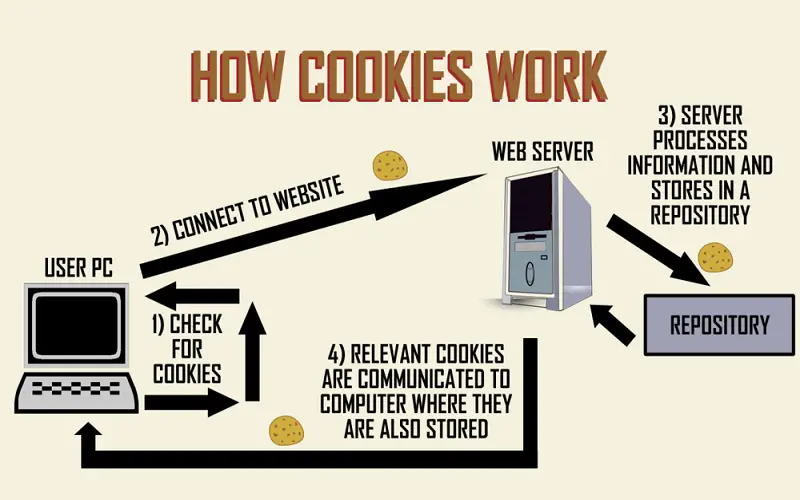
A cookie is a collection of data that is stored in a web browser. When users revisit a particular website, a cookie enables the site to retrieve previously selected settings and content. Here are the Top 10 facts about cookies.
1. Security
A cookie cannot identify essential data, such as email addresses. According to the General Data Protection Regulation, there is transparency with cookies. EU cookie law regulates the usage of cookies, email marketing, and other electronic communication. Cookie consent refers to the consent required by websites before placing cookies and trackers on the user’s devices.
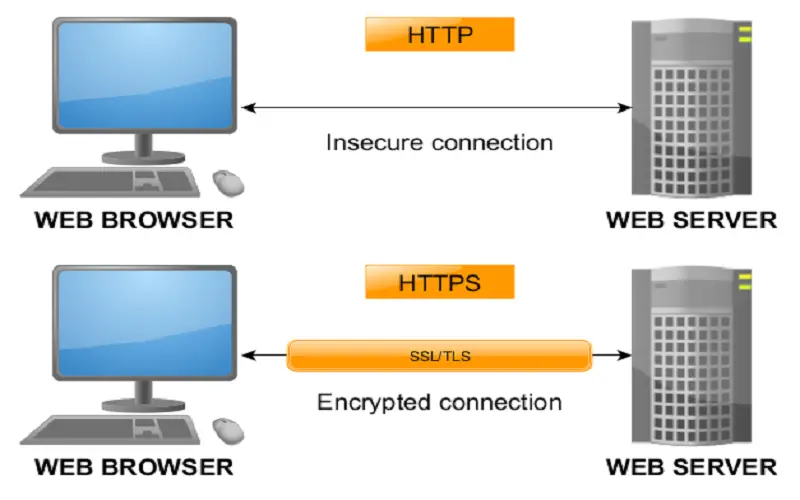
2. Versatility
Supercookies are not downloaded or stored on browsers but privacy concern is rising as they can neither be deleted nor blocked by ad blockers. Zombie cookies are third-party cookies that can restore once deleted. Flash cookies are stored and accessed by Adobe Flash, commonly used by YouTube. Secure cookies ensure that cookies are deliver to SSL connections via encrypted connections.

3. Usage
The website’s operator stores the information in website’s database. Database allows personalizing one’s experience by recording the browser history, and collecting insights for improving services. For example, e-commerce sites and YouTube allows exploring and discovering our interest.

