Many computer users trying out Linux do so because they have been told that the operating system is more customizable and uses fewer system resources. However, even though you install Linux on your computer and reap those benefits, you may still feel like your system can still use an accelerator to speed it up – even if you use a high-end machine. Here are ten ways that you can follow quickly and easily speed up your system to get the best performance possible out of it.
1. Reduce Grub Time
If your Linux system uses Grub as the boot loader, you will find that it will display the GRUB boot loader in ten to thirty seconds. Did you know you can reduce the bootloader’s duration or skip the countdown altogether? Open the terminal and type “/etc/default/grub” to open the file in a text editor. Look for the GRUB_TIMEOUT variable and replace its value with 5 or 3. You can also set t to 3 to disable the countdown. Run the file after saving it.

2. Reduce Start-Up Application
If you feel your system has become slower after installing a bunch of programs, you may need to go through the list of start-up applications. The location varies between desktop environments, but Ubuntu users can open the Dash and type “start-up” to find the Start-up Applications program. Then uncheck the apps that don’t necessarily run when you first log in. Again, this is only useful if you have multiple programs installed – the list will be empty after a fresh install of the operating system.
3. Disabling Special Effects And Features
A handful of desktop environments (KDE and GNOME in particular) want to add a desktop effect to your desktop experience. However, if your system has been running slow since you installed the operating system, you can disable some of them. Ubuntu users should install the CompizConfig settings manager to change desktop effects, GNOME users should force fallback “Classic” mode, and KDE users should check their system settings for Effects on the screen and turn them off. Another special note for KDE users: Turn off Nepomuk.
4. Reduce Overheating
Overheating is a very common problem in computers these days. The overheated computer runs very slowly. It takes years to open a program when thermal throttling affects your system. There are two tools that you can use to reduce overheating and thus achieve better system performance in Ubuntu, TLP, and cpufreq. To install TLP and CPUFREQ, follow the command: Restart your PC and use the power save mode in it.


5. Check For Unnecessary System Services
Keep in mind that not all applications your machine runs at start-up are immediately visible without first running the following special command from your terminal:
sudo sed -i ‘s/NoDisplay=true/NoDisplay=false/g’ /etc/xdg/autostart/*.desktop
After doing, you will see quite a lot more in start-up applications than you did before, including system services. You can change these if needed.
6. Lightweight Desktop Environment
Another easy speed improvement you can make comes from optimizing your desktop environment. This option also has some interface changes, so it might not be suitable if you prefer your current setup. If you’re ready for a change and up for the pace, this can work very well. There are a few desktop environment options that intentionally emphasize speed above other factors.
- Xfce
- LXDE
- KDE
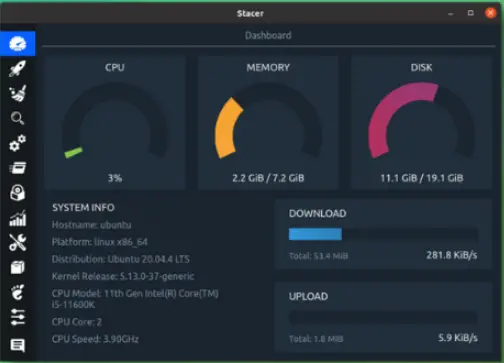
7. Use A System Cleaner App
If cleaning up your system takes more effort than expected, you can try using system optimization apps like Stacer. It can help you clean junk files, manage the start-up process, monitor system resources and let you do many things from a single application. With all the features available, you can end up with a well-functioning Linux system.
