New advances in food technology indicate a move towards individualized and sustainable food options. Alternative protein sources, regional cuisines, nutraceuticals, and individualized nutrition are a few of them. FoodTech firms and brands are incorporating waste reduction techniques and zero-waste processes due to environmental concerns. Additionally, the COVID-19 epidemic strongly influences Industry 4.0 technology adoption across the whole food value chain and raising food quality. With the use of robots, eCommerce, and electronic food management technologies, food companies are digitizing their manufacturing lines. Additionally, restaurants are pushing eCommerce and using robots to serve customers and prepare food. The food business is employing all of the aforementioned techniques to combat the COVID-19 situation’s ongoing effects to run effective, open, and sustainable operations
1. Alternative Proteins
One of the most noticeable developments in food technology is that consumers are moving away from traditional protein sources owing to environmental and health concerns. The main sources of alternative protein include cultured meat, lab-grown food, plant-based nutrition, edible insects, and mycoprotein. Unlike protein from cattle, they are not only nutrient-rich but also require fewer resources from farm to fork. Since alternative protein sources only need minimal dietary changes and health monitoring, they lower total expenditures. Startups can create viable alternatives to traditional protein manufacturing methods thanks to developments in 3D printing, fermentation, and molecular biology. This helps food firms balance out the moral dilemmas and environmental impact of industrial meat production.

2. Nutraceuticals
Concerns about how eating habits affect health are growing, as is the demand for vital nutrients for leading a healthy lifestyle. Nutraceuticals are a leading trend in the food market as customers focus more on eating healthily as a result of the COVID-19 epidemic. This is a key factor in generating demand for nutraceuticals. These include dietary supplements, therapeutic foods, functional foods, and foods that improve the gut microbiota, such as prebiotics, probiotics, and postbiotics. Numerous nutraceuticals are believed to have health advantages against oxidative stress-related conditions like allergies, Alzheimer’s, diabetes, and immunological illnesses, according to scientific studies on the subject.

3. eCommerce
For a time now, the food and beverage business has been focusing on eCommerce. However, the COVID-19 crisis encouraged even further improvements to food supply systems. Digital platforms are used by food manufacturers to provide on-demand online delivery services and direct-to-customer (D2C) distribution strategies to reach consumers. Additionally, the rise of “ghost kitchens” or “cloud kitchens,” which solely provide takeaway and delivery of meals, is being fueled by safety concerns during the epidemic. In addition to direct-to-consumer marketing, firms are concentrating on omnichannel distribution to boost customer satisfaction and revenue. Additionally, food makers may better contact their clients and guarantee supply thanks to food & beverage eCommerce.

4. Food Safety & Transparency
Given that people are growing increasingly picky about the quality of the food products they buy, food safety is a key concern. Thanks to the availability of smart labelling and independent food grading technology, customers can choose food products with ease. Thanks to advancements in blockchain technology and real-time food monitoring using Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, food firms may now offer end-to-end traceability. Startups are improving food safety and transparency by creating scalable and affordable monitoring tools. In turn, this enhances sales and brand reputation by increasing consumer and food producer trust.

5. Personalized Nutrition
The need for personalised nutrition solutions is being driven by consumers’ growing nutrition knowledge. They also include dietary preferences such as sugar- and gluten-free eating regimens, vegan diets, and clean-label food products in addition to nutrigenomics-based diets. Food manufacturers may now provide nutrition customization on a large scale thanks to the incorporation of robots into food production lines and advancements in 3D printing. Additionally, customers may choose eating patterns that best match their genetic profiles thanks to at-home blood and urine testing kits. To optimize their diet, individuals may track their diet and health issues using a variety of tracking devices. As a result, customer convenience and sales are increased since it gives consumers control over their dietary choices.

6. Restaurant Digitization
Restaurant digitalization improves customer experience and facilitates efficient administration of operations. Additionally, it enables data-driven decision-making across operations by enabling restaurant companies to collect data points at each stage. Additionally, COVID-19’s impact on the food and beverage sector is forcing a change in the way restaurants are embracing digital management systems throughout the supply chain. Restaurants include computerized menus, self-service kiosks, and cashless payment options to lessen the direct human touch. Additionally, emerging solutions for aiding consumers with meal orders and other restaurant-related questions include chatbots and speech bots. AI-enabled solutions provide culinary suggestions to consumers and create new recipes using data on customer preferences and behavior.

