Cloud computing is an evolving technology and dominates IT businesses and infrastructure. There are a lot of benefits, from cost reduction to performance optimization. One can manage your files and services over a network rather than a storage device. But it doesn’t mean that working on the cloud is 100% safe. As cloud utilization keeps increasing around the globe, the chances of exposure to sensitive material are at high risk. Most cloud service providers provide you with standard cybersecurity tools, but they do not cover an organization’s security needs. With more data and software moving to the cloud, there are a lot of challenges a company faces with cloud security. Here, we will discuss the top ten cloud security risks that will help build users a secured cloud environment.
1. Accountability And Data Confidentiality
The security of a traditional centre is taken care of by the organization itself. But when the data moves to the cloud, how will the security measures be taken for accounts and data? While deploying services in the cloud, it is vital to consider security risks carefully and mitigate them. Companies must ensure data protection regulations like General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) to ensure data protection, recovery, backup, and encryption.

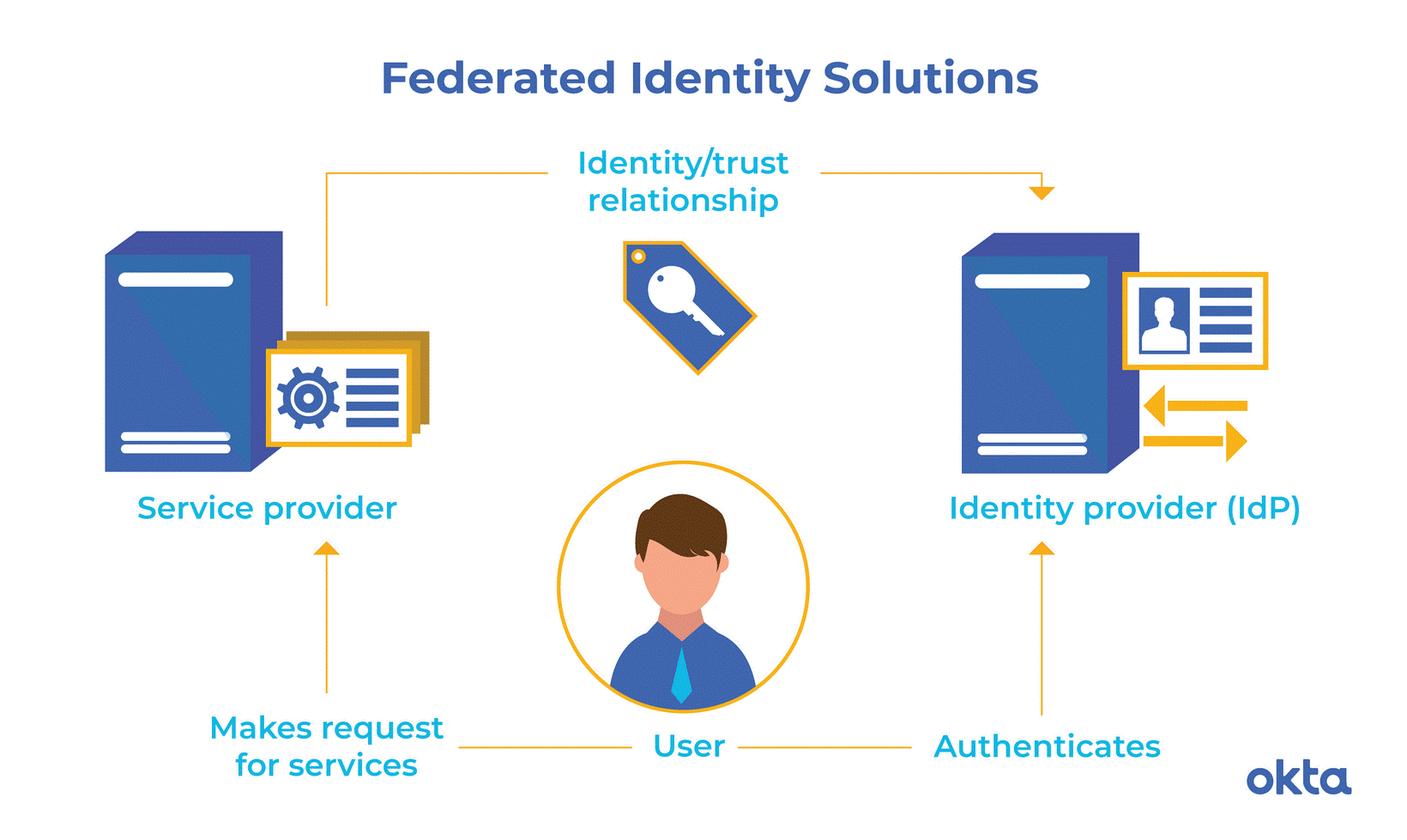
2. User Identity Federation
User Identity and authentication in cloud computing are critical to an organization’s safety and security. It provides privileged access to sensitive data. In traditional infrastructure, user identities are in control of the organization. In the cloud, access to resources increases with the number of users. Companies must use safety protocols like Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) to implement verified identity controls and federate across Cloud apps and providers.
