Virtual reality (VR) technology is discussed as a way to increase the availability of exposure therapy. Incorporating VR in therapy can increase the ease, acceptability, and effectiveness of treatment for anxiety. VR exposure treatment (VRET) allows for customised, controlled, progressive, immersive exposure that is simple for therapists to use and frequently more tolerable for patients than in-person or fictitious exposure. It is suggested that VR can improve access to and the efficacy of exposure therapy, enhancing the management of anxiety disorders. VR also has the potential to help with assessment and with therapist training standardization. The authors advocate for providing continuing education in VRET to practicing clinicians and including training in exposure therapy and VRET in training programs. Ongoing development of VR applications for clinical use is encouraged, especially when developed in collaboration with software developers, clinical users, therapists who are experienced in VRET, and researchers.
1. Artificial Intelligence
AI is the ability of computers to think and work like a human and to perform the same tasks with higher accuracy and speed. It requires fewer resources and the success rate is high. Various health institutions use AI in their tools which helps them complete tasks more efficiently. Though there is always a chance of error, AI is still trusted by many.
2. Telehealth
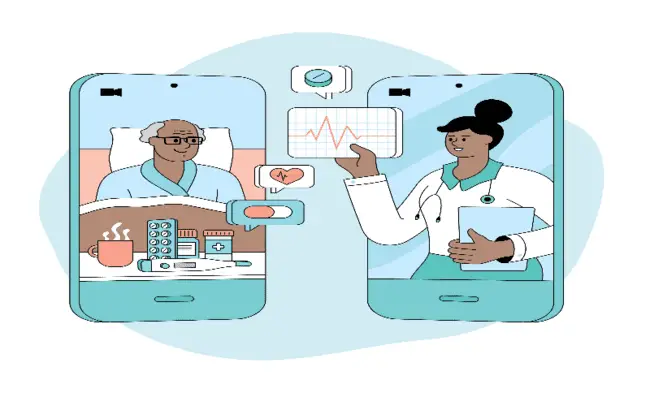
Telehealth refers to the use of online information and communication tools to manage your health care and receive medical treatments from a distance. Computers and mobile gadgets like tablets & smartphones are examples of technologies. You might utilise this technology at home. Or, in remote places, a nurse or other healthcare provider might offer telehealth services out of a clinic or mobile van. The use of technology by your healthcare practitioner to enhance or support healthcare services is known as telehealth.

3. 3-D Printing
3-d printing is used nowadays in every field of society. It helps to reduce the cost and can provide perfection in design up to user customization. Various medical devices are made from 3-d printing at a reasonable price point. Models have been used in treating liver tumors and other radiation treatment methods.
4. Neurotechnology
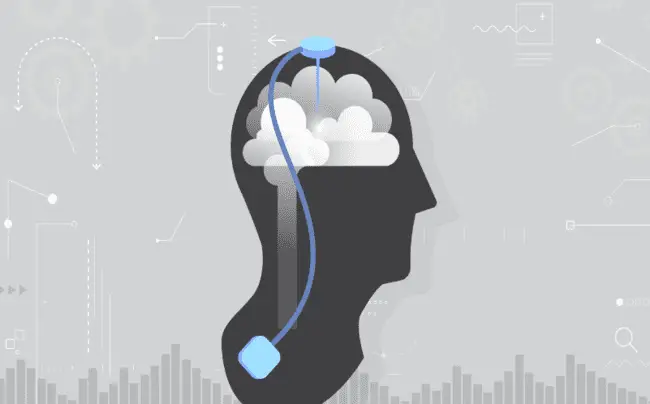
Any technique or gadget that interacts with the nervous system to track or control brain activity is referred to as neurotechnology. Using brain activity readings to control external devices like neuroprosthetics, modifying neural activity via neuromodulation to restore or normalise function impacted by neurological illnesses, or enhancing cognitive capacities are common design aims for neurotechnologies. Neurotechnologies serve a variety of purposes, including medicinal and commercial ones, but they also serve as effective research tools that help to understand the basics of neuroscience.

5. Genomics
Genomics is a field of biology that focuses on genomes. A genome is a set of DNA’s consisting of all the genes of an organism. Genomics includes studying and editing genomes to yield breakthrough results. It can help quantify a person’s genes and modify them accordingly. It is still under research and various experiments are being conducted.

6. Virtual Reality
3D near-eye displays and pose tracking are used in virtual reality to provide users with an immersive experience of a virtual environment. Virtual reality in healthcare uses computer-generated technology for several healthcare applications, like providing virtual medical training to students, and doctors or carrying out diagnoses, and many others. Giving students and clinicians virtual medical instruction or performing diagnoses, among many others, using computer-generated technology, is the key feature of VR in healthcare.
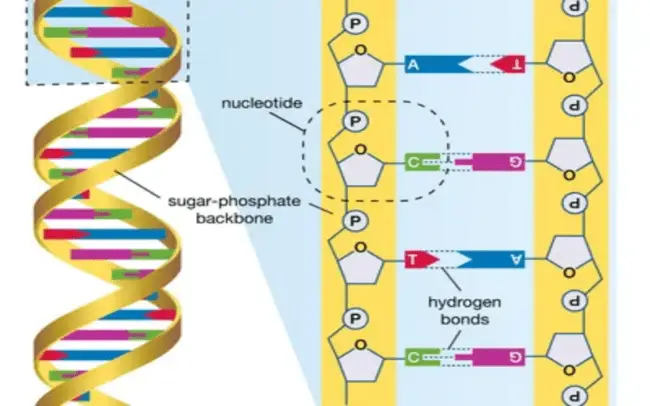
7. Genetic Sequencing
Finding the nucleic acid sequence, or the order of nucleotides in DNA, is the process of DNA sequencing. The four bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine—are arranged in this way using any technique or technology. One of the applications of genetic sequencing is to spot at-risk groups or pick individuals who will react well to treatments.
8. Wearable Devices
Using various sensors and trackers one can keep check of their health on their own. Fitness bands and trackers come equipped with heart rate sensors and oxygen level sensors. Various trackers, also include a blood pressure monitoring sensor. These devices collect and analyze a user’s health information.

9. Machine Learning
Machine learning is defined as how a machine can learn through various given datasets and produce a result. In the case of healthcare, machine learning helps to determine if a patient is facing a listed problem. The machine is provided with old data of patients, and it determines the symptoms that the next person can have.

10. Internet of Things
The Internet of Medical Things, often known as Healthcare IoT, is a networked infrastructure of medical software, and hardware. Machine-to-machine communication is made possible by Bluetooth and Wi-Fi-enabled medical equipment, making it simple to track and diagnose medical issues. One example of IoMT is Fitbit, which uses Bluetooth on your smartphone to track your steps.