So, let’s start with knowing what network security is. Network security is a technique or measure that is taken by an enterprise business or organization to secure its system networks and data using software and hardware implementations. Network security aims to secure data and network by maintaining confidentiality and accessibility of secure data and network. A basic example of network security could be password protection, which is chosen by users. Network security provides solutions to protect data, users, location access, devices, and application access. Network security has become a similar topic as cyber security, and companies are willing to hire more professional engineers in this field. So now, let’s look at the top 10 advances in network security that safeguard our data and information.
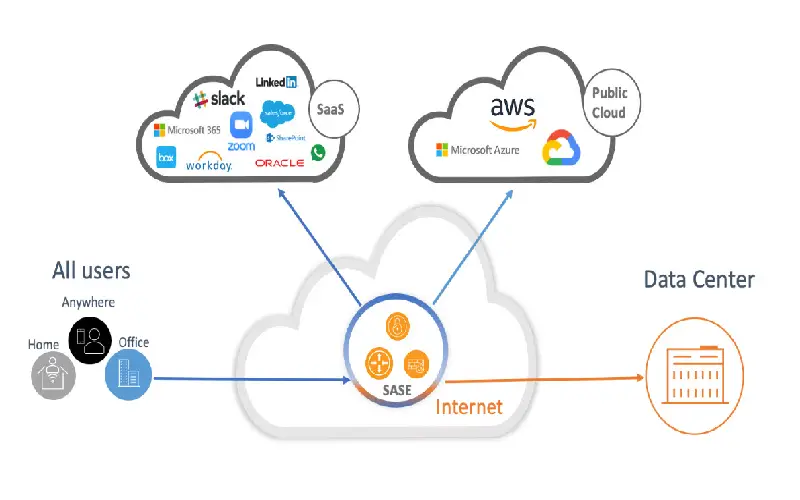
1. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
Secure access service edge is an architecture that provides cybersecurity-grade advanced protection to the farthermost edge of the network. This architecture provides the user with robust security features to their devices directly from the cloud, making connections secure from any and everywhere. SASE architecture provides direct cloud security in user devices such as laptops and smartphones so, users don’t have to worry about latency issues while connecting. SASE consists of several functional components such as cloud-hosted security, FWaas (Firewall-as-a-Service), secure web gateway (SWG), cloud access security broker (CASB), and other traditional components such as authentication, authorization, and control, etc.
2. Quantum-Safe Cryptography
Quantum safe cryptography is a technique that secures sensitive data, access, and communication of data. This is made possible by using cryptography in almost everything a computer has. Modern cryptography is so good that whenever a system or data is leaked or hacked, it’s because of some human error, such as sharing the password accidentally or leaving the backdoors to systems (access point used to gain access over some network or system). These are so secure that most intruders can’t access your data, read your email, or post from your social media account.

3. Threat Intelligence Sharing
We can only protect things that we can see. Companies like Fortinet, McAfee, Symantec, and Palo Alto Networks started the cyber threat alliance (CTA) and provided intelligence and technology to security professionals that they needed to identify any attack. Threat intelligence sharing aims to collect data from multiple sources and then process it to correlate to get the most valuable form of data present. CTA has expanded and successfully protected organizations from around the world. Any organization around the globe can gain benefits by participating in collecting, processing, and sharing threat intelligence.

4. AI And Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and Machine learning in networks are becoming more and more critical as networks are becoming complex and distributed across ranges. Using AI and ML improves troubleshooting problems, issue resolution, and guidance on how to tackle issues. AI ML helps find solutions to real-time problems as well as predict future issues that can occur. Using AI and ML analytics and crowdsourced data, it’s easier to reduce unknown issues and improve decision-making while tackling problems.

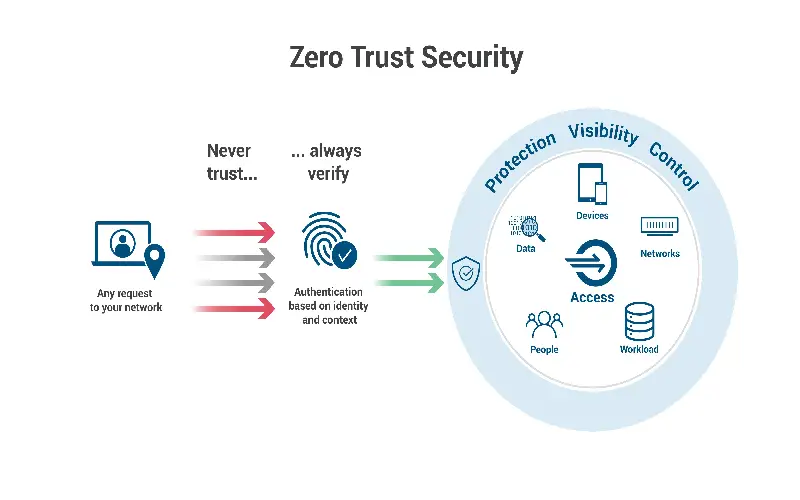
5. Zero Trust Security
The zero trust security model is one of the most well-known models in cyber security and network security. The zero trust security model aims to work on a few network security perimeters, open and flat networks, minimal threat protection, static traffic filtering, and unencrypted internet traffic. It focuses on network segmentation, threat protection, and encryption. Zero trust security believes in least privileged access, explicit verification of user, and assuming a breach has already occurred.
6. Cloud Network Security
Cloud network security is the term for protecting public, private, and hybrid cloud networks by technology, policies, controls, and processes. This helps cloud networks from unauthorized access, misuse, exposure, or modification. Cloud network security is one of the primary layers keeping the cloud secure. Cloud network security provides policy-based security, automated monitoring, threat prevention, and more.

7. Endpoint Detection And Response (EDR)
EDR also referred to as EDTR (Endpoint detection and threat response) is an endpoint security system that monitors user devices to detect and respond to threats such as ransomware and malware. EDR tool provides incident data search, threat alert, activity validation, threat treatment, and threat containment. A few essential functions of EDR are the automatic uncovering of attackers, integration with threat intelligence, and providing real-time and historical visibility of threat data.
8. Multi-Factor Authentication
Basic password-based security has become old and is easy to crack. Organizations store a lot of customer data, which involves risk and the need for more security. Authentication based only on username and password is no longer reliable and secure. On top of that many people reuse the same password across various platforms. That’s why the use of multi-factor authentication is important, and as the name suggests, it means using several different layers of protection whenever a user logins. MFA includes authentication based on biometrics (fingerprint or face scan), with new technologies that use GPS, cameras, and microphones for authentication. Single-tap login allows the user to get push notifications that only require a single tap from the user’s smartphone, enabling user login in other devices.

9. Blockchain For Security
Blockchain is a simple set of blocks, in which each block contains information related to transactions, identifying hash, etc. Companies use Blockchain as it is convenient and can perform transactions from any time and anywhere. It can also help in rapid size and scale increases. Blockchain users should be verified before gaining access to its features all transactions inside the business are validated by business users.

10. Container Security
Containers are dedicated virtual machine that hosts or run the applications. Container security is a term that comes under DevSecOps, and there are many layers of security in a container, such as a container image, the interaction between the container, host machine, operating system, and runtime environment (in Kubernetes cluster). There are several container security ecosystems in the market a few of them are Docker container security, Kubernetes container security, GKE (Google Kubernetes Engine), AKS (Azure kubernetes service), and EKS (Amazon Elastic kubernetes service).



