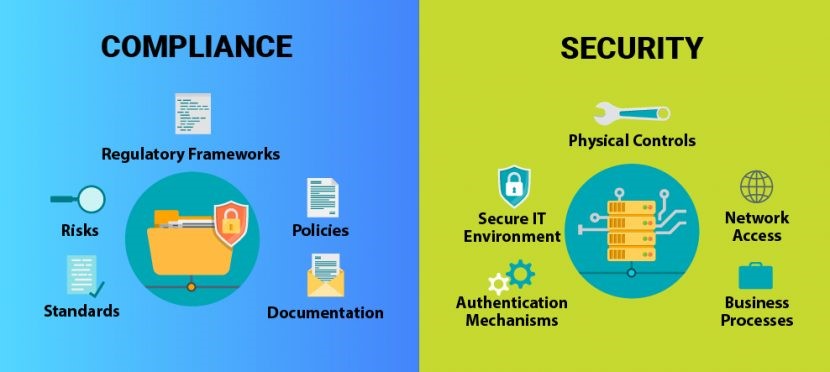
3. Legal And Regulatory Compliance
Businesses must be diligent with legal and regulatory compliance and the requirements specific to the industry and geographical location. Service providers must comply with Personally Identifiable Information (PII) with HIPAA security and privacy rules, GDPR, and other regulations specific to the business. For large-scale data access in the cloud, companies must confirm proper access controls and security measures are in place.
4. Business Continuity And Resiliency
Business Continuity is an ability of an organization to maintain business operations in unfavourable circumstances. Resilience is an achieved state of capability through emergency response, crisis management, IT disaster recovery, and business continuity. In bad weather or natural disasters, the data centre gets disrupted. Hence, companies must have Service Line Agreements (SLAs) to cover data resilience and a data recovery plan to keep their business running.
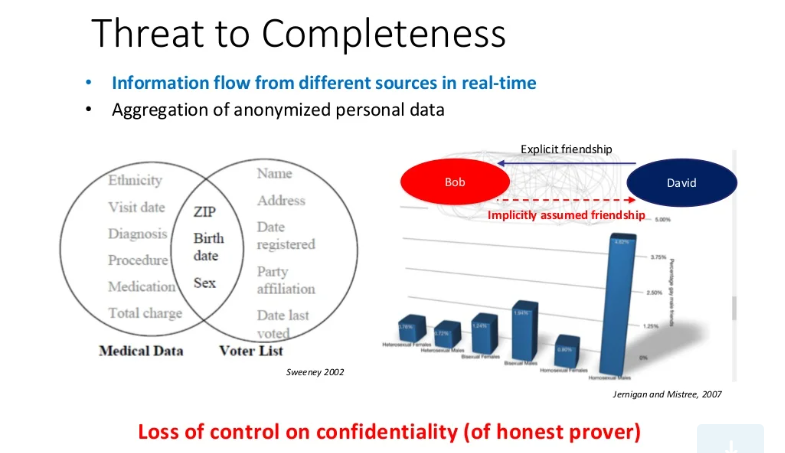
5. User Privacy And Secondary Data Usage
Once you move the data to the cloud, one loses control over the data. If one shares the data for secondary purposes on social media sites, there is less or no restriction on data sharing. Companies must provide security awareness training to employees to reduce data exposure. Another approach to ensure data privacy is to perform Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA), 24/7 monitoring, encryption technologies, and multi-factor authentication.
