A telescope is an object used to see far-away things. It is primarily used in astronomy as an investigation tool. Most telescopes use curved mirrors to gather and focus light from the sky. The greater the lens or mirror, the more the light telescope can gather. It detects different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum like X-rays, UV rays, Gamma rays, visible light, radio waves, and microwaves. Telescopes can be either space-based or Earth-based. Below mentioned are some of the most powerful telescopes in the world:
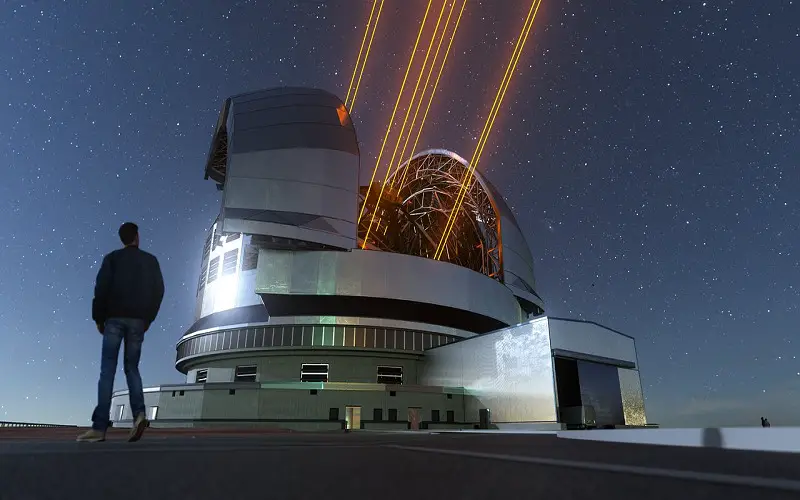
1. Extremely Large Telescope
It’s part of the European Southern Observatory. After completion, it will be the largest optical or near-infrared telescope in the world. It has a primary mirror of a 39.3-meter diameter and a secondary mirror of a 4.2-meter diameter. This telescope will be located in the Chilean Atacama Desert and can focus 100 million times more light than the human eye. Its goals include discovering Earth-like planets and extrasolar planets and measuring speeding up universe expansion. Its construction is scheduled to be completed in 2027.

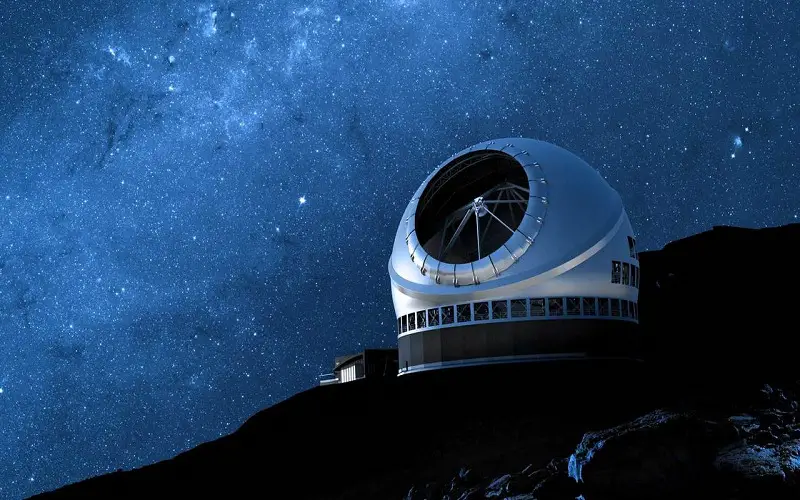
2. Thirty-meter Telescope
It will be set up in Mauna Kea Observatory, Hawaii, in the United States. In a collaboration between India, Japan, China, the United States, and Canada, the project is currently in progress. The telescope with a primary mirror diameter of 30 meters will observe from ultraviolet to mid-infrared wavelengths and give an 80 times clearer picture of space. It will observe cosmic objects, analyze black holes, and study some of the earliest light sources, which will further help in understanding dark matter.

