Neuroscience technology is linked to a thorough examination of the structure, functioning, and operation of the nervous system through a number of technical tests and research. Physiology, anatomy, engineering, chemistry, biology, and other fields are all covered in depth in this course. Over the past few years, neuroscience research has advanced more swiftly than any other field. Neuroscience is the scientific field that focuses on understanding the structure and function of the nervous system and the brain.
1. Live 3D Brain Function Mapping
The first time this has been effectively accomplished, MIT scientists earlier this year created a novel approach to connecting structural mapping (brain architecture) with functional mapping (how the brain functions). Additionally, mapping across mouse brain areas was carried out in real time while the mice were still alive. This movie illustrates how intriguing it is to observe how a mouse’s brain architecture and live activity change in reaction to various visuals being presented to it.
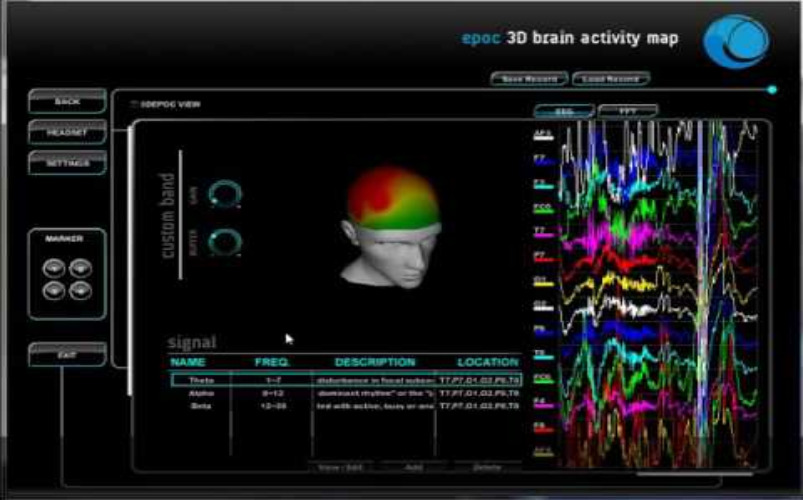
2. Seeing Decisions Being Made In The Brain
With the development of COSMOS, a novel bifocal microscopy technology, Stanford University achieved significant progress. Their research produced videos of neuronal activity in a mouse brain’s whole cerebral cortex. A live movie of macroscopic activity over the left and right hemispheres was produced by computationally extracting the data after basically shooting the brain from three distinct perspectives. Here is an example where the amazing electrical activity of a genuine brain is demonstrated.
3. Sleep Breakthrough For Artificial Brains
By simulating the neo-cortical columns of the human mind, Google’s Deep Mind artificial intelligence programe made a significant advancement. As a result, intelligence was greatly boosted while utilizing a small amount of computer power. This human-modelled AI has now defeated the finest chess, go, and eSports players in the world at their respective games. The importance of sleep for animal and human brains cannot yet be fully understood, although sleep deprivation has major negative effects. In this year’s research, Los Alamos National Laboratory found that AI systems’ spiking computational networks also experience a sort of sleep deprivation that causes them to become unstable when operating for extended periods without breaks.

4. Tiny Implant Allows Paralyzed Patients To Control A Computer
Patients who suffer from severe upper limb paralysis brought on by motor neuron disease have reported an improvement in quality of life because of a tiny brain gadget. This experiment, which was conducted at the University of Melbourne, implanted innovative microtechnology into the participants’ brains. Through keyhole surgery, the StentrodeTM device was put into the neck, where it traveled via blood arteries to the motor cortex. By using this minimally invasive technique, open brain surgery’s hazards, and recovery issues are avoided.