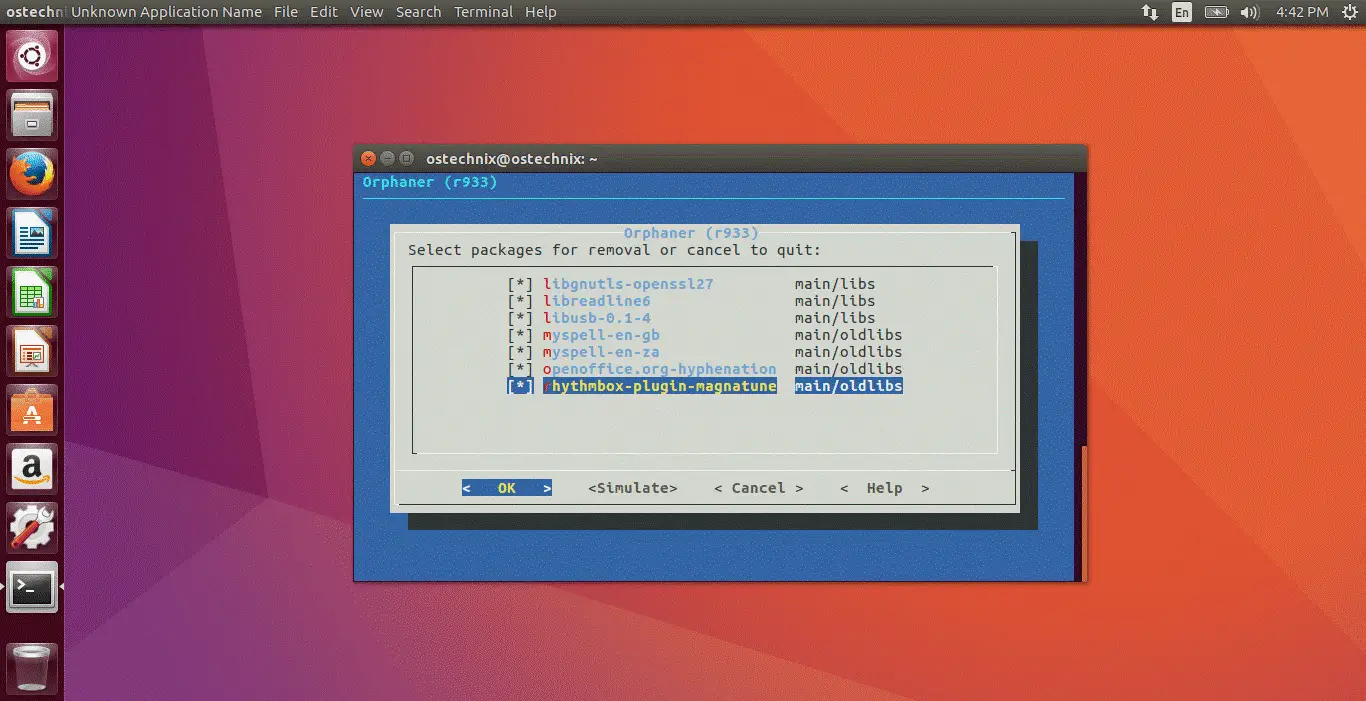
8. Uninstall Unnecessary Software
Of course, it’s fun to install a variety of software to enhance the desktop experience. However, we often forget to remove them from our system even when we stop using them. Therefore, you should get in the habit of regularly evaluating installed software and removing unnecessary software based on your current needs.
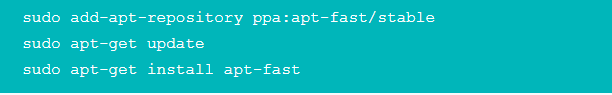
9. Use Apt-Fast Inplace Of Apt-Get For A Quick Update
Apt-fast is a shell script wrapper for “apt-get” that improves package download speed and updates by simultaneously downloading packages from multiple connections. If you often use terminal and apt-get to install and update packages, you can try apt-fast. You can install apt-fast via the official PPA using the following commands:
10. Using Lighter Alternatives For Some Applications
Some default or popular applications consume a lot of resources and may not be suitable for older computers. What you can do is use alternatives to these apps. For example, you can use App-Grid instead of Ubuntu Software Centre or Use Gdebi to install packages. You can use AbiWord instead of LibreOffice Writer, etc.



















