Cyber Security is crucial in current times, as the availability of information and knowledge has spread because of the rapid growth of the internet and artificial intelligence. As Cyber-attackers are becoming more intelligent and wiser and coming up with more ways to gain unauthorized data, money, and information, a rise in Cyber security is also required with equal invocations to counter the attackers. The current general public relies on a combination of VPN/firewalls to safeguard their data, but this technology is not enough with the current growing cyber threats, attacks, and frauds. In response to these attacks, let’s examine the Top 10 involutions in current Cyber Security Technology.
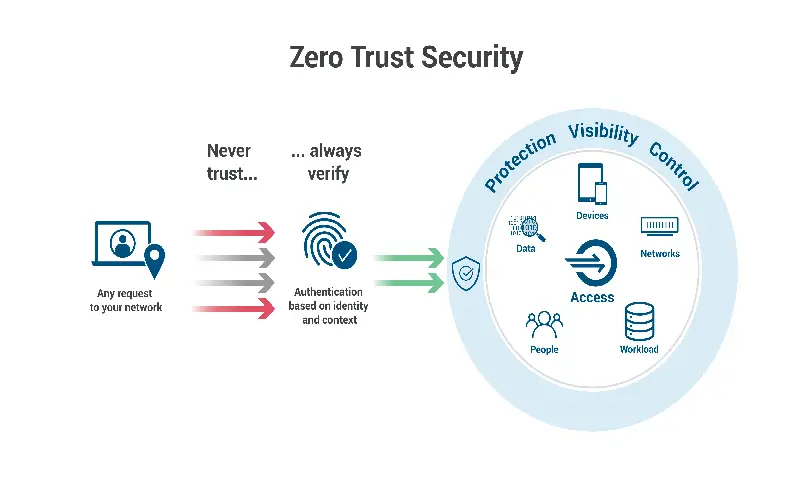
1. Zero Trust Security Model
Zero Trust Security or Architecture (ZTA) is a security measure that stands on the principle of least privilege. Least privilege means that applications and devices only get permission for the tasks that the user needs, this make attackers lose access to sensitive data and information in user applications and devices, making it more difficult for them to gain access. You can perform this on your devices right now by authorizing your app permissions, which are not required by you. Zero trust architecture does not believe in any view of security, which assumes that everything inside the organization is safe.
2. Attack Surface Discovery
Attack Surfaces are vulnerability loops such as pathways, methods, and vulnerabilities that can grant hackers (attackers) unauthorized access to systems, networks, services, or sensitive user data. Attack surface discovery is also referred to as attack vectors. As organizations grow and adapt to various architectures and infrastructures involving hybrid as well as cloud service models, due to larger and more complex structures, the chances of vulnerabilities increase. According to Randori (a subsidiary of IBM Corp.), 67 percent of the organization’s attack surfaces have grown in size within the past two years.
3. Cybersecurity Posture Assurance
Cybersecurity vulnerability standards of an organization are checked by an assessment called Cybersecurity posture assurance. This security evaluation checks for security policies, workflows, procedures, and measures to protect sensitive information and data. This helps organizations understand and identify possible risks and vulnerabilities in their systems and infrastructure, which can be improved and rectified, preventing potential cyber threats and attacks.
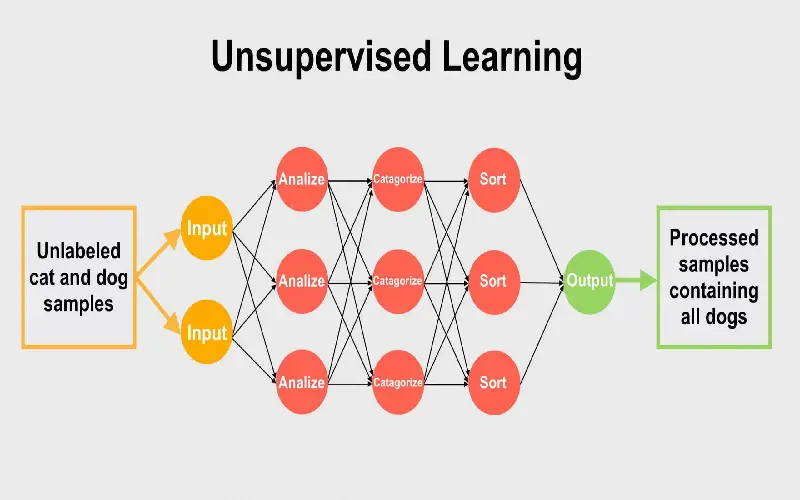
4. Unsupervised Machine Learning
Unsupervised Machine learning (UML) plays a crucial role in cybersecurity. Unlike supervised learning, unsupervised learning is a technique that uses unlabeled or unstructured data to train machine learning models. Supervised machine learning is only capable of identifying threats that it has seen before and trained on. Instead, UML is an algorithm that can find unseen patterns and relationships between data and structure without much human interaction. This makes them helpful in identifying new cyber-attack patterns or unusual connections in more extensive databases.
5. Behavioural Fuzz Testing
Behavioral fuzz testing is a type of fuzz testing. In this test, testers send two types of inputs into the application one is random or semi-random input, and another is based on specifications (actual inputs) and checks for application behavior in both aspects. The bugs and possible vulnerabilities found by checking the difference in the behavior of the application in both cases (actual behavior and expected behavior). It helps developers get real-time insight into possible application risks that can be rectified quickly to avoid attacks.

