External events like international conflicts, political pressures, economic disasters, competition, or diseases are frequently turning points for rapid technological advancements. The COVID-19 pandemic has fueled the desire for technological progress.
1. Covid-19 Diagnostic Kit At Point Of Care
Diagnostic tools for COVID-19 detection are at the top. The most crucial aspect of communicable infection is determining the infectious agent. Because of this unique way, COVID-19 infects people determining the level of disease is complicated.
2. Telemedicine And Remote Monitor
Internal meetings and online consultations significantly increased communication innovation. In the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine provides medical care remotely to people via communication technology. Telemedicine continues to gain popularity in the healthcare system as sophisticated technologies such as videoconferencing and new emerging applications are used.

3. Portable Dialysis Machine
Dialysis required for COVID-19 patients in intensive care units. Dialysis equipment and supplies are short in supply, according to emergency room doctors. Aside from kidney failure, the patient’s immune solid response to the infection frequently causes blood clots. These blood clots jam the dialysis filters, which are in short supply. Dialysis machines are located in clinics where patients visit on a regularly. However, due to social alienation and need for procedure in COVID-19 patients, a new therapy paradigm is emerged.

4. UV-C Disinfection
Sanitation and disinfection are critical tools in our healthcare system for preventing illness spread. It is essential in hospital settings for operating rooms and intensive care units (ICUs) routinely cleaned and sanitized. Any human or procedural error during the disinfection process can result in hospital-acquired illnesses. UV radiation, when used correctly, kills 99.9% of bacteria, fungus, and viruses. There are also innovative product concepts for regularly sanitizing individual workstations and meeting spaces using UV lights.

5. MRNA Vaccinology
Advances in RNA production, purification, and cellular transport have facilitated the creation of mRNA vaccines for applications, including cancer and Zika virus infection. The technique is inexpensive, easy to build, and induces immunity unusually. The appearance of the COVID-19 pandemic emphasized for speedy development of a vaccine globally.

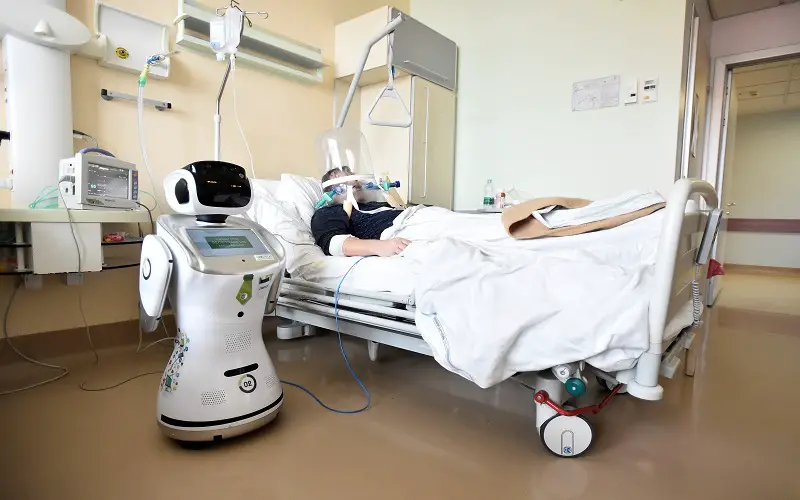
6. Robotics
Robots are created to communicate with patients and doctors from a distance, disinfect surface with UV light, deliver essential medical supplies, monitor vital signs, remind people of infection prevention measures such as social distancing, and scale-up production of diagnostic tools, drugs, and vaccines. Telepresence robots are used in nursing facilities to link family members with lonely elderly via social media platforms. They monitor patients and direct the link to medical specialists in the hospital and at home during the COVID-19 recovery period.
7. Treatment For The Reduction Of LDL
High-level blood cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein is a cardiovascular diseases. Inclisiran, authorized by the FDA in December 2021, is a game changer for heart disease sufferers. Its long-lasting impact aid in reducing drug noncompliance, which is the cause of failure to decrease cholesterol levels.
8. Rapid Testing
Rapid antigen tests for SARS-CoV-2 are used. However, best practices for their utilization are still evolving. When performed at a single time point, rapid antigen tests have lower sensitivities and specificities than RT-PCR-based tests, which is why many testing programs have deployed confirmatory RT-PCR for positive antigen tests in asymptomatic (low pretest probability) individuals and negative antigen tests in symptomatic individuals and close contacts of positive cases (high pretest probability) settings.

9. Screening For Infection
Systematic screening methods are costly and need skilled people, which limits their adoption in many countries. The incubation time, as well as relatively high frequency of asymptomatic illness compared to other infectious diseases limit the usefulness of digital system that scan vital signs or self-reporting of symptoms.

10. Planning And Tracking
Big data and artificial intelligence (AI) have aided with COVID-19 preparation and monitoring of persons, and hence the transmission of illness, in some nations. Machine learning models are constructed using this data to estimate the regional transmission dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 and guide border inspections and surveillance.


















