The BioTech sector implements automation, data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) trends to maximize productivity. As a result, consumer biotechnology and products marketed to consumers rather than biopharmaceutical or healthcare companies have increased. While businesses are working on solutions ranging from food and materials to environmental monitoring, the industry is still primarily focused on healthcare. With startups and businesses biomanufacturing fast diagnostic kits repurposed medications, and vaccinations, the COVID-19 pandemic clearly emphasized the industry’s broad influence.
1. Artificial Intelligence
Startups in the biotechnology industry can scale up their operations by automating a variety of procedures thanks to AI. For example, AI is used by biopharma startups to expedite the medication discovery process by screening biomarkers and scouring the scientific literature for novel medicines. Image classification algorithms enable the quick identification of many qualities, such as the detection of cancer cells in medical scans or the symptoms of crop diseases in leaf photos. Startups also use deep learning to filter phenotypes, study microbiomes and create quick diagnostics.

2. Big Data
Due to the development of omics technologies, the incorporation of sensors, and the Internet of Things (IoT) devices, there is currently an unprecedented amount of data available in biotechnology. Startups in the biotechnology industry may use this vast amount of data to fuel innovation thanks to big data and analytics tools. It makes it possible for biopharmaceutical companies to find participants for clinical trials. Startups and businesses use bioinformatics tools to improve crop and animal types, create a better feed, and look for unknown bacteria.

3. Gene Editing
The precise editing of genomes through genetic engineering has advanced dramatically from the time when foreign DNA was randomly inserted. Because of the invention of synthetic nucleases and, more recently, CRISPR, as molecular scissors, gene editing has become more effective. By using gene editing techniques to add, replace, or silence specific genes, gene therapy can now be used to treat both hereditary illnesses and other conditions. Better transgenic plants and animals can be created thanks to targeted gene alteration.

4. Precision Medicine
Gene editing and gene sequencing are used increasingly frequently in clinical practice due to their decreasing prices. It makes precision medicine possible, enabling doctors to choose the preventive and therapeutic measures that will be most effective for a specific population. Additionally, it makes it possible to treat various illnesses, including cancer, with individualized care. Biotechnology entrepreneurs use precision medicine to find new medication targets, find innovative pharmaceuticals, provide gene therapies, and create new drug delivery methods.

5. Gene Sequencing
Since the early 2000s, DNA sequencing prices have decreased by five orders of magnitude, enabling a variety of new uses for the technology. The decreased cost of whole genome sequencing is made possible by the ability to identify pediatric illnesses, create individualized treatments, and set up sizable cohorts with in-depth phenotyping. Additionally, sequencing offers a quick and affordable way to identify the presence of microorganisms, including pathogens in dairy and clinical samples and beneficial soil bacteria. Biotechnology startups are developing new sequencing methods and creative uses for gene sequencing.

6. Biomanufacturing
Biomaterials, food & drinks, specialty chemicals, medical devices, and medicines are all produced using biological systems through biomanufacturing. To make biomanufacturing affordable and scalable, startups are expanding various cell culture, fermentation, and recombinant production technologies. Compared to conventional manufacturing paradigms, it is also significantly more sustainable due to utilizing biological raw materials. Automation and machine learning are also incorporated into the industry’s manufacturing methods. Biotechnology entrepreneurs provide bioprocessing 4.0 to optimize each stage of the production process by integrating Industry 4.0 models.
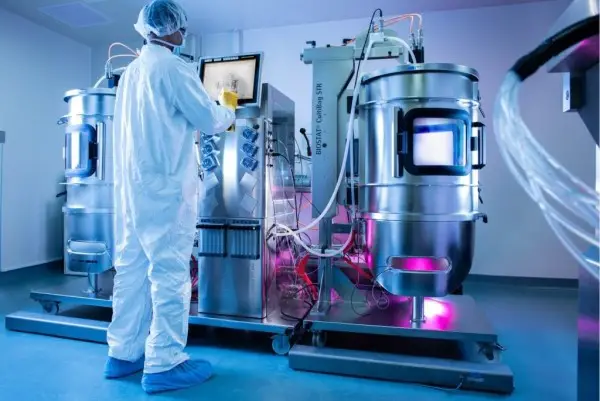

7. Synthetic Biology
A previously unheard-of capacity to read and write genomes enables biotechnology startups and established businesses to produce products more quickly than ever. Synthetic biology also permits modifying organisms at the level of gene networks, increasing standardization and repeatability. Startups in synthetic biology tackle problems like computational drug design, cellular agriculture, and microbiome-based remedies. Bacterial cell factories produce beneficial biochemicals in large quantities for use in pharmaceutical, material, and food applications. Startups are creating human synthetic biology solutions in addition to solutions for bacteria.

8. Bioprinting
Bioprinting firms now provide a wide range of materials and products thanks to the emergence of additive manufacturing in biotechnology. These startups use bioprinters that use bio-inks made of bio-based or biomaterials. Cells serve as substrates and develop around a scaffold in medicinal applications. This makes it possible for personalized medicine to create bone, skin, or vascular grafts using the patient’s cells. Other startups use bioprinting for quick prototyping and the creation of biopolymers.