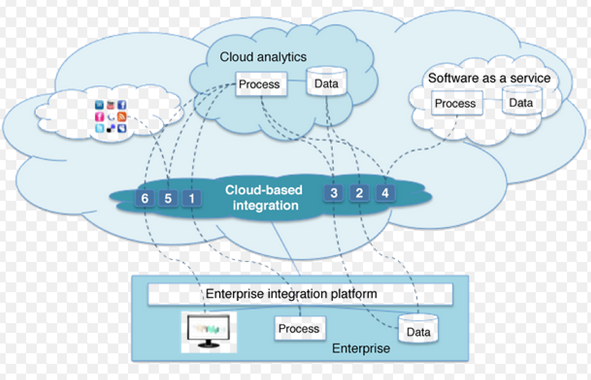
6. Service And Data Integration
Data transmission is the highest risk in cloud computing. During data transmission between cloud consumers and data centers, one must ensure the safety and security of REST API (Representation State Transfer Application Programming Interface), databases, and data encryption. To avoid compromising sensitive data, companies must implement safety protocols like Secure Socket Layer (SSL) that allow safe data transfer across the network.
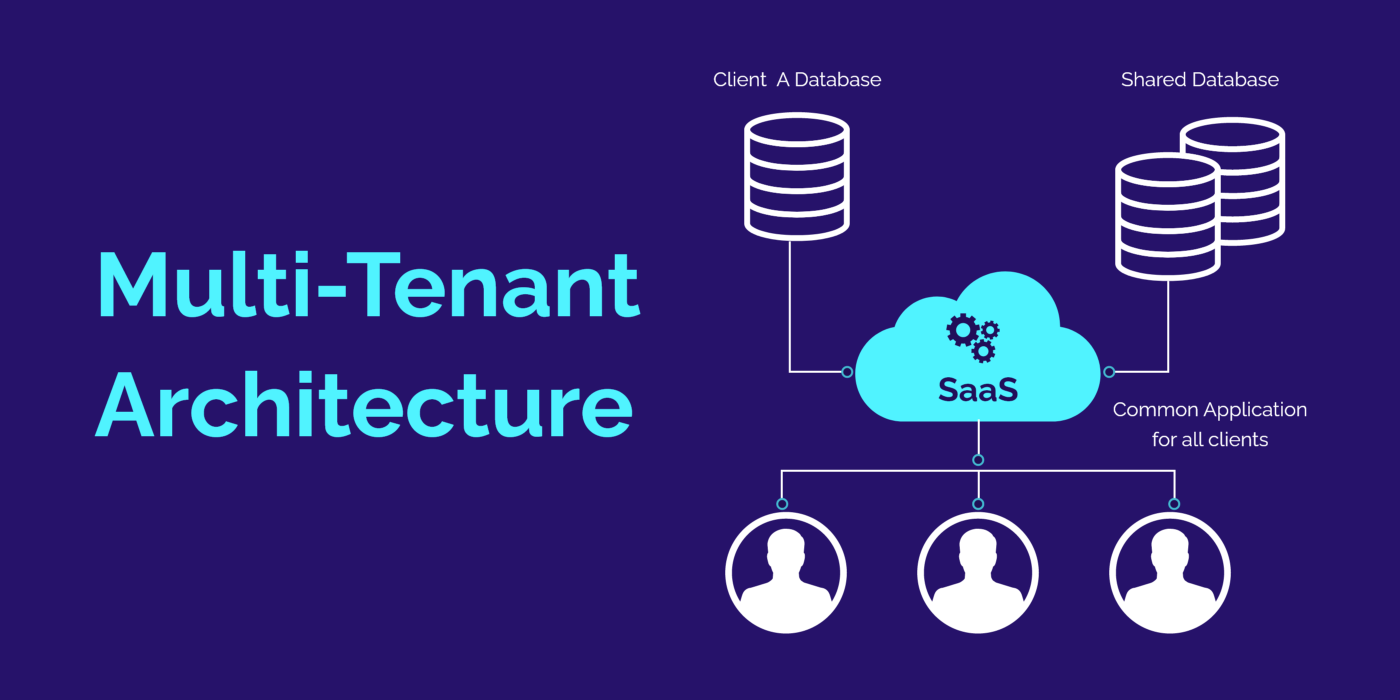
7. Multi-Tenancy And Physical Security
With multi-tenancy, there is sharing of resources and services between multiple users and tenants. The best benefit of multi-tenancy is cost reduction, and the highest risk is data isolation. Companies must prevent other tenants from impacting confidentiality, integrity, and data availability. Cloud vendors can configure the server for logical separation with good design. Data encryption also helps to prevent data exposure.
8. Incident Analysis And Forensics
Forensic Incident Analysis is the process of identifying, investigating, and recovering from cybercrime. In case of a data breach, companies must understand how to identify and manage critical vulnerabilities to respond to