The way we interact with digital devices has been revolutionised by gesture-based interfaces, which allow for more intuitive and immersive experiences. These user interfaces offer an alternative to conventional input devices like keyboards and mice by allowing users to control and navigate through a variety of apps using hand and body motions. We will examine the top ten gesture-based interface developments over the past several years in this post, demonstrating how technology has improved to improve user interactions and close the gap between people and robots.
1. Depth-Sensing Cameras
The use of depth-detecting cameras, such as Microsoft’s Kinect or Intel’s RealSense technology, is a significant advancement in gesture-based interfaces. These cameras can precisely follow human motions because they can record depth information. These technologies let users operate gadgets without making physical touch by mapping the location of joints and identifying motions. Depth-detecting cameras have enabled a new level of engagement and immersion for virtual reality and gaming applications.

2. Machine Learning And Gesture Recognition
Machine learning algorithms have played a crucial role in advancing gesture-based interfaces. By training models with vast datasets, computers can recognize and interpret various hand movements accurately. This has led to more sophisticated gesture recognition systems capable of understanding complex gestures and differentiating between intentional actions and incidental movements. Machine learning techniques have significantly improved the responsiveness and accuracy of gesture-based interfaces, making them more reliable and user-friendly.
3. Wearable Gesture Control Devices
Users may communicate with their wearable gadgets using simple hand motions thanks to gesture control capabilities built into smartwatches and fitness trackers, for example. These gadgets recognise gestures using in-built sensors, making it simple and convenient to use them to choose options, take calls, or manage music playing. By eliminating the need for physical input devices, wearable gesture control improves user convenience by facilitating more efficient and seamless interactions.

4. Augmented Reality And Gesture Interaction
Using gesture-based interfaces in augmented reality (AR) brings fascinating new possibilities. Users may interact with virtual things through hand movements thanks to AR, which projects digital information over the physical environment. Numerous industries, including industrial design, gaming, and education, stand to benefit greatly from this breakthrough. Through simple hand gestures, users may edit 3D objects, perform virtual instruments, and explore immersive augmented reality worlds. By bridging the gap between the actual world and the virtual world, AR-based gesture interfaces provide a more engaging and natural user experience.

5. Haptic Feedback And Gesture Interfaces
To improve user interactions, gesture-based interfaces have included haptic feedback, which generates tactile sensations. Users receive tactile confirmation of their motions when haptic feedback is used, making interactions more natural and intuitive. Users, for instance, can experience the sense of touching or moving virtual items by using haptic feedback. By bringing a new degree of realism and enhancing the sensation of presence in virtual settings, this technology has enhanced the entire user experience.
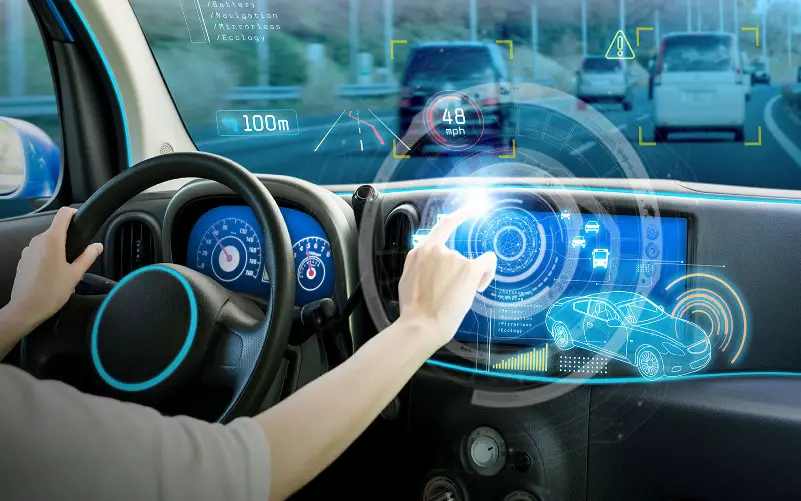