9. Microfluidics
The demand for lab-on-a-chip (LOC) devices is the driving force behind the interest in microfluidics in the BioTech sector. These compact labs make point-of-care (PoC) diagnostics easier by enabling quick, low-cost testing for infectious diseases. Startups are also creating paper-based microfluidics for environmental monitoring and diagnosis. Organ-on-a-chip (OOC) devices that imitate the physiology of organs or organ types on tiny chips are where the technology finds more biopharma applications. OOC systems are used in disease modeling and medication screening.

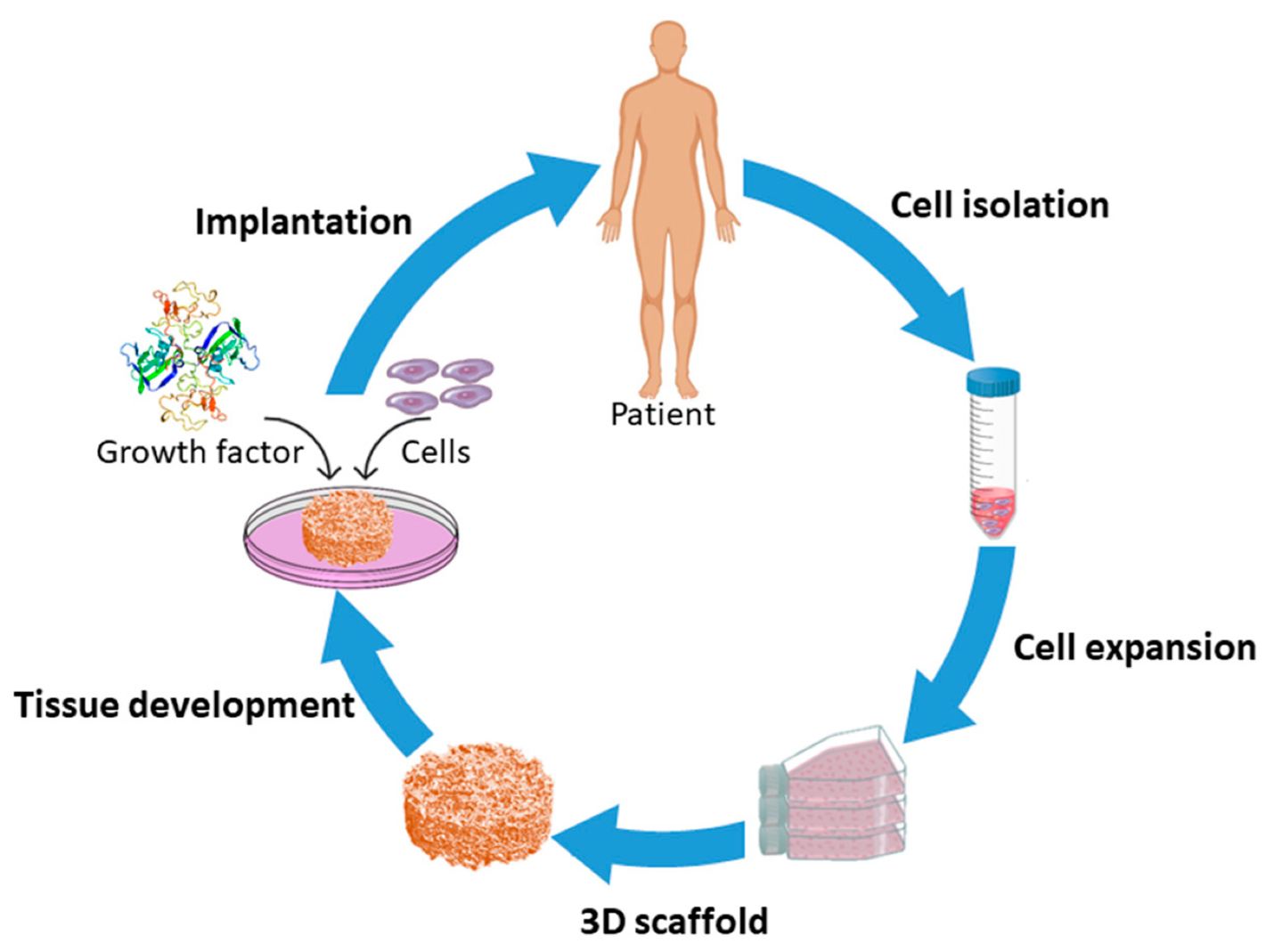
10. Tissue Engineering
The number of tissue engineering startups has increased significantly in recent years, in large part due to advancements in bioprinting and microfluidics. It facilitates regenerative medicine and the production of autologous tissue grafts for treating burns or organ transplantation. Startups are engineering tissues to develop sustainable alternatives to animal goods like meat and leather, which have traditionally only been used for biomedical purposes. To the point where the food items are cost-comparable to those derived from animals, this must be done on a massive scale.