft Telnet>. In trying to connect a remote computer, key in: open site name. After connecting the remote computer, you may close the window by keying in “quit”.
The following program codes can be run on Telnet for Windows and UNIX systems starting with sfuclnt until sfucrvr.