Electronic voting technology aims to speed up ballot counting, minimize the number of people tallying votes and enhance voter accessibility. Long-term investments in new systems projected to pay off since operating expenditures are predicted to fall. Other projected benefits are speedier reporting, publication of results, and the ability for individuals to vote independently from their location, which may boost total voter turnout. Individuals residing overseas, individuals living in rural regions far from polling locations, and mobility disabilities gain the most from online elections.
1. The Security Of Online Voting Systems
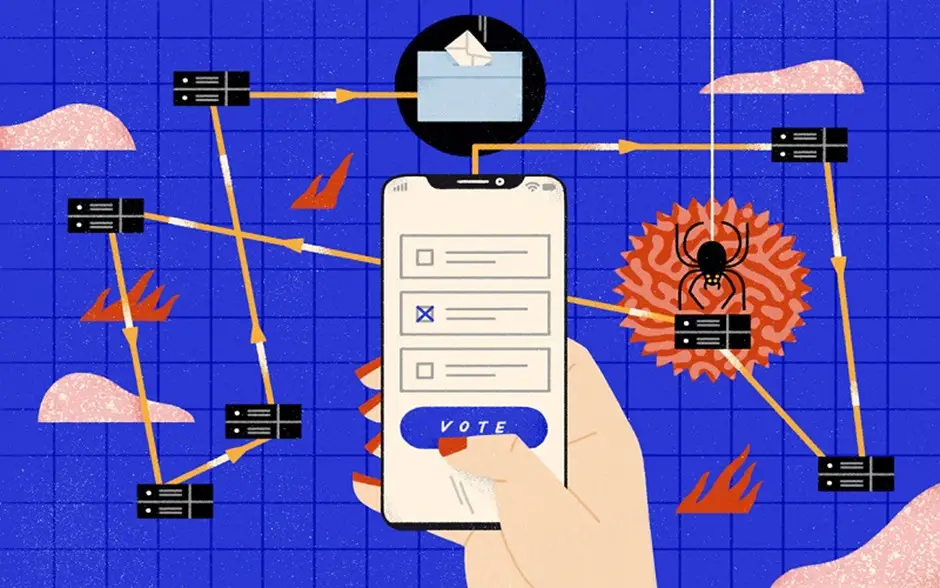
Online voting systems are not safe as traditional paper-based systems since hackers always tamper with the results. Election security protects data via encryption, and independent security specialists must test the system.

2. Lack Of Transparency
Internet voting is opaque. Voters witness the personal counting of ballots in conventional paper-based voting. Online voting is purely electronic, and it is difficult to validate the results. It is critical to seek an online voting system with transparency characteristics, giving a live election results website where voters watch the results as they come in. The voting technology provides election auditing, which means that votes cast using the system scrutinized. It provides independent verification, in which a third-party accountant certifies the election process is fair.

3. A Self-administered Vote May Take More Planning
Online voting software has advanced to the point that anybody can access and utilize it. Major events and multistage votes necessitate additional knowledge and skill. In these instances, using an online voting service to manage votes is the best option.

4. Some Software Requires An App
Online voting software is used safely through the browser, others necessitate the use of a downloading program or app. These tools work properly, ensuring everything is set up appropriately, which will be a nuisance for voters or IT staff.

5. Vulnerability To Hacking
The Congressional Research Service on Election Reform and Electronic Voting Systems, vendors, and election jurisdictions state that they do not transmit election results from precincts via the Internet but may do so via a direct modem connection or a Virtual Private Network. The strategy is vulnerable to internet-based assault if encryption and verification are not sufficient because telephone transmission networks connected to the Internet, and computers that receive server are connected, such as via a local area network.

6. Susceptibility To Fraud
Voting fraud does not exist everywhere. The losing political parties accused of fraud, scam comes in many degrees. A malicious voting system designed and deployed by a single vendor to hundreds of thousands of polling stations has the potential to make fake millions of votes. People have access to the machines and know to use them. They remove the memory card that holds the votes and replace it with their memory card with a virus that tamper the results. It is a large-scale and widespread deception.
7. Malicious Software Programming
Computer software is created through software development and coding. This software is tampered with by a computer programmer having access to the source code. It is difficult to test the electronic voting systems for security flaws if they are added and camouflaged. The malicious coding placed by the programmer into commercial software is activated by a combination of instructions and keystrokes, and election results are altered.

8. Physical Security Of Machines
In the United States Government Accountability Office, all the locks on a DRE model are picked and operated by the same keys. A DRE model is coupled with others to establish a rudimentary network. If the devices disconnected from others, the voting functions on other machines would be affected. Reviewers discovered switches used to turn a DRE system on or off are used to shut polls on a specific DRE terminal and were not safeguarded.

9. The Initial Costs For Digital Voting Are High
There is a high expense of installation at the front. It saves money in the long-term, but the initial outlay is more than the paper voting. The voting equipment, maintenance and installation, testing of the infrastructure, and safeguarding the premises is the cost.

10. Manufacturer Bias Can Influence Votes
The elections have a significant impact on business, and corporation bias becomes a factor when acquiring voting devices or systems. The government employs a corporation to install the machines, putting its confidence in that company to collect and record votes accurately, and people argue that no system should introduced if it can’t provide fair and unbiased voting.



