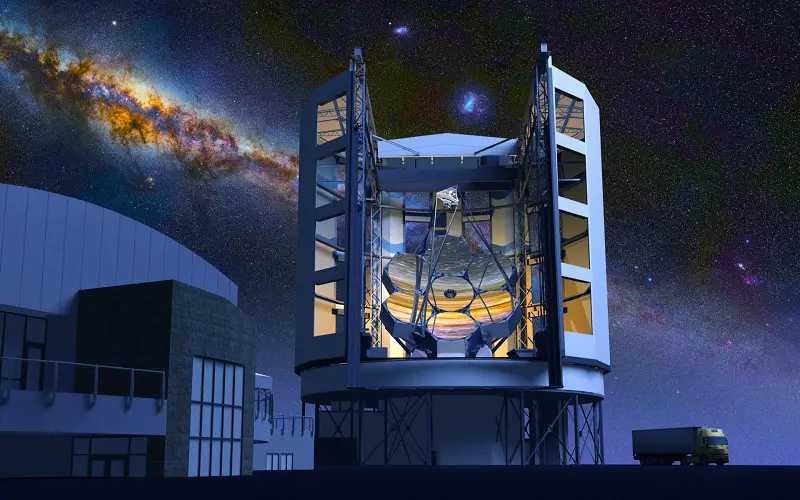
3. Giant Magellan Telescope
Designed to discover the unknown, it is the most powerful telescope on Earth. Seven primary mirrors each with an 8.4-meter diameter, collectively forming 25.4-meter-wide light collecting surface, will observe optical and near-infrared light to understand the deep space. This design of mirrors is the world’s first and largest telescope to date. The scientific instruments in this telescope will provide chemical analysis of celestial objects and their origin and analyze distinct planets’ atmospheres in search of light. It will be placed in the Chilean Atacama Desert, the best location to view space from Earth.

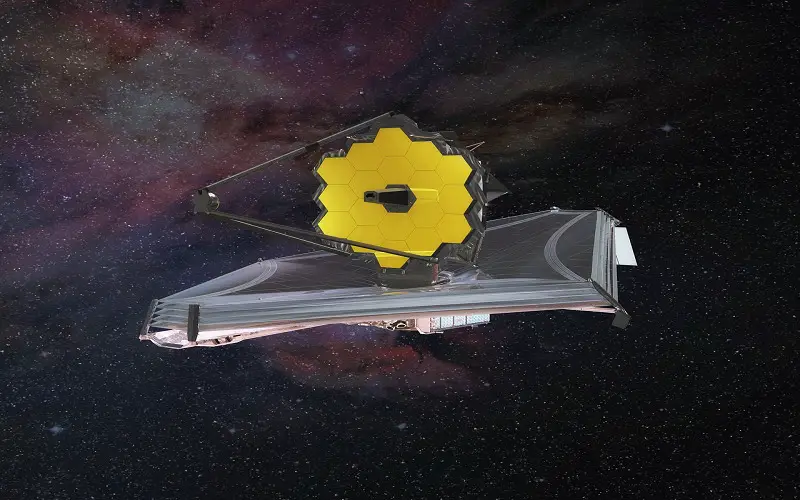
4. James Webb Space Telescope
It is the most powerful infrared telescope ever built in space. NASA, the European Space Agency, and the Canadian Space Agency collaborated to launch it on Dec 25, 2021. Its instruments allow us to study the history of our universe, from the Big Bang to the formation of our solar system and its evolution. Its primary mirror is made up of gold-plated beryllium, which consists of 18 hexagonal mirror segments which create a 6.5-meter diameter mirror. It is currently at Lagrange point 2 in Sun-Earth orbit, which is 1.5 million km from the Earth. JWST Telescope is the successor of the Hubble Space Telescope.

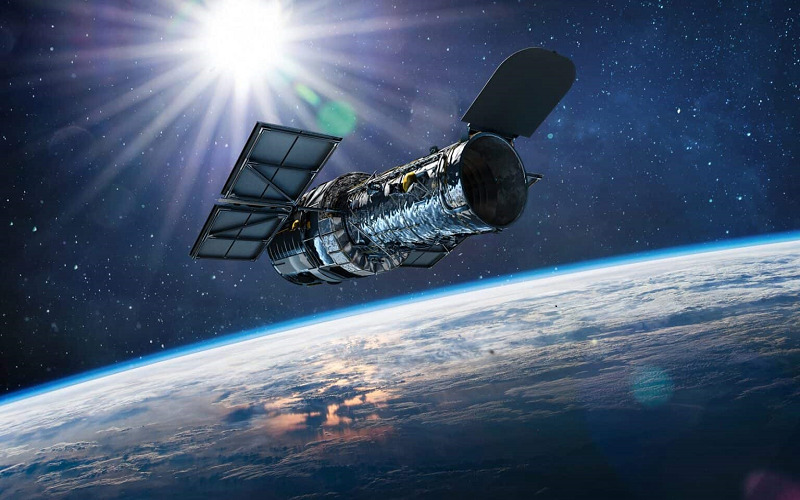
5. Hubble Space Telescope
HST was launched by NASA in 1990 and is one of the largest and most versatile telescopes in space. It will observe areas in visible, ultraviolet, and near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It is stationed in a low Earth orbit. It is the first ever observatory maintained by astronauts in space throughout service missions and has the lifetime of the telescope. It has a primary mirror of 2.4-meter diameter. It continues to collect data to date after its launch.

