Companies and consumers have shifted their attention in recent years to what individuals and global society can do to improve environmental protection. Many people believe that technology can significantly contribute to helping us generate “green” energy, manage pollution, and decrease waste because of the tremendous advancements achieved by the tech industry in areas like remote work, healthcare, transportation, and more. Technology experts are enthusiastic about several targeted technological breakthroughs and practices that could substantially protect our planet, earth. However, is no “magic bullet” answer to the world’s environmental problems.
1. Ecological Architecture
Urban resource use can be drastically reduced by using green buildings, which also makes urban growth sustainable. To reduce energy consumption, the green design enables buildings to be built in a way that takes advantage of existing natural light and ensures proper insulation. With such building techniques, the demand for heating will be eliminated, together with the reduction of energy used for lighting. Additionally, landfills and urban garbage will be used as a supply for building supplies. This technology will soon enable all facilities to be “passive,” producing minimal new emissions during construction and use.

2. Wastewater Electricity Generator
Engineers at Oregon State University have created a hybrid electricity generator that uses sewage water as part of the power generation process. They have developed a device that uses wastewater to generate electricity by combining two different power generation technologies, reverse electrodialysis, and microbial fuel cells. In addition, the generator can generate enough electricity to support the primary power grid and water treatment. As a result, when scaled up, this technology will serve as the foundation for sustainable energy and water use, which is essential given the declining availability of natural resources.

3. New Nuclear Material
Nuclear energy has many potentials but has yet to be fully realized because of the risks posed by radioactive waste. Only 1% of the potential energy in Uranium is now used in nuclear power reactors; the remainder is radioactive waste. Thorium is one element that can replace Uranium and enable atomic power to fulfill its potential. Since all of the thorium mined is in the isotopic form required for the reactor, thorium-based fission produces minimal waste. Furthermore, the crust of the planet contains more thorium. Cost is the main factor keeping it from replacing Uranium, but R&D in this field is gaining steam, and experts are optimistic that the technology will soon become affordable.

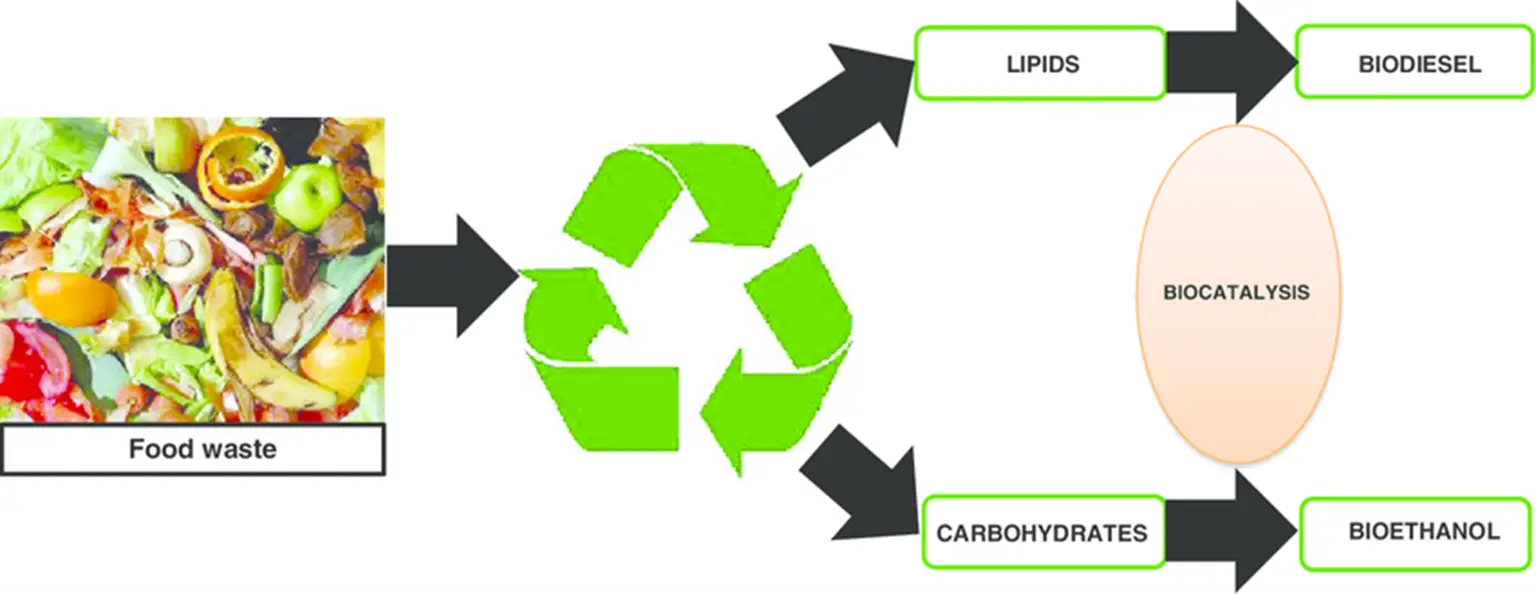
4. Waste-Sourced Biofuel
We are constantly looking for more intelligent ways to recycle our waste, and we have finally found one. Biomass waste, such as paper, grass, or wood chips, can now be converted technologically into gas and ethanol. The conversion processes utilize less water and produce less carbon dioxide than conventional ethanol production. Companies are creating standardized, simple-to-install facilities that will allow communities worldwide to turn rubbish into cleaner biofuel. Several pilot projects are about to be launched in the UK, Canada, and Australia. Deforestation is a significant cause of greenhouse gas emissions, contributing significantly to climate change. Plants are essential carbon sinks. Agriculture and food crops cannot be maintained, but forests can. As a result, a procedure known as PYROLYSIS has been developed to offset some of the carbon release related to agriculture. Agricultural waste can be burned in a controlled, low-oxygen atmosphere, which not only helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions but also yields charcoal as a byproduct. Due to its dual advantages, this technique has enormous potential.
5. Biomimicry
Self-healing materials have emerged as a result of biomimicry. The self-healing materials can “repair” themselves when sliced, ripped, or cracked. As a result, most consumer goods will have longer lifespans, lowering the need for raw resources and trash.