5. Neuroscientists Turn Normal Neurons Into Regenerating Ones
We noted in 2018 that scientists had discovered a method for transforming certain neurons from stem cells. Researchers from four various US colleges have made greater progress this year towards the coveted goal of life extension. They have been able to modify regular cells to transform into progenitor cells, which can differentiate into any cell type to replace dying cells, by finding the gene networks that control cellular regeneration. They used the glial cells of Zebrafish as a proof-of-concept experiment, successfully turning them into stem cells that found and repaired damaged retinal cells to restore eyesight loss.
6. Preventing Neurodegeneration
Scientists at Heidelberg University have pinpointed crucial procedures involved in the loss of brain cells, often known as neurodegeneration, rather than replacing failing cells. It involves figuring out the mechanism by which, in healthy individuals, cellular glutamate absorption prevents cell death, but becomes inactive in illness states like stroke, when oxygen supply to brain cells is constrained. Cells essentially start to destroy themselves as a result of not receiving the proper chemical cues to keep them alive. The scientists later created an exclusive family of inhibitors that may intervene and prevent the cellular “death complex” from happening.
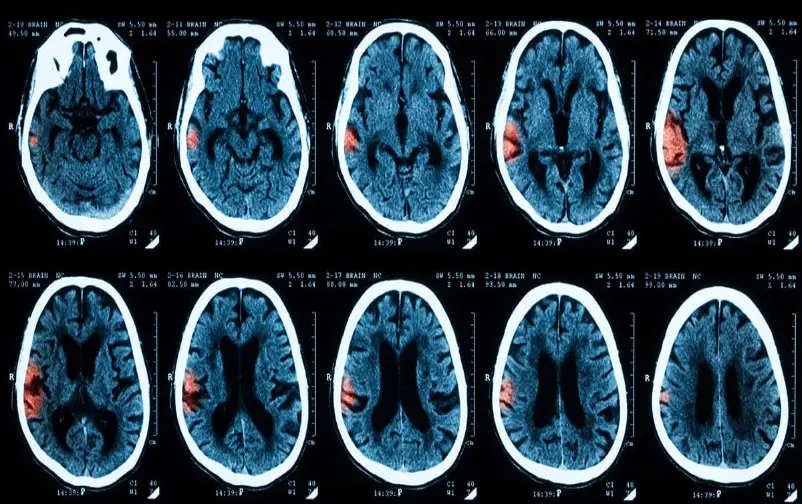
7. AI Advances The Challenging Diagnoses Of Brain Injuries
Researchers from Imperial College London and the University of Cambridge have created a novel AI system that can recognize and distinguish between several forms of brain lesions using topographical CT scan data. To trace the growth of a disease or the course of a patient’s recovery, a team of professionals must spend hours analyzing the vast amounts of data that CT scans provide. This new AI technique looks to be far quicker and less expensive than human specialists in spotting these changes.
8. The Secret Of Super-Agers Discovered
The term “super-ager” refers to those who keep their mental faculties long into their 70s and 80s while outpacing their peers in terms of cognitive ability. To date, nothing is known about the technique they use to keep their peak shape. A significant biological distinction between University Hospital Cologne and the Research Centre Juelich has been found. They discovered via PET scans that super-agers have significantly higher levels of resistance to the tau and amyloid proteins. These proteins had been challenging to investigate until recent years.

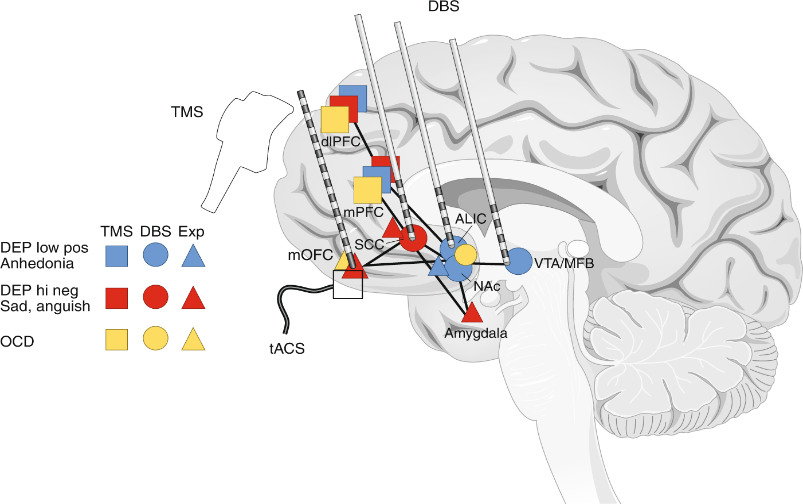
9. Treating Severe Depression With Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) has been successfully used by a research team at the University of California, San Francisco, to adaptively treat depression symptoms only when they manifest. Implanting electrodes into the brain to administer electrical currents to change brain activity is known as deep brain stimulation. Because DBS devices could only provide consistent electrical stimulation in one area of the brain, previous trials on the treatment of depression with DBS were only partially successful. However, different parts of the brain can be affected by depression, and its neurological hallmarks can fluctuate erratically.
10. Beyond Human Hearing
Like light waves, only a small portion of the sound waves that surround us can be perceived by humans. Normally, the range of frequencies we can hear is 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz; anything higher is termed ultrasonic. This frequency range is also used in ultrasound medical imaging and is where creatures like bats function. Scientists at Aalto University have developed a novel technique using cutting-edge technology that has resulted in a gadget that essentially offers people bat-level hearing.