4. First-party Cookies
The host domain store and access First-party Cookies directly. They help to analyze data, change language settings, provide a good user experience, and keep the session open. First-party Cookies allow cross-site tracking, which means tracking software or script hosted by the website’s domain.
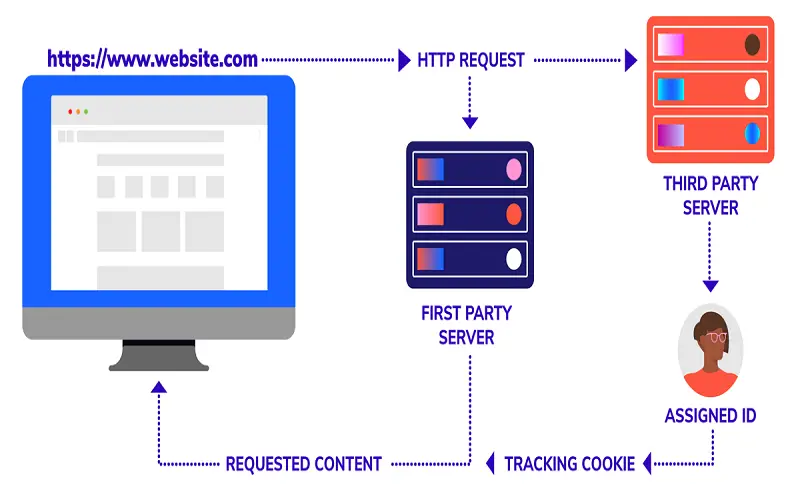
5. Third-party Cookies
Third parties include publishers, advertisers, and ad tech companies. They provide ads, companies, or a service that allows websites to add some aspects like live chat, Google Maps, social media buttons, etc.
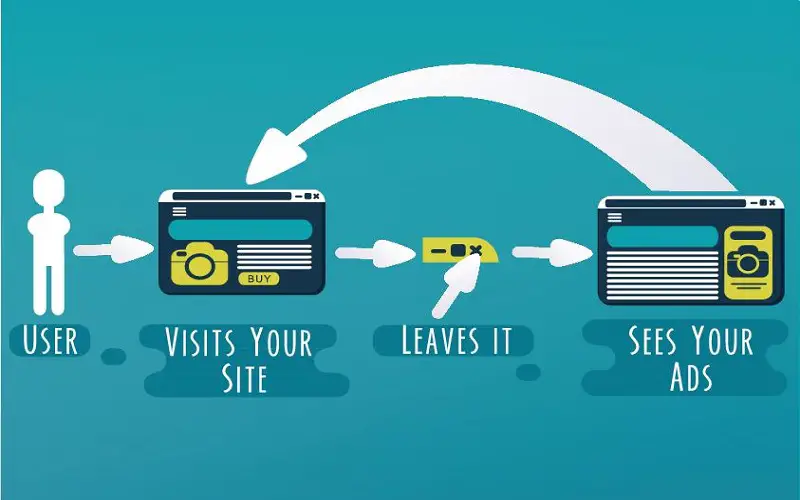
6. What If We Delete Or Block Cookies?
Removal of cookies prevents risks of privacy breaches. It reset browser tracking and personalization. Removing cookies make other websites harder to navigate. Without cookies, users need to re-enter their details. Cookies improve the web experience. The advertiser sets a cookie so that same ad is not repeated. If cookies are deleted regularly we end up receiving more interstitial ads.

7. Virus And Spyware
Some people believe cookies contain viruses or spyware. If the hidden folder is tracked down, cookies cannot execute, as they are simply text files. Most anti-spyware applications can track or remove cookies. Cookies cannot affect computers with any type of malware, spyware, or virus, but some cyberattacks hack cookies and can access the browsing history.

8. Easy Login
Many websites enable cookies by which they create an account and keep it logged in. If we disable the cookies in our browser, many of the browsers don’t function efficiently.

9. Types
Some cookies are necessary for a website to function effectively. They provide essential features such as signing in, signing out, adding or removing items to the cart, and allows online transactions. Performance cookies provide an enhanced user experience. Functional cookies allow the website to function correctly by improving its performance and functionality.

10. Working
Websites generate cookies to store data for both the user and the server. It ensures a user-friendly site. Once we take an action on a website, a text file is transferred and held on the user’s web browser. When the user revisits the sites, the server displays cookie and recall previously stored information, such as previous browsing activities on the site.