6. Fermi Gamma Ray Space Telescope (GLAST)
GLAST, also known as Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope, detects gamma rays. As gamma rays are absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere and cannot be focused with a lens or mirror, this telescope is placed outside the Earth’s atmosphere carrying two instruments, a Large Area Telescope and a Gamma-ray Burst Monitor. This telescope can help understand supermassive black holes, quasars, and neutron stars. It was launched in 2008 by NASA in collaboration with France, Germany, Italy, Japan, and Sweden and is still in operation.
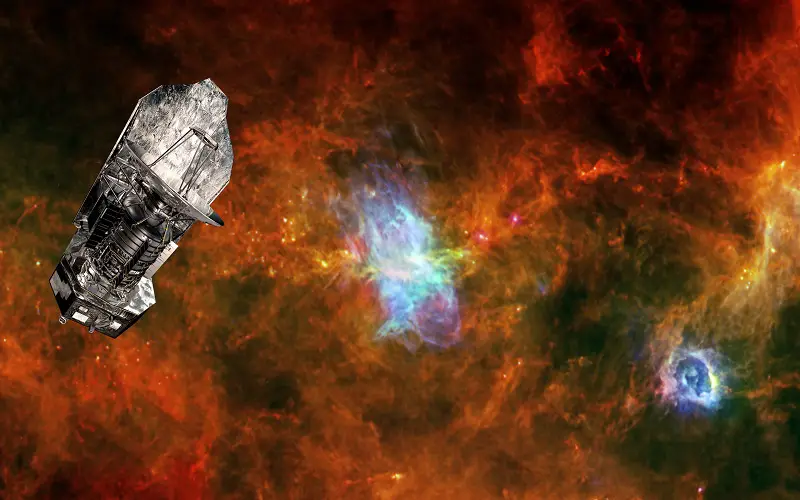
7. Herschel Space Observatory
It is a space-based telescope operated by the European Space Agency. Its mirror diameter of 3.5 meters is used at mid-infrared, far-infrared, and sub-mm wavelengths. It was designed to study the darkest and most remarkable regions of the universe and find out about dark matter, understand the molecular chemistry of the universe, and other cosmic mysteries. It was placed in a halo orbit around the second Lagrange Point (L2) near the Sun-Earth system. It was operational until it ran out of coolant in 2013.

8. Chandra X-ray Observatory
As the name suggests, it is the most powerful X-ray telescope in the world. It was launched in 1999 by NASA in Geocentric orbit. Its equipment captures the energy produced by emissions from quasars and particles in black holes. This telescope is named after an Indian-American astrophysicist, a Nobel prize winner.

9. Keck Telescope
It was built in 1992. It has two identical mirrors 10 meters in diameter, which is larger than some of the most powerful telescopes in the world. It is set up on Mauna Kea, Hawaii, which is 13,599 above sea level. This setup makes less atmospheric distortion. They observe the deep space at optical to mid-infrared wavelength. This Earth-based telescope has detected the birth of stars using infrared. These telescopes function at below-freezing points to prevent heat from interfering with infrared images.

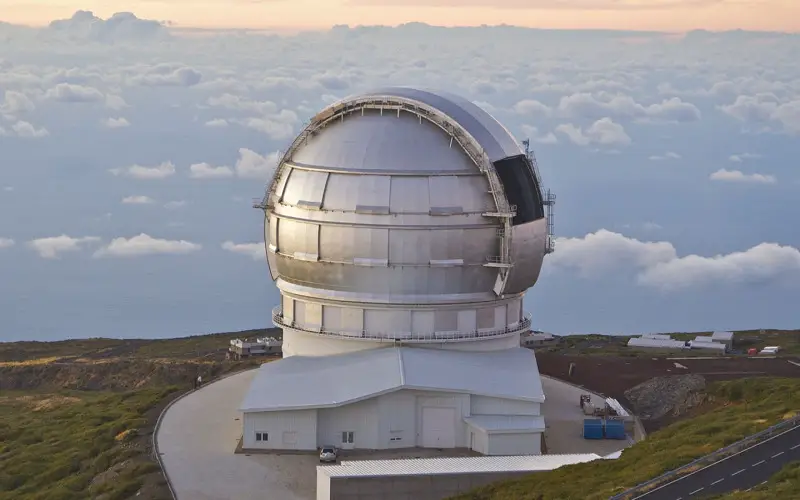
10. Gran Telescopio Canarias Telescope
Located in the Canary Islands of Spain, it is the world’s largest optical telescope. It has a mirror diameter of 10.4 meters with 36 hexagonal segments, controlled by an active optics control system. It began its first observation in 2007. It observes visible and infrared light and has a special camera for each light, i.e., CanariCam for infrared light and OSIRIS for visible light. It will study the nature of black holes and the physics of planets around other stars, the formation of galaxies in the early universe, dark matter, and dark energy.



