an incident quickly and effectively. Also, they must be aware of all the logs across the connected resources. Companies can opt for cloud vendor policy on handling, evaluating, correlating event logs, and forensic analysis of security incidents.

9. Infrastructure Security
Infrastructure Security includes configuring tiers and security zones and ensuring the use of pre-established network and application protocols. Lack of this security can create damage to technology assets and data. Companies must implement various access control mechanisms to improve security. For instance, they can provide privileged access management using robust authentication, a secured configuration of services, and a tiered architecture.

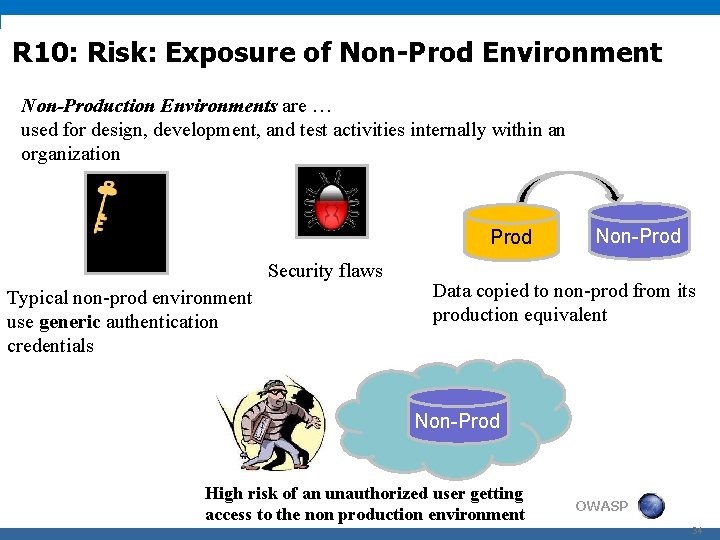
10. Non-Production Environment Exposure
Non-production environments are best for security testing purposes. Since these environments have less stringent security, they are prone to security and privacy risks. One must avoid using factual or sensitive data in non-production environments. Companies must also ensure that users working on non-production systems have privileged access to security measures. Also, they must implement appropriate technical and organizational measures and data protection principles.