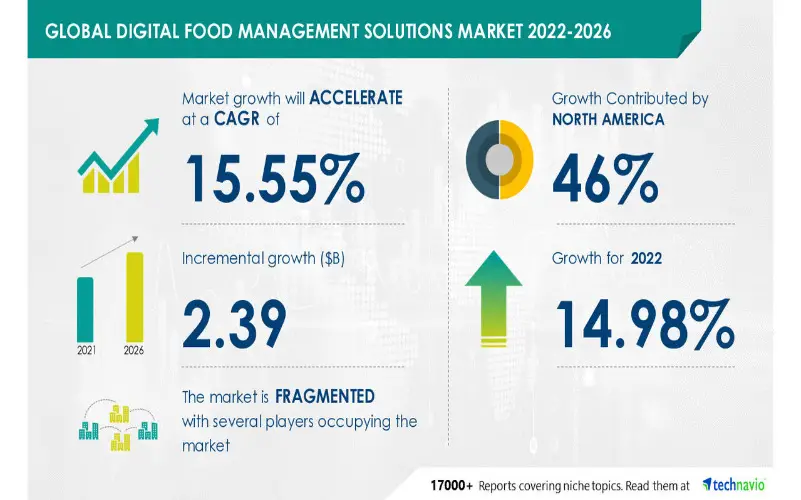
7. Digital Food Management
Digital food management from farm to fork is made possible by big data analytics, artificial intelligence, and real-time monitoring. Startups create food management systems to streamline production procedures and supply chain management. Additionally, customer behaviour research and demand forecasts based on consumer preferences are made possible by restaurant digitalization. Together, these options help farmers manage losses and surplus food by helping them comprehend market demands and anticipate interruptions. Startups, for instance, may effectively mimic market swings and analyse major disruptions like pandemics, thanks to quantum computing. Additionally, customer and market knowledge enables businesses to enhance their marketing plans and successfully target the right audience, which increases revenue.
8. Food Waste Reduction
Food that is produced across the world is wasted or lost in large amounts. So, if we’re going to fight food poverty, cutting down on food waste is crucial. Major businesses and food entrepreneurs are now concentrating on reducing food waste in order to save money and lessen their environmental effects. Restaurants, food producers, and smart cities may reduce food waste with the use of solutions for food monitoring. Additionally, there has been a paradigm change in the food processing industry from waste reduction to zero waste methods. To create value and broaden their appeal to customers who care about sustainability, food firms are repurposing and upcycling food waste. For instance, food waste in restaurants and other food outlets is reduced by 3D food printing technologies that employ food waste to manufacture edible food products.
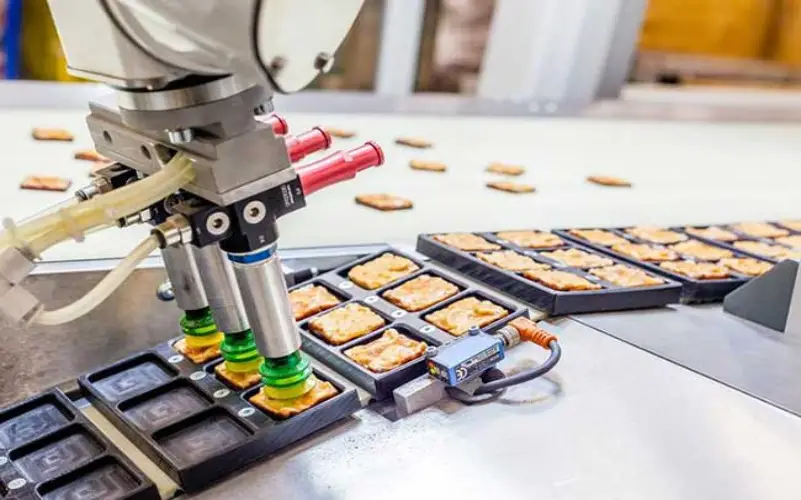
9. Robotics
The value chain for food and drink uses robotics to improve manufacturing uniformity, scalability, and efficiency. Food industries increasingly utilize hospitality robots in hotels and restaurants to improve client comfort and safety. Food robotics is a major development in food technology, and robotic chefs and food processors are helping to drive it. Autonomous drones and trucks are proving to be cost-effective alternatives to manual delivery services.

10. 3D Food Printers
Personalized diets, alternative protein-based meals, and accurate and repeatable nutrition are all made possible by 3D food printers. Although material extrusion is the most popular way of printing food, entrepreneurs are increasingly adopting laser, inkjet, and bioprinting techniques to create food items. These methods emphasize improving the accuracy and quality of food products produced through 3D printing. More study is being done on 3D food printing for large-scale food production because food businesses require items with exact specifications and reproducible quality.



