6. Behavioural Analytics
Behavioural Analytics (BA) is a cybersecurity technique based on artificial intelligence and machine learning (AL and ML). Organizations perform behavioral analytics on every connected element, such as users, admins, databases, relationships, networks, security protocols, and the cloud environment of an application. Behavioural analytics tools can actively check and provide real-time insights and recommendations into organization application vulnerabilities. There are a few subtypes of behavioral analytics tools, such as User and Entity Behaviour analytics (UEBA) and network behavior analytics (NBA) which provide specific threat information and insights.

7. Blockchain
Everyone must have heard about Blockchain for sure. Blockchain is a decentralized technology that helps store information and data transparently because of immutable storage and access to only members. Blockchain ensures data confidentiality, which means that data is only available to people who are authorized to access it. Blockchain does not contain any single point of failure, which reduces the chances of IP-based DDoS (Denial-of-service) attacks. Blockchain also has PKI (Public key infrastructure), which ensures authentication during transactions.

8. Hardware Authentication
Hardware Authentication is a user authentication method based on hardware and cloud software authentication (traditional login authentication). This hardware is a dedicated physical device such as a smartphone, computer, laptop, etc., owned by an authorized user, which acts as an authentication token to grant access to resources in addition to primary password login. 2FA (2-factor authentication) is a combination of hardware and traditional password-based login.

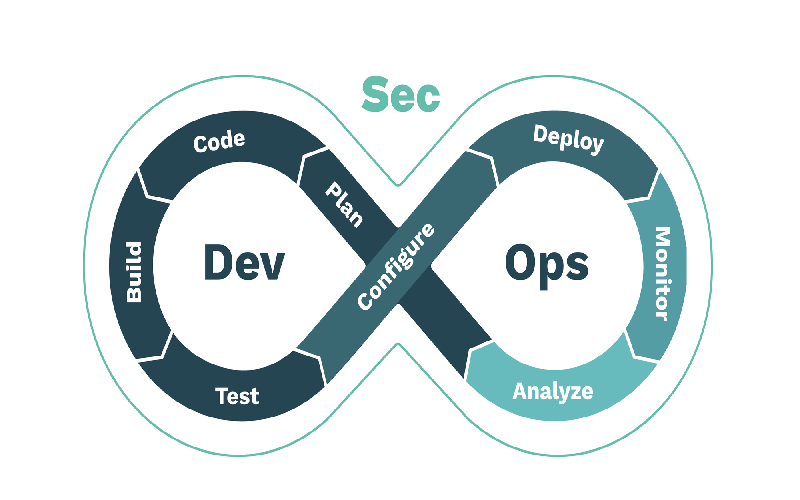
9. DevSecOps
DevSecOps is a short form of development, security, and operation framework. DevSecOps is a framework that aims security aspects in all phases of software development. This helps organizations avoid the risks of releasing code that may contain potential security vulnerabilities. Through using automation and transparent processes, the team focuses on security while building the software rather than leaving for the end with issues and vulnerabilities. The DevSecOps framework believes in reducing misconfiguration while making the product instead of fixing it after the attack.
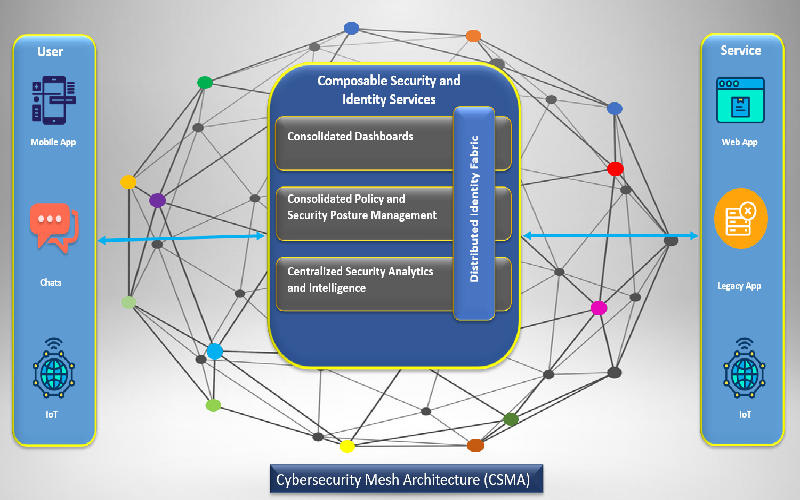
10. Cybersecurity Mesh
Cybersecurity Mesh is an architecture that follows scalable techniques to extend security-related controls and distributed assets. It consists of multi-cloud architectures for a modular approach. Cybersecurity mesh uses several supportive layers, such as consolidated policy management (CPM), identity fabric, and security intelligence. By using individual security products, organizations gain a more integrated security policy due to protecting individual endpoints instead of all data components. Cybersecurity Mesh provides an environment designed for the rapid deployment and maintenance of cybersecurity technologies.