6. Gesture Control In Automotive Systems
With the incorporation of gesture-based interfaces into automotive systems, drivers now have a safer and more user-friendly method to engage with in-car controls. Without taking their hands off the wheel, drivers may use hand gestures to change the temperature, operate infotainment systems, or answer calls. By minimising distractions and offering a more organic and hands-free engagement mode, this invention increases driving safety. The goal of gesture control in automobile systems is to improve the entire driving experience while maintaining the driver’s attention on the road.
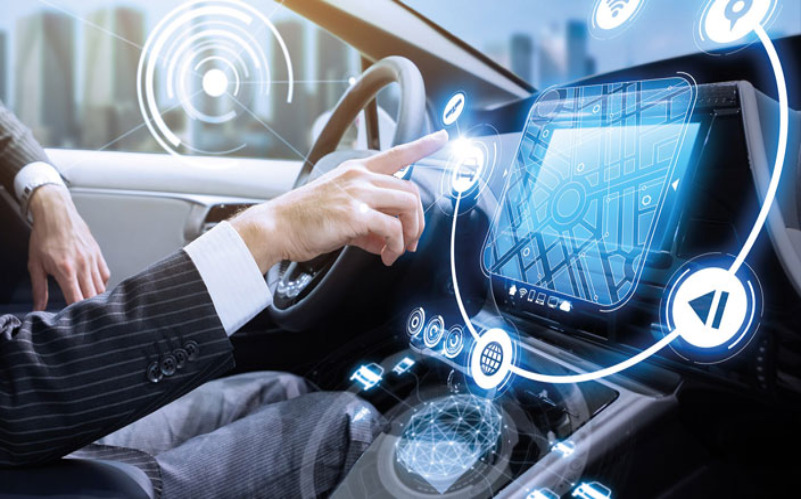

7. Gesture-Based Accessibility Solutions
Gesture-based interfaces have greatly benefited individuals with physical disabilities by providing alternative input methods. By recognizing specific gestures, users with limited mobility can control various devices, interact with software, or communicate more effectively. These innovations have opened new possibilities for individuals with conditions like paralysis or limited dexterity, empowering them to access technology and engage with digital content. Gesture-based accessibility solutions have made significant strides in promoting inclusivity and ensuring that everyone can benefit from technological advancements.

8. Gesture-Based Gaming
Since gesture-based interfaces have been used in gaming, the industry has seen a significant transition. Players may control characters and carry out tasks by moving naturally thanks to motion-sensing controllers and cameras. The gaming industry has seen a revolution because of this invention, which has increased gameplay’s tactile, immersive, and interactive elements. Users may now engage in virtual sports, dance, and exercise activities thanks to gesture-based gaming systems, offering a pleasant and active way to enjoy gaming.

9. Gesture Control In Smart Home Systems
The way we interact with our living environments has been made simpler by the inclusion of gesture control in smart home systems. Users may operate appliances, change the lights, and even open and close curtains using hand gestures rather than by physically touching switches or other hardware. Home automation is now more practical and has a futuristic feel, opening it up to a larger spectrum of consumers. The way we interact with our living environments has changed thanks to gesture-based control in smart home systems, which creates a smooth and simple user interface.

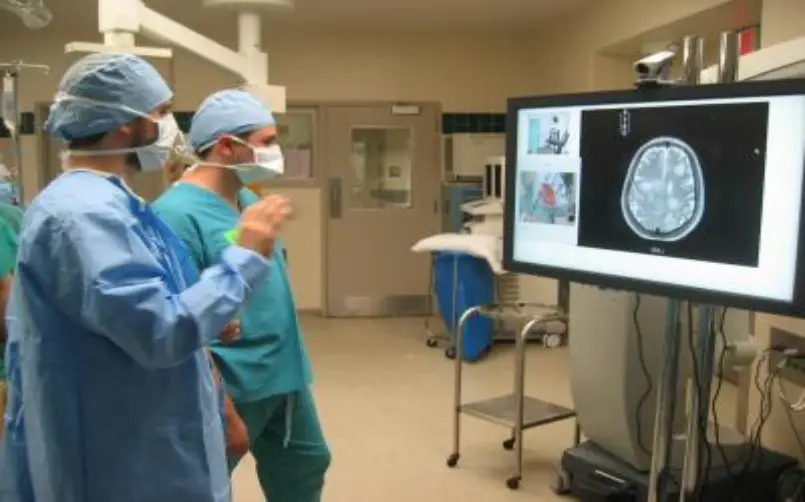
10. Gesture-Based Medical Applications
Gesture-based interfaces have made significant contributions to the healthcare industry. Surgeons can use gesture control to manipulate medical images and data during procedures, improving precision and efficiency. Gesture-based interfaces also find applications in rehabilitation therapy, where patients can engage in interactive exercises and track their progress through hand movements. These innovations enhance medical professionals’ capabilities and provide patients with more engaging and effective treatment options.