6. Electric Vehicles
Without mentioning electric vehicles, no discussion of future green technology is complete. Wireless technology will be able to supply electric power to moving vehicles, which is an improvement over conventional electric cars. Devices receiving power remotely via an electromagnetic field broadcast from cables laid beneath the road will be standard equipment in all-electric vehicles. These cars are presently undergoing road tests in South Korea, and when they are produced, they will undoubtedly change some of the opinions people have about electric automobiles.

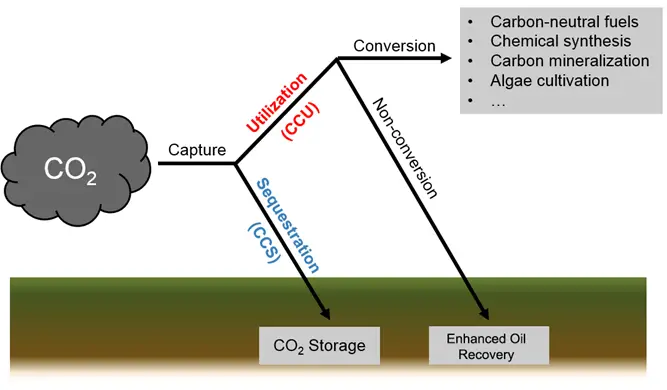
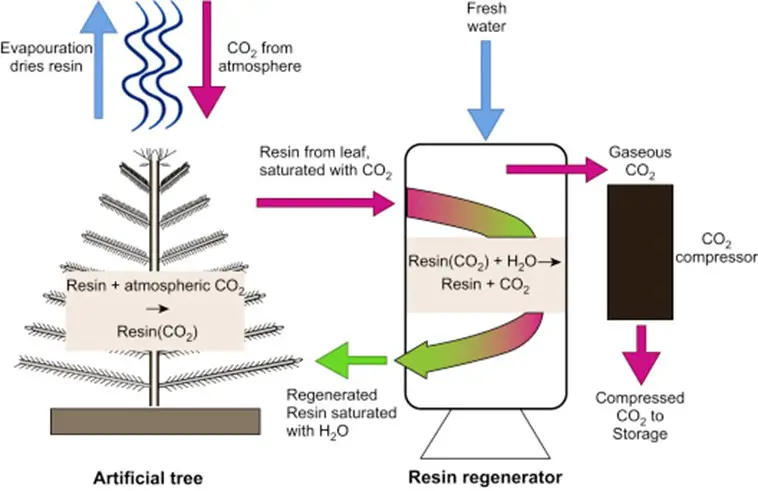
7. Capture Of Carbon
The practice of “carbon capture,” or “putting carbon underground,” is immediately appealing. However, there have always been unknowns around this technique, including leak and storage concerns. Two novel compounds, however, have been discovered that will contribute to the cost-effectiveness, safety, and efficiency of carbon capture. First, some methods will enable quick replication of ZIFs and amines, two unique cage-like molecules proven to function effectively under practical situations.
8. Molten Salt Storage
Molten salt can be a beneficial energy storage tool for producing solar energy. Large quantities of salt, which can absorb and store vast amounts of heat, can be heated using the excess heat produced during the day. Without the sun, this salt can generate steam and power an electric turbine, making solar energy a more attractive alternative to non-renewable resources.
9. Artificial Photosynthesis
Engineers and scientists are working to create a technology that will allow them to produce electricity using carbon dioxide and sunshine. Scientists have established the technique’s viability, but scaling it up still presents challenges. The obstacles of efficiently converting solar energy into power and storing captured carbon will undoubtedly be overcome if this technology is to succeed.
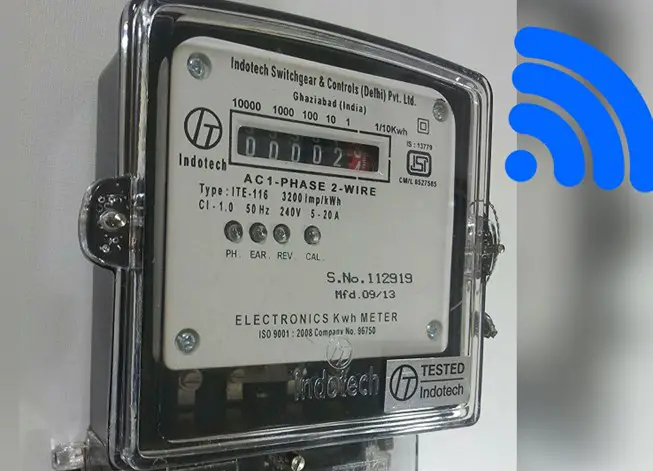
10. Smart Meters
We will be able to use our limited resources, including power and water, more effectively thanks to smart grids and smart meters. Electricity smart meters will enable us to use our equipment more effectively while lowering energy costs. Thus, they will allow us to schedule our washing machines to run exclusively during periods of low energy consumption. Similarly, intelligent water networks can assist utilities in conserving water by minimizing leaks, etc. To ensure more efficient supply and even out demand, these gadgets offer great potential to help us get more use out of our current